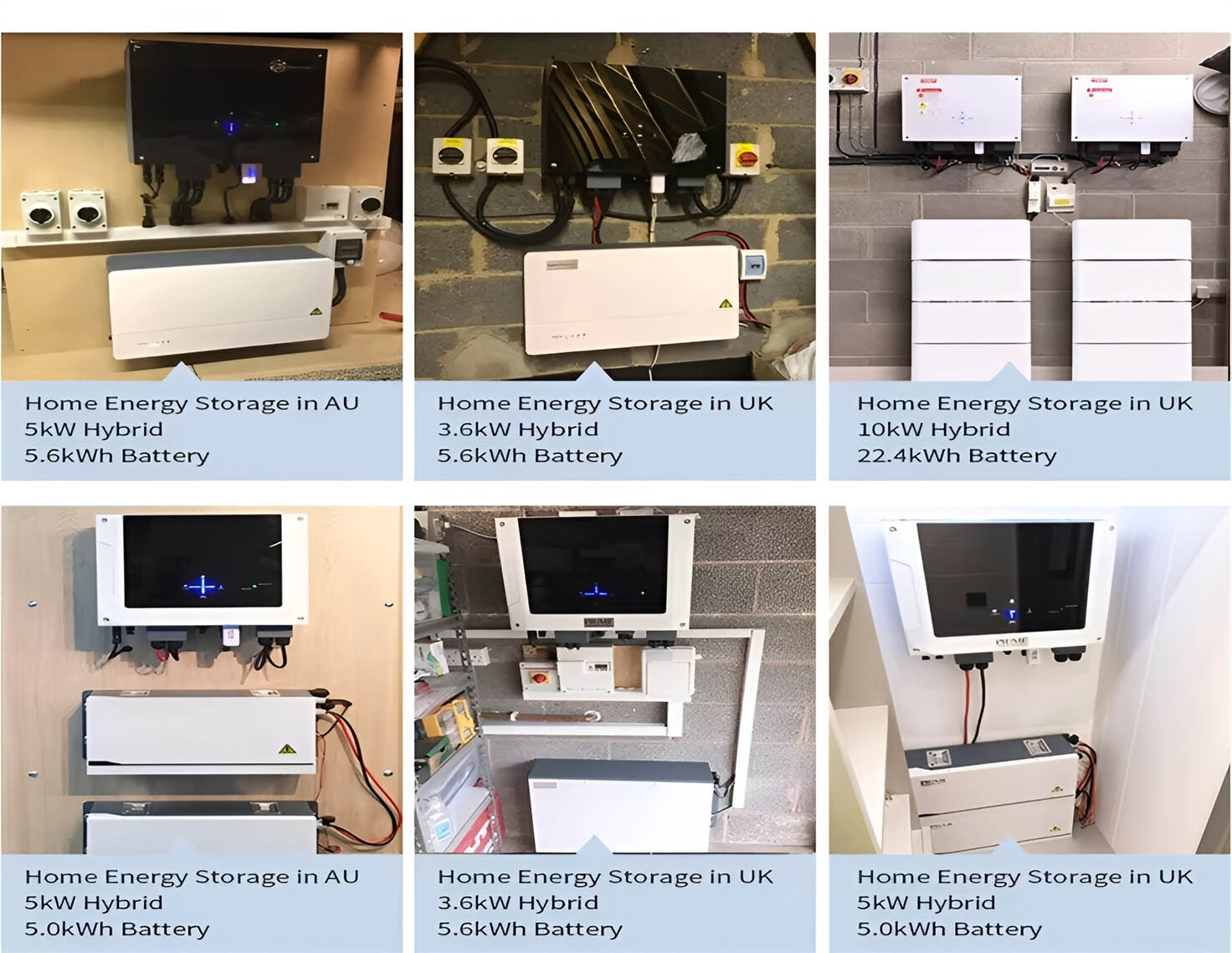
How To Use Safety Precautions: A Comprehensive Guide To Risk Mitigation And Prevention
Safety precautions are not merely rules to follow but a fundamental mindset and systematic approach to preventing harm in any environment. Whether in the workplace, at home, or during recreational activities, integrating robust safety protocols is essential for protecting people, property, and processes. This guide provides a detailed framework for understanding, implementing, and maintaining effective safety precautions.
Understanding the Fundamentals: The "Why" Behind Safety
Before diving into steps, it's crucial to internalize the purpose of safety precautions. They are proactive measures designed to:Prevent Accidents: The primary goal is to stop incidents before they occur.Minimize Injury: If an incident does happen, proper precautions reduce the severity of harm.Protect Assets: This includes safeguarding equipment, infrastructure, and the environment.Ensure Compliance: Adhering to local, national, and international safety regulations is a legal and ethical obligation.Promote a Culture of Safety: When everyone is engaged in safety, overall morale and productivity improve.
A Step-by-Step Guide to Implementing Safety Precautions
Implementing safety is a continuous cycle, not a one-time task. Follow these steps to establish a strong safety framework.
Step 1: Risk Assessment and Hazard Identification The foundation of all safety precautions is knowing what you're up against.Action: Conduct a thorough walk-through of your environment. Look for potential hazards—these can be physical (slippery floors, exposed wiring, heavy machinery), chemical (toxic substances, flammables), biological (mold, bacteria), or ergonomic (poor posture, repetitive strain).Tool: Use a Risk Matrix. Evaluate each identified hazard based on two factors: theseverityof potential harm (from minor injury to death) and thelikelihoodof it occurring (from improbable to certain). This helps prioritize which risks need immediate attention.
