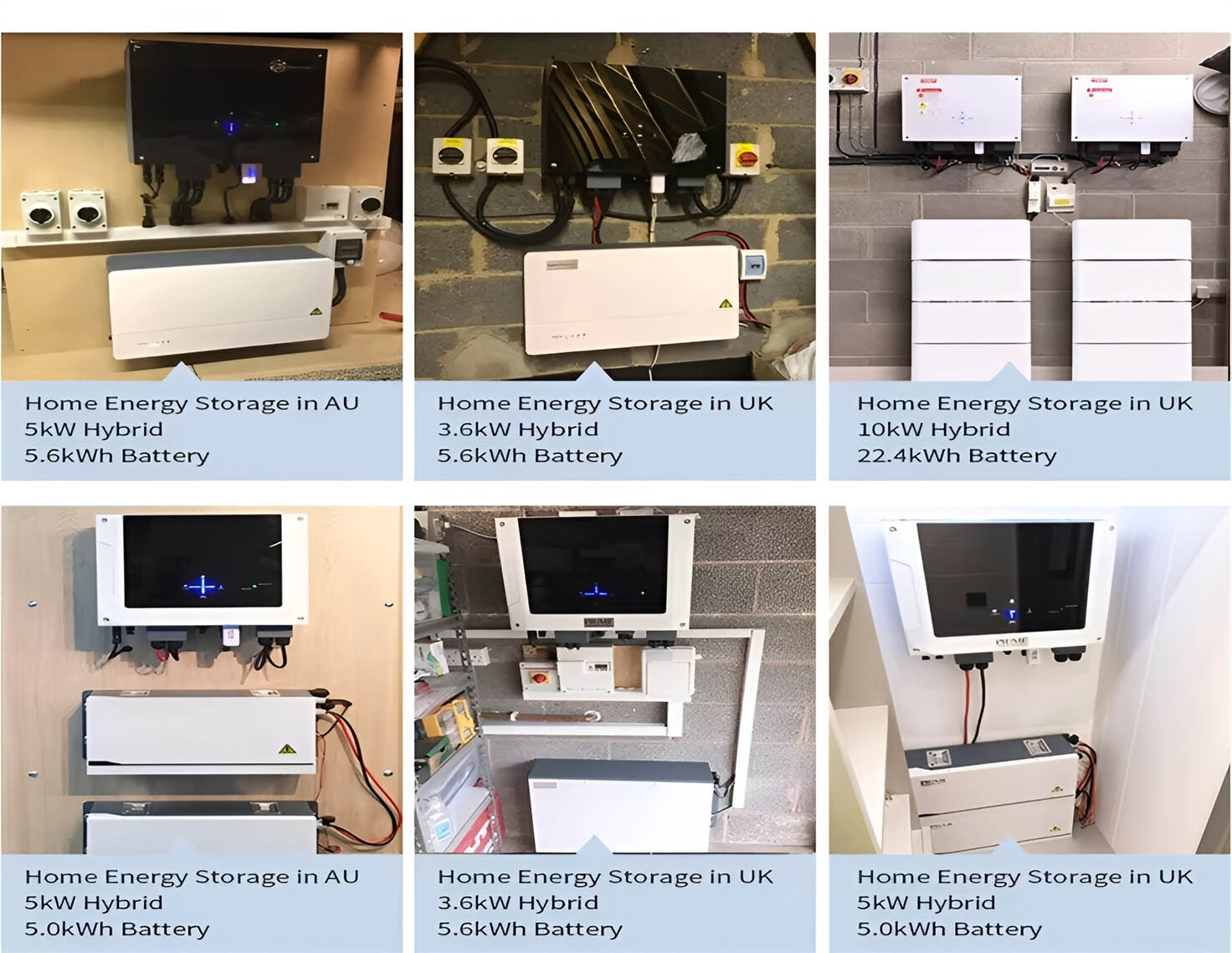
How To Use Terminals: Mastering The Command Line For Efficiency And Control
The terminal, often referred to as the command line interface (CLI) or shell, is a text-based portal to the heart of your computer. While modern graphical user interfaces (GUIs) are intuitive, the terminal offers unparalleled power, speed, and precision for developers, system administrators, and power users. This guide will demystify the terminal, providing you with the foundational knowledge and practical skills to use it effectively.
