How To Use Temperature Range: A Practical Guide For Optimal Performance And Safety
Understanding and correctly utilizing the concept of a "temperature range" is fundamental across countless applications, from scientific research and industrial processes to culinary arts and everyday electronics. A temperature range defines the spectrum of temperatures within which a system, material, or device operates effectively, safely, and as intended. Misapplying this range can lead to equipment failure, inaccurate data, spoiled products, or even hazardous situations. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of how to identify, apply, and respect temperature ranges for optimal outcomes.
Step-by-Step Usage Guide
1. Identification and Definition: The first and most critical step is to accurately identify the relevant temperature range for your specific context. This information is rarely universal and must be sourced from reliable references.For Equipment/Devices: Consult the official user manual, manufacturer's datasheet, or product specifications. Look for terms like "Operating Temperature Range," "Storage Temperature Range," "Ambient Temperature," or "Rated Temperature." The operating range is typically narrower than the storage range.For Materials/Chemicals: Review the Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS or SDS), chemical supplier specifications, or technical data sheets. These documents will specify melting points, flash points, recommended storage conditions, and stability ranges.For Biologicals/Food: Refer to food safety guidelines (e.g., USDA, FDA) for safe holding temperatures. For cell cultures or reagents, the protocol or product documentation will specify the required range, often a very narrow window around 4°C or -20°C.
2. Environmental Assessment: Before deployment or use, measure the environment where the item will be used or stored. Do not assume room temperature is constant or uniform.Use a calibrated thermometer or data logger to record the minimum and maximum temperatures over a relevant period (e.g., 24 hours). Consider factors like direct sunlight, proximity to heat sources (ovens, engines, radiators), drafts, and cooling vents.Compare your measured environmental conditions against the identified required temperature range.
3. Implementation and Control: If the environment does not naturally fall within the required range, you must implement control measures.For ranges above ambient: Use incubators, ovens, heating mantles, or heated enclosures. Ensure the heating element is appropriately sized and has a reliable thermostat.For ranges below ambient: Use refrigerators, freezers, chillers, or cryogenic units. Consider the unit's recovery time after being opened.For precise ranges: Use environmental chambers or water baths that offer both heating and cooling capabilities with high-precision controllers. These are essential for sensitive scientific work.
4. Continuous Monitoring and Validation: Simply setting a thermostat is not enough. Continuous monitoring is key to ensuring the range is maintained, especially for long-term processes.Use independent monitoring tools like digital thermometers with min/max memory, chart recorders, or wireless data loggers that can alert you via SMS or email if a temperature excursion occurs.Regularly calibrate all monitoring and control equipment against a known standard to ensure accuracy.
Practical Tips and TechniquesUnderstand the "Why": Knowing the consequences of exceeding the range provides motivation for diligence. For instance, exceeding the upper range of a lithium battery can lead to thermal runaway and fire, while going below the range of a enzyme can permanently destroy its activity.Build in a Safety Margin: Whenever possible, operate in the center of the specified range, not at its extreme edges. This provides a buffer for minor fluctuations in control systems and prevents accidental excursions. For example, if a server's operating range is 10°C to 35°C, aim to maintain a room temperature of 20-25°C.Consider Rate of Change: Some materials and devices are sensitive not just to absolute temperature, but to the speed at which temperature changes (thermal shock). Gradually ramp temperatures up or down when working with glassware, certain metals, or biological samples to prevent cracking or damage.Account for Self-Generated Heat: Electronic devices and chemical reactions often generate their own heat. The ambient temperature might be within range, but the internal temperature of a densely packed circuit board or a reacting vessel could be significantly higher. Provide adequate ventilation or cooling to dissipate this heat.Document Everything: Keep a log of temperature readings, any excursions, and corrective actions taken. This is crucial for quality control, troubleshooting, and validating processes (e.g., in a lab or food service setting).
Important Considerations and WarningsDo Not Ignore Storage Ranges: An item in storage is often unattended, making it more vulnerable. A product stored outside its range may be degraded or unsafe before you even begin to use it. This is critical for pharmaceuticals, chemicals, and food.Beware of Condensation: When moving a cold item into a warm, humid environment, condensation can form on and inside it. This water can cause short circuits in electronics, clump powders, or compromise sterile environments. Allow items to acclimatize gradually in a dry atmosphere or use protective, sealed packaging.Interpret Ranges Correctly: A range like "-20°C to +40°C" means the unit is designed tofunctionwithin those limits. It does not necessarily mean it can be stored at -20°C and then immediately operated at +40°C. Always allow for thermal equilibration to avoid shock.Safety First: Pushing beyond the stated limits of pressurized systems (like gas cylinders or boilers) or flammable materials can be extremely dangerous. Respect these limits absolutely.Legal and Warranty Implications: Using a product outside its specified temperature range will almost certainly void its warranty. In regulated industries (medical, automotive, aerospace), failing to adhere to documented temperature ranges can have serious legal and compliance repercussions.