At its core, a terminal is an application that accepts text commands and passes them to your computer's operating system to execute. It's a direct line to the system, bypassing the graphical layers. Common terminals include:macOS & Linux: Terminal, iTerm2, GNOME Terminal. These typically run shells like `bash` or `zsh`.Windows: Command Prompt (`cmd`), PowerShell, and Windows Terminal. The Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL) also provides a genuine Linux terminal environment.
The prompt you see (e.g., `username@hostname:~$`) is where you type your commands. It usually shows your username, computer name, and current directory.
Step 1: Navigation The first skill is moving through your file system.`pwd` (Print Working Directory): Shows the full path of your current directory.`ls` (List): Displays the files and folders in the current directory. Use `ls -l` for a detailed list or `ls -a` to show hidden files (those starting with a dot).`cd` (Change Directory): Moves you to another directory.`cd /path/to/folder` moves to an absolute path.`cd Documents` moves into the "Documents" folder relative to your current location.`cd ..` moves up one level to the parent directory.`cd` or `cd ~` takes you directly to your home directory.
Step 2: File and Directory Management`mkdir
Step 3: Viewing and Editing Files`cat
Step 4: System Monitoring and Process Control`ps`: Displays your currently running processes.`top` or `htop`: Shows a real-time, dynamic view of all running processes and system resource usage.`kill
1. Harness the Power of Tab Completion This is the single greatest time-saver. Start typing a file or command name and press the `Tab` key. The terminal will automatically complete it for you. If there are multiple possibilities, press `Tab` twice to see a list.
2. Master Command History and Recall
Press the `Up Arrow` key to cycle through your previous commands. Use `history` to see a full list, and `!
3. Understand Redirection and Piping The terminal allows you to chain commands together powerfully.Redirection (`>` and `>>`): Sends the output of a command to a file.`ls > file_list.txt` creates a new file with the output of `ls`.`echo "new line" >> file_list.txt`appendsthe text to the end of the file.Piping (`|`): Takes the output of one command and uses it as the input for another.`ls -l | grep ".txt"` lists all files and then filters the result to show only lines containing ".txt".
4. Search Like a Pro with `grep` The `grep` command is indispensable for searching text.`grep "search_term" filename` searches for "search_term" inside a file.`ls | grep "project"` lists all files and only shows those with "project" in the name.
5. Manage Permissions with `chmod` Files have read (r), write (w), and execute (x) permissions for the user (u), group (g), and others (o). Use `chmod` to change them.`chmod +x script.sh` makes a script executable.`chmod 755 filename` is a common permission set for scripts (read, write, execute for owner; read and execute for others).
1. Double-Check Your Commands, Especially `rm` and `mv`. There is no "undo" button. A misplaced space can be catastrophic. For example, `rm -rf / important_folder` (note the space) is a classic, devastating mistake. It's a good practice to use `ls` to verify files before deleting them with `rm`.
2. Be Wary of Commands You Don't Understand. Copying and pasting commands from the internet without understanding what they do is a significant security risk. A malicious command can compromise your system. Always take a moment to look up unfamiliar flags or syntax.
3. Use Superuser (`sudo`) Privileges Sparingly. The `sudo` command gives you superuser (administrator) powers. It's necessary for system-wide changes but should not be used for everyday tasks. A command run with `sudo` can alter or destroy critical system files.
4. Keep Your Terminal Organized. A cluttered terminal can lead to mistakes. Regularly clear your screen with the `clear` command or `Ctrl+L` shortcut. Use meaningful directory structures and names.
5. Customize Your Environment. Your shell can be customized with a configuration file (e.g., `.bashrc` or `.zshrc`). You can change the prompt, set aliases for long commands (e.g., `alias ll='ls -la'`), and define environment variables to streamline your workflow.
By embracing the terminal, you move from being a passive user of your computer to an active operator. Start with the basic commands, practice regularly, and gradually incorporate the advanced techniques. The initial learning curve is well worth the climb, as it unlocks a level of efficiency and control that GUI tools simply cannot match.
Customized/OEM/ODM Service
HomSolar Supports Lifepo4 battery pack customization/OEM/ODM service, welcome to contact us and tell us your needs.


HomSolar: Your One-stop LiFePO4 Battery Pack & ESS Solution Manufacturer
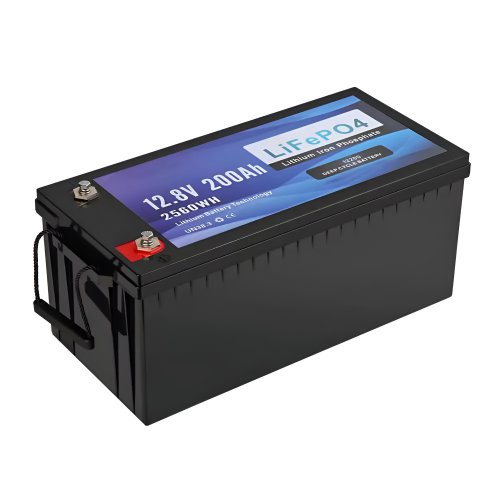
Our line of LiFePO4 (LFP) batteries offer a solution to demanding applications that require a lighter weight, longer life, and higher capacity battery. Features include advanced battery management systems (BMS), Bluetooth® communication and active intelligent monitoring.

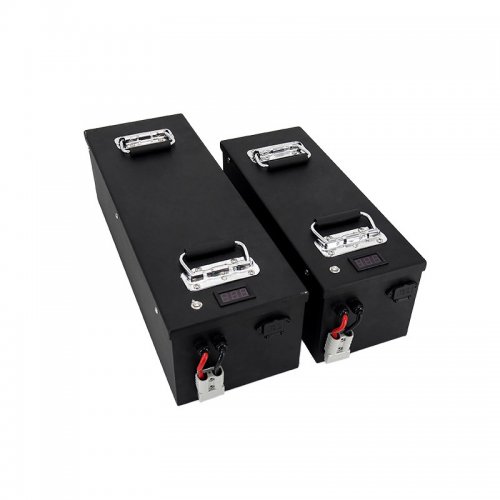
Customised Lithium Iron Phosphate Battery Casing
ABS plastic housing, aluminium housing, stainless steel housing and iron housing are available, and can also be designed and customised according to your needs.

HomSolar Smart BMS
Intelligent Battery Management System for HomSolar Energy Storage System. Bluetooth, temperature sensor, LCD display, CAN interface, UART interface also available.


Terminals & Plugs Can Be Customized
A wide range of terminals and plugs can be customised to suit the application needs of your battery products.

Well-designed Solutions for Energy Storage Systems
We will design the perfect energy storage system solution according to your needs, so that you can easily solve the specific industry applications of battery products.