By meticulously identifying, implementing, monitoring, and respecting temperature ranges, you ensure the integrity of your work, the longevity of your equipment, and most importantly, the safety of yourself and those around you. Treat the specified range not as a suggestion, but as a fundamental rule for successful operation.
Customized/OEM/ODM Service
HomSolar Supports Lifepo4 battery pack customization/OEM/ODM service, welcome to contact us and tell us your needs.


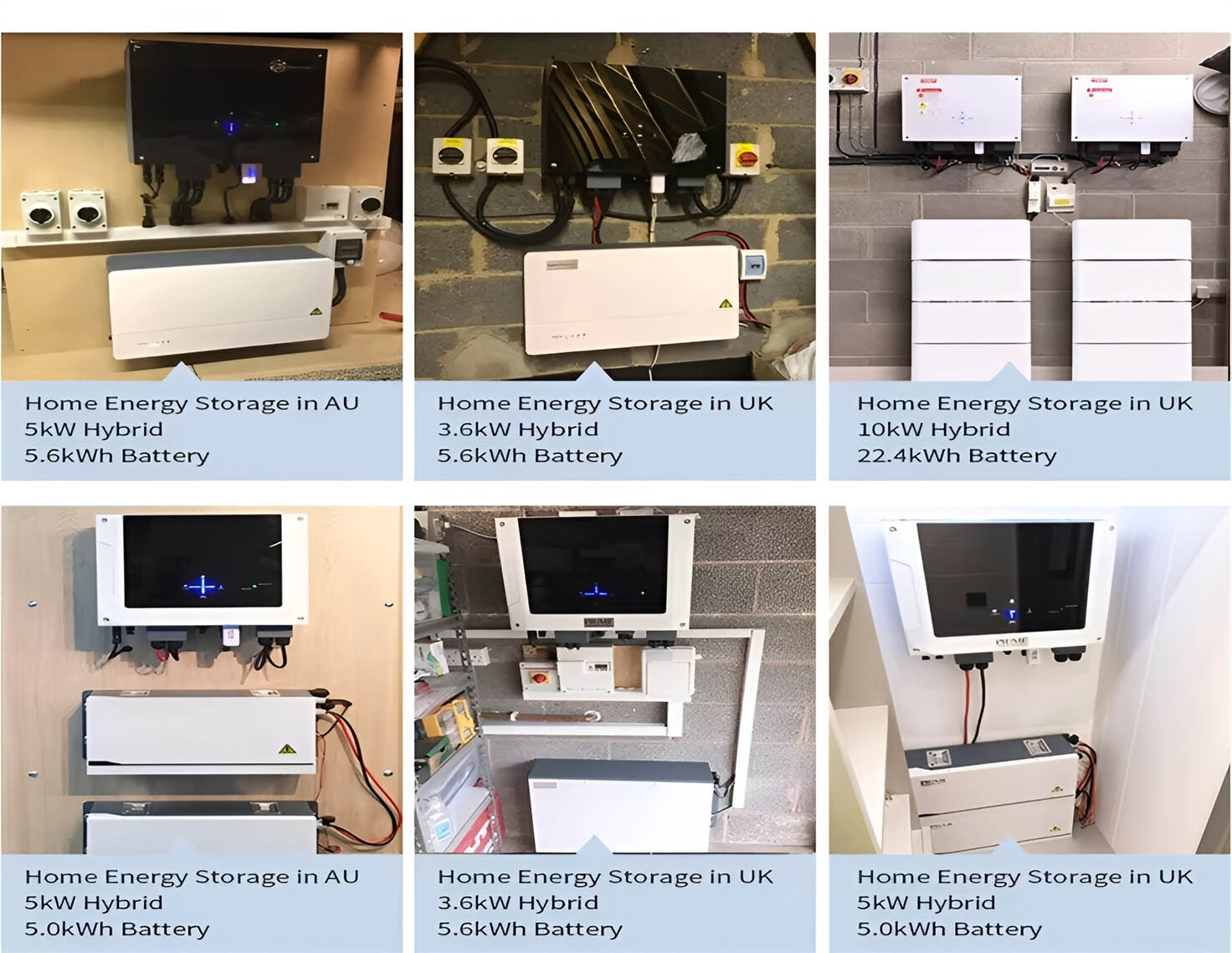
HomSolar: Your One-stop LiFePO4 Battery Pack & ESS Solution Manufacturer
Our line of LiFePO4 (LFP) batteries offer a solution to demanding applications that require a lighter weight, longer life, and higher capacity battery. Features include advanced battery management systems (BMS), Bluetooth® communication and active intelligent monitoring.

Customised Lithium Iron Phosphate Battery Casing
ABS plastic housing, aluminium housing, stainless steel housing and iron housing are available, and can also be designed and customised according to your needs.

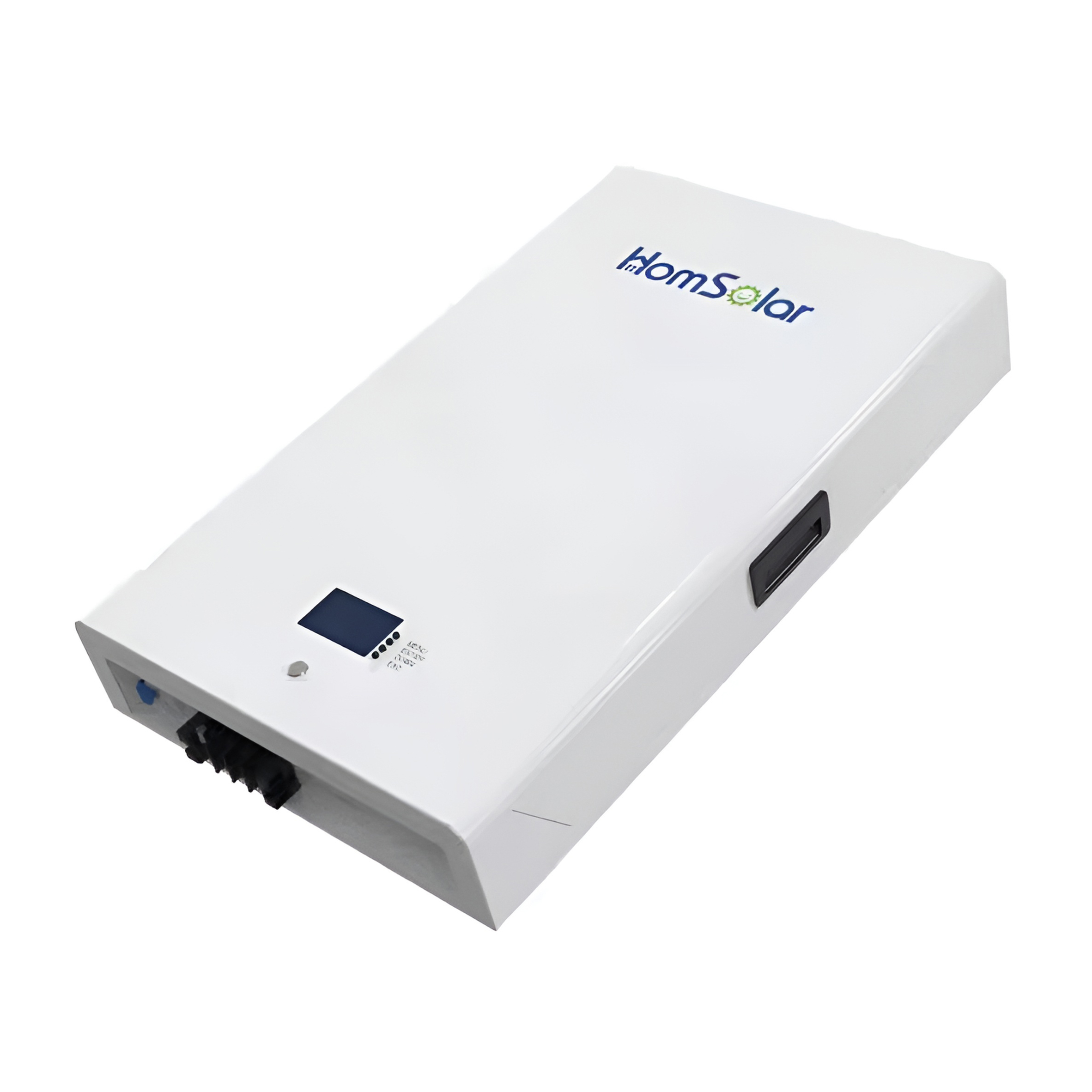
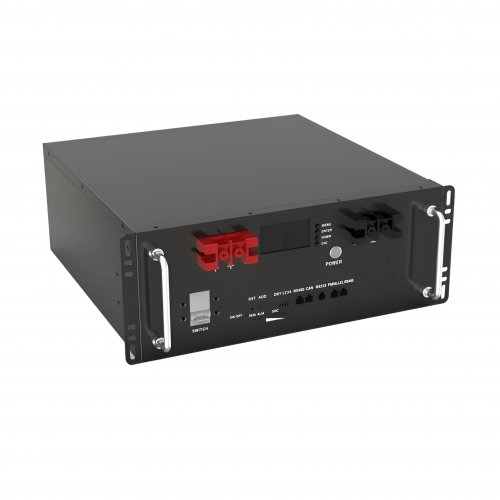
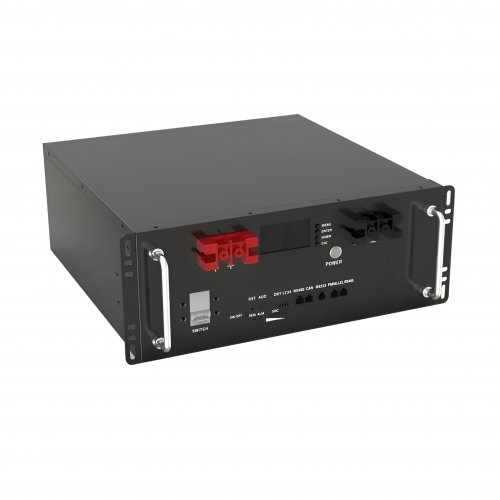
HomSolar Smart BMS
Intelligent Battery Management System for HomSolar Energy Storage System. Bluetooth, temperature sensor, LCD display, CAN interface, UART interface also available.