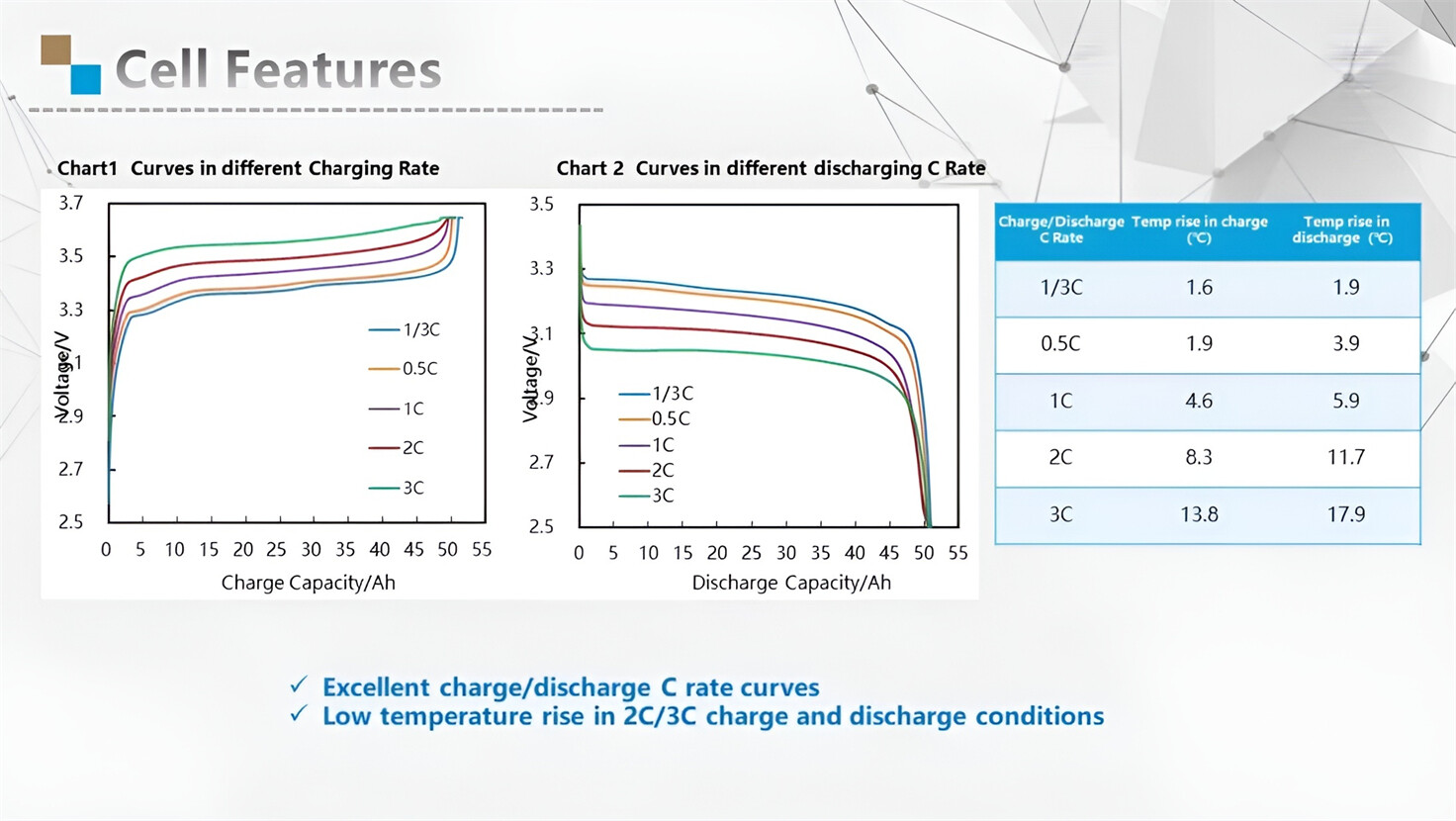
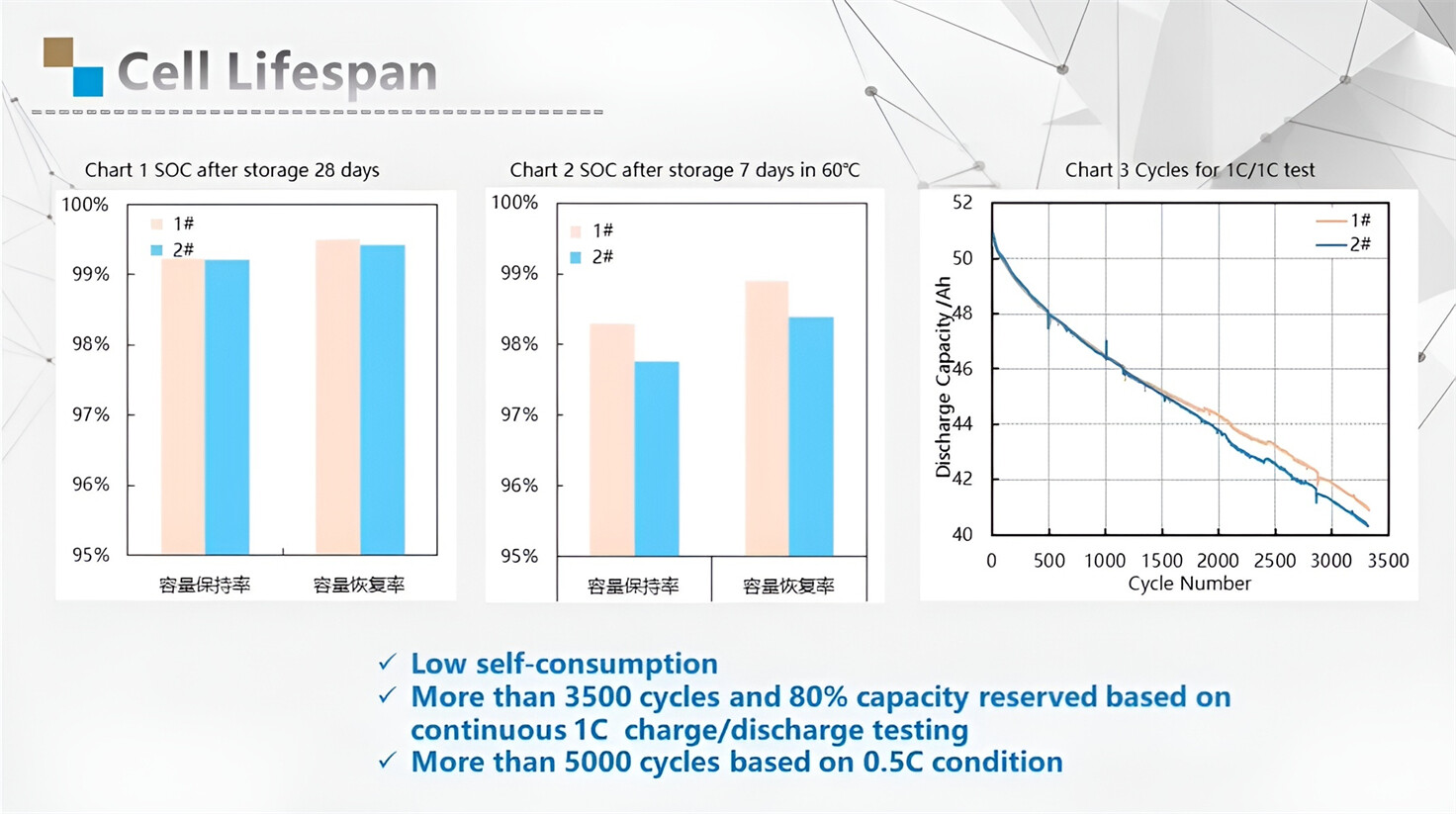
About Our Battery Cells
Our energy storage system products use brand new grade A LiFePO4 cells with a battery lifespan of more than 4,000 charge/discharge cycles.