Terminals & Plugs Can Be Customized
A wide range of terminals and plugs can be customised to suit the application needs of your battery products.

Well-designed Solutions for Energy Storage Systems
We will design the perfect energy storage system solution according to your needs, so that you can easily solve the specific industry applications of battery products.

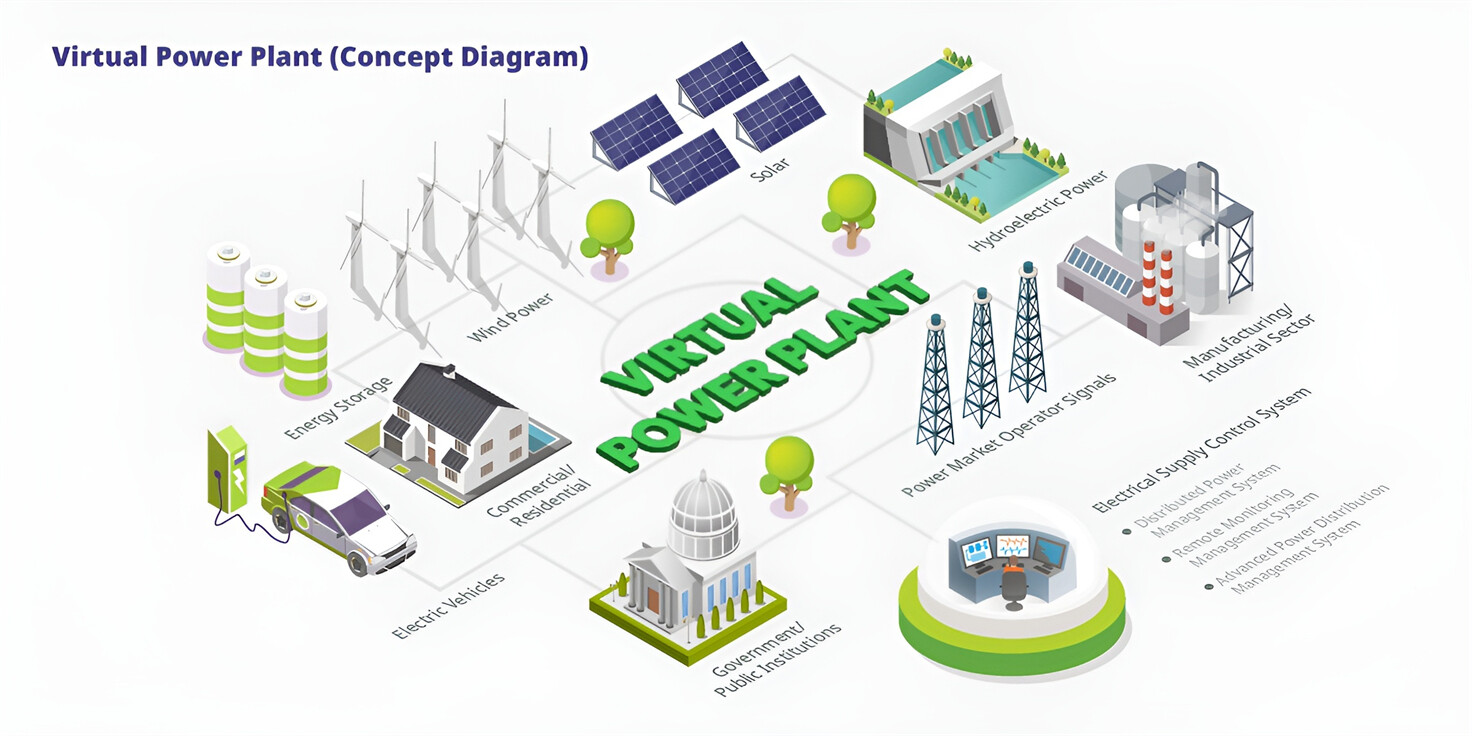
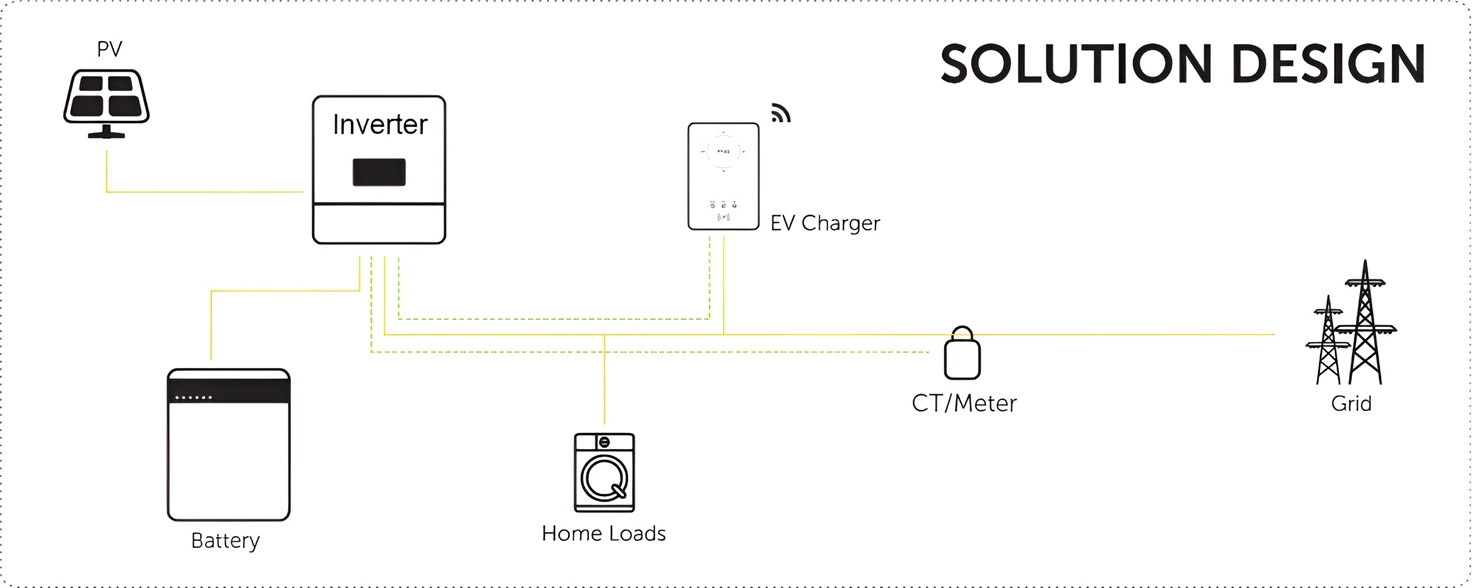
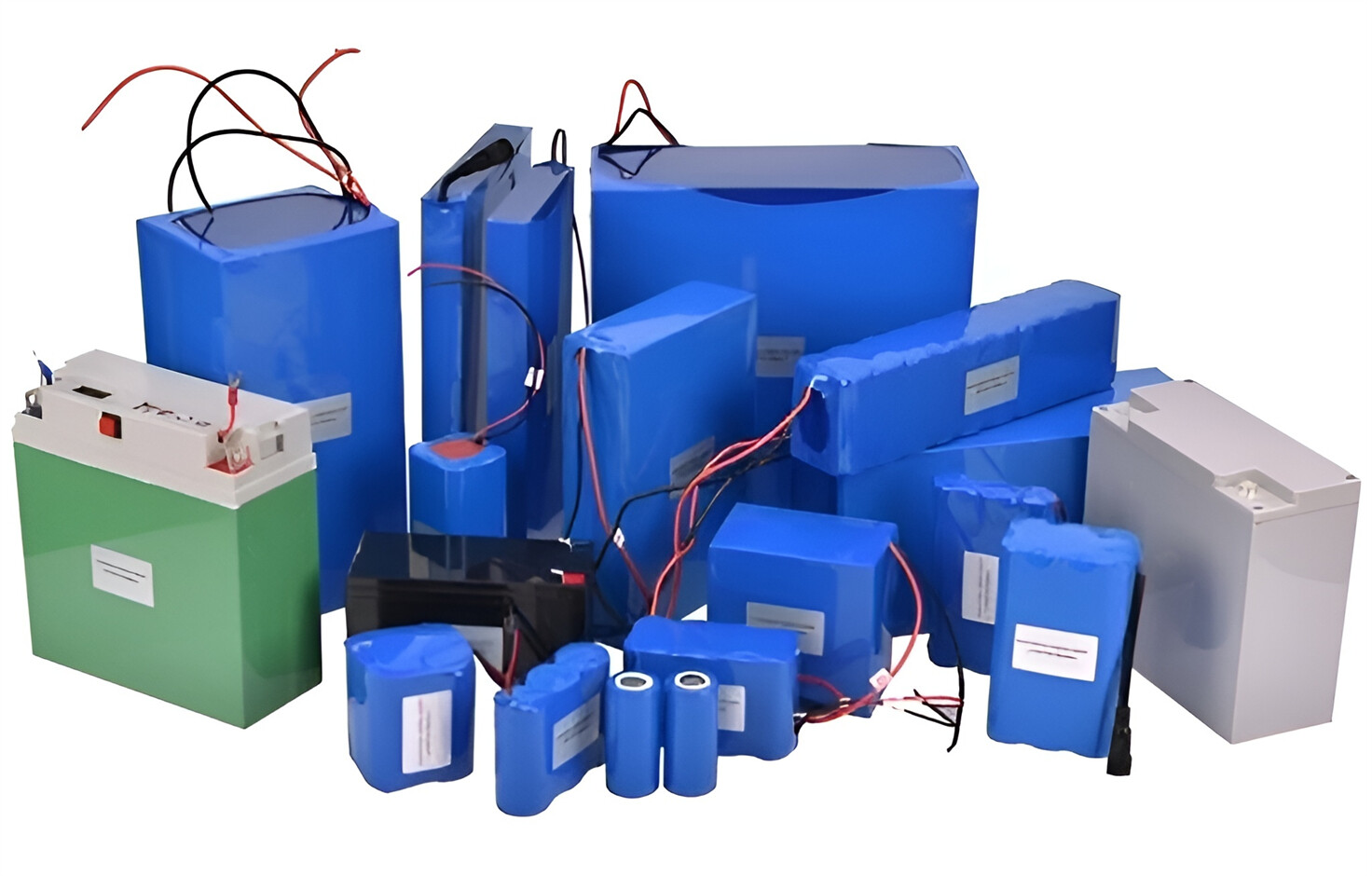
About Our Battery Cells
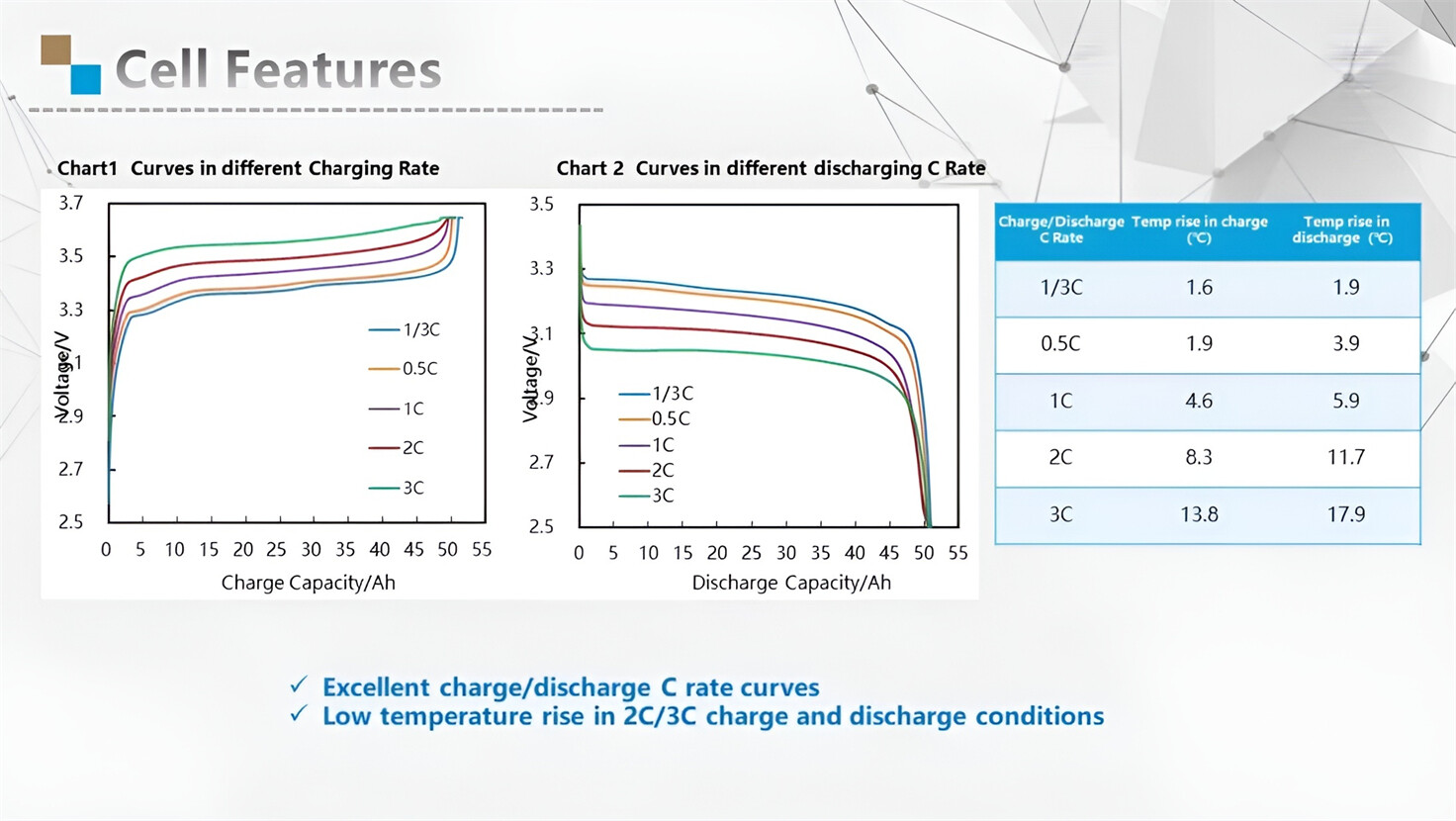