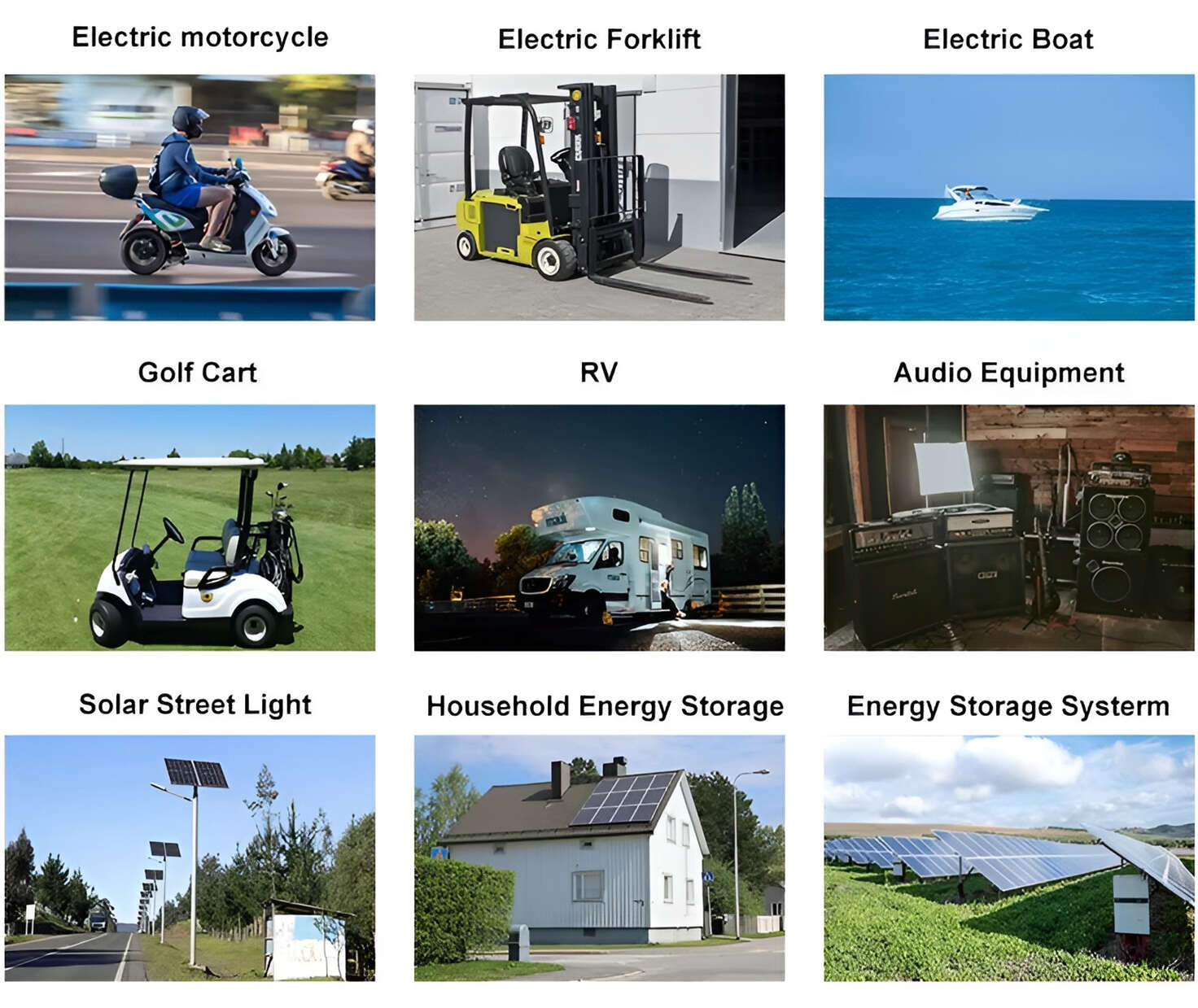
Applications in Different Industries
We supply customized & OEM battery pack, assemble cells with wiring, fuse and plastic cover, all the cell wires connected to PCB plug or built BMS.
Applications: E-bike, Electric Scooter, Golf Carts, RV, Electric Wheelchair, Electric Tools, Robot Cleaner, Robot Sweeper, Solar Energy Storage System, Emergency Light, Solar Power Light, Medical Equipment, UPS Backup Power Supply.
We can provide you with customized services. We have the ability to provide a vertical supply chain, from single cells to pack/module and to a complete power solution with BMS, etc.

HomSolar (Shenzhen) Technology Co., Ltd
