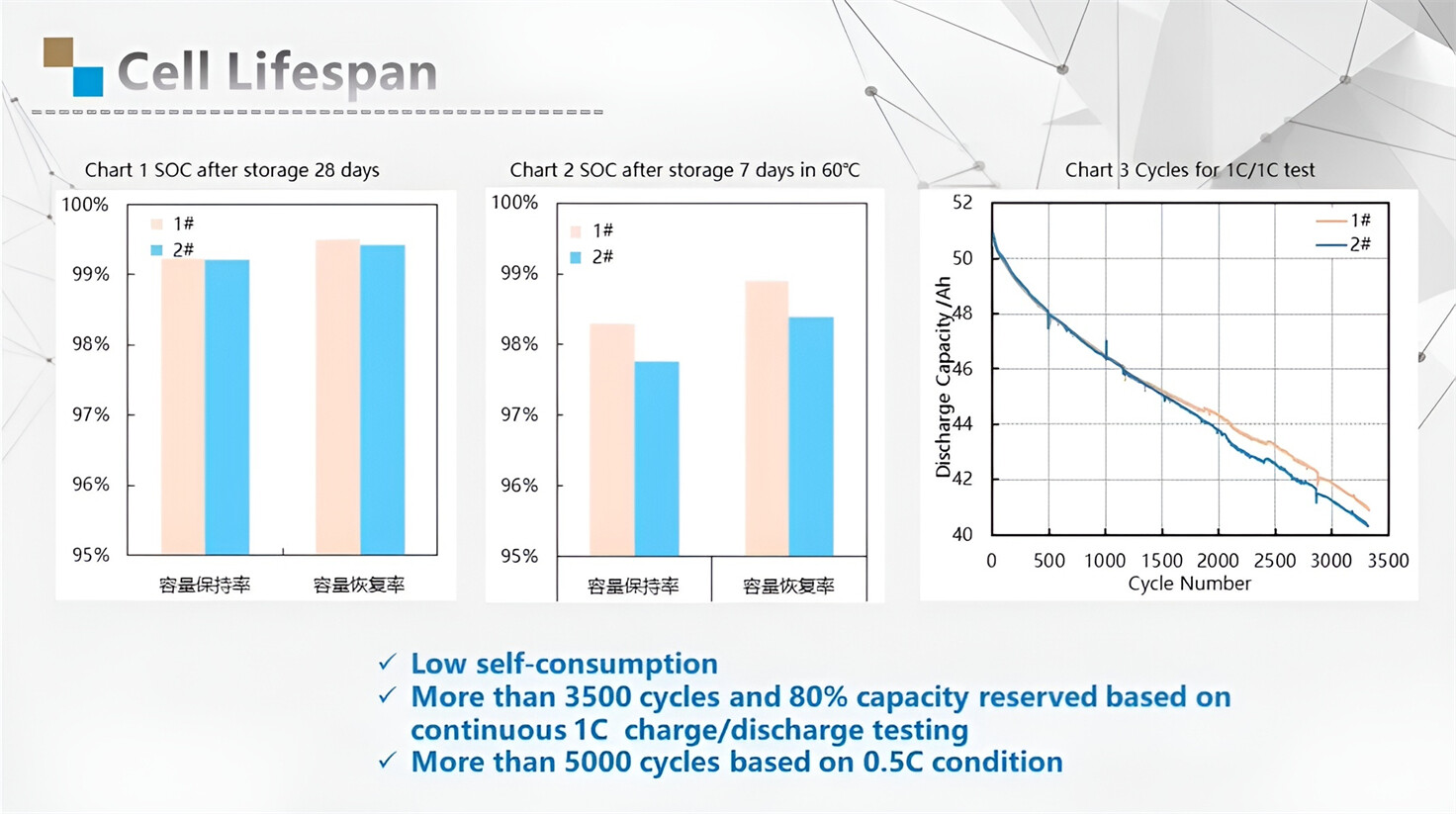
Our energy storage system products use brand new grade A LiFePO4 cells with a battery lifespan of more than 4,000 charge/discharge cycles.

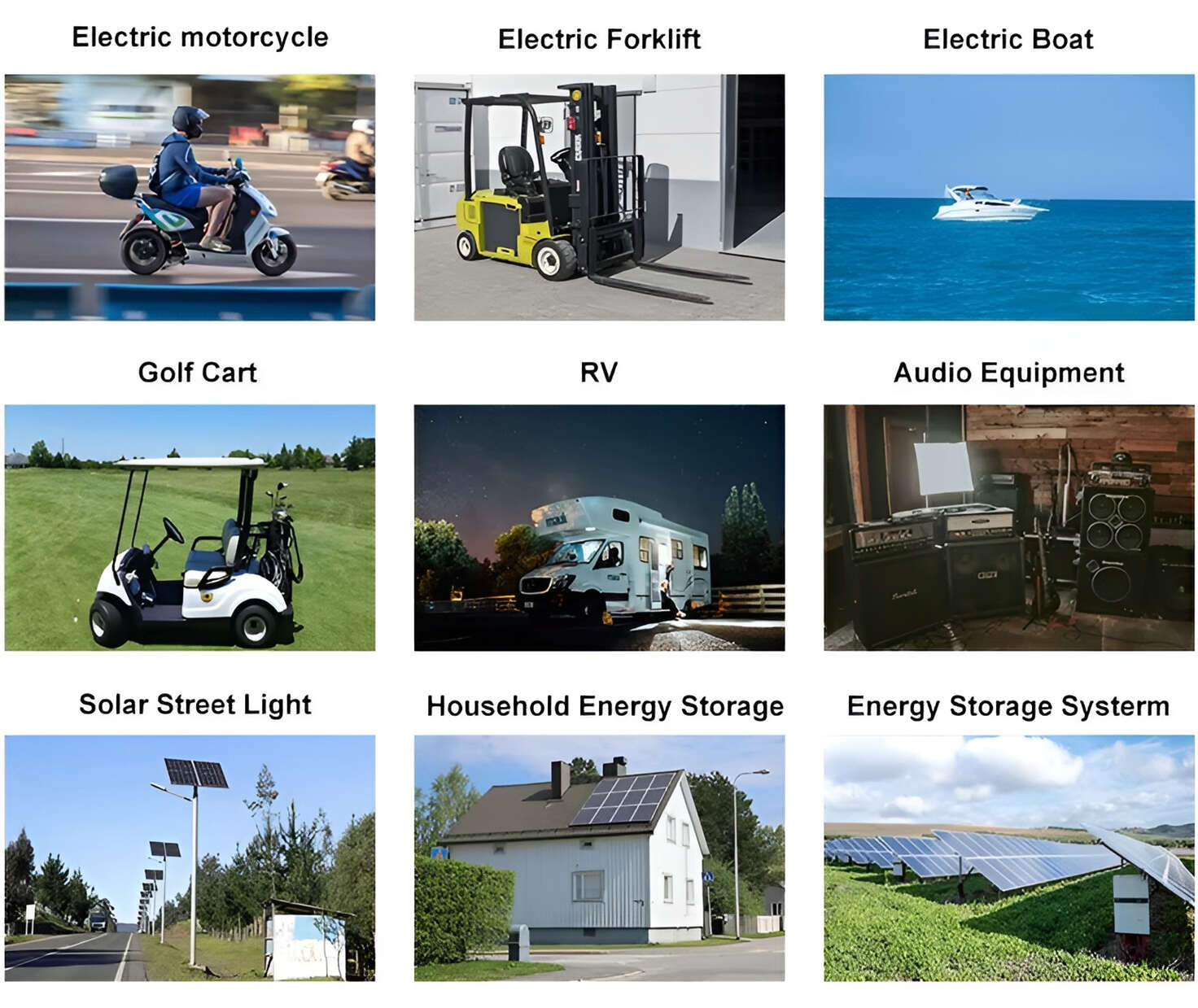
Applications in Different Industries
We supply customized & OEM battery pack, assemble cells with wiring, fuse and plastic cover, all the cell wires connected to PCB plug or built BMS.
Applications: E-bike, Electric Scooter, Golf Carts, RV, Electric Wheelchair, Electric Tools, Robot Cleaner, Robot Sweeper, Solar Energy Storage System, Emergency Light, Solar Power Light, Medical Equipment, UPS Backup Power Supply.
We can provide you with customized services. We have the ability to provide a vertical supply chain, from single cells to pack/module and to a complete power solution with BMS, etc.

HomSolar (Shenzhen) Technology Co., Ltd
