Step 2: Develop and Document Procedures Once risks are identified, formalize the precautions needed to control them.Action: Create clear, concise, and accessible Safe Work Procedures (SWPs) or guidelines. These documents should outline, step-by-step, how to perform a task safely, including the required Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) and what to do in an emergency.Tool: Use simple language and visuals. Diagrams, flowcharts, and icons can make procedures easier to understand than large blocks of text.
Step 3: Procure and Provide Safety Equipment Having the right tools for the job is non-negotiable.Action: Based on your risk assessment, equip your team with the necessary safety gear. This ranges from fundamental PPE like hard hats, safety glasses, gloves, and respirators to larger equipment like machine guards, ventilation systems, and emergency showers.Tip: Don’t just provide equipment; ensure it is the correct type for the specific hazard (e.g., chemical-resistant gloves vs. cut-resistant gloves) and that it fits the user properly. Ill-fitting PPE can be as dangerous as none at all.
Step 4: Comprehensive Training and Communication Knowledge is the most critical safety tool. Precautions are useless if people don't know about them or how to apply them.Action: Conduct mandatory training sessions for all relevant personnel. Training must be ongoing, not just a one-off event during onboarding. Include:How to identify hazards.How to use PPE correctly and maintain it.How to follow established safe procedures.Emergency response drills (evacuation, first aid, spill control).Tip: Use diverse training methods—hands-on demonstrations, videos, and interactive workshops—to cater to different learning styles. Ensure all safety information is communicated in a language and manner all workers understand.
Step 5: Consistent Monitoring and Enforcement Safety protocols can degrade over time without vigilance.Action: Supervisors and safety officers should regularly observe work practices to ensure compliance with established precautions. This is not about punishment, but about coaching and correction.Tool: Implement a routine inspection schedule to check the condition of safety equipment and the physical environment. Encourage near-miss reporting—investigating incidents thatalmosthappened provides invaluable data to prevent future accidents.
Step 6: Review and Continuous Improvement Safety is dynamic. New technologies, processes, and materials introduce new risks.Action: Schedule periodic reviews of your safety protocols. Re-assess risks after any significant change in the workplace or after an incident. Solicit feedback from employees on the front lines; they often have the best insights into practical hazards and solutions.Tip: Foster an open culture where employees feel empowered to report unsafe conditions without fear of reprisal.
Essential Safety Tips and Best PracticesThe Hierarchy of Controls: This model prioritizes the most effective types of safety precautions: 1. Elimination: Physically remove the hazard (e.g., removing a toxic chemical from a process). 2. Substitution: Replace the hazard with a safer alternative (e.g., using a less volatile solvent). 3. Engineering Controls: Isolate people from the hazard (e.g., machine guards, sound-dampening enclosures). 4. Administrative Controls: Change the way people work (e.g., job rotation, training, signage). 5. PPE: Protect the worker with personal equipment.Note: PPE is the last line of defense, not the first.Stay Alert and Focused: Complacency is a major cause of accidents. Avoid distractions and never take shortcuts, especially with familiar tasks.Good Housekeeping: A clean, organized, and clutter-free workspace is a safer workspace. It prevents trips, falls, and fires and helps identify hazards more easily.Ergonomics: Adjust your workspace to fit your body. Proper chair height, monitor placement, and tool handling prevent chronic musculoskeletal disorders.
Critical Considerations and WarningsOne Size Does Not Fit All: Safety precautions must be tailored to the specific context, risk, and individual. Assumptions can be dangerous.PPE is a Last Resort: Relying solely on PPE means the hazard is still present. Always strive to use higher-level controls from the hierarchy first.Mental and Emotional State: Stress, fatigue, and rushing significantly impair judgment and reaction time, increasing the likelihood of an error. Never engage in high-risk activities when you are not mentally prepared.Emergency Preparedness: Knowing the precautions for daily tasks is vital, but so is knowing what to do when things go wrong. Ensure everyone knows the location of emergency exits, first-aid kits, fire extinguishers, and emergency contact numbers.
By treating safety precautions as an integral and non-negotiable part of every action, we build a resilient defense against the unpredictable. It is a continuous commitment to vigilance, education, and improvement that ensures everyone goes home safe at the end of the day.
Customized/OEM/ODM Service
HomSolar Supports Lifepo4 battery pack customization/OEM/ODM service, welcome to contact us and tell us your needs.


HomSolar: Your One-stop LiFePO4 Battery Pack & ESS Solution Manufacturer
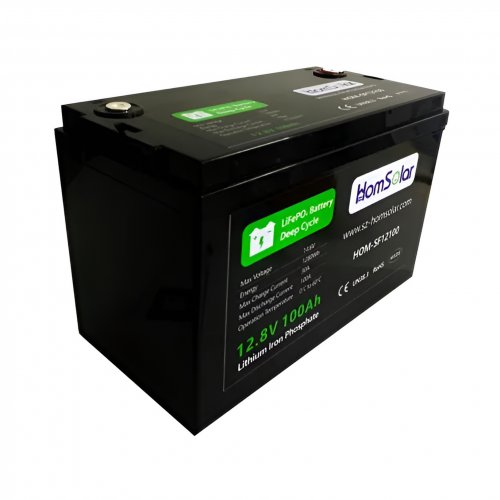
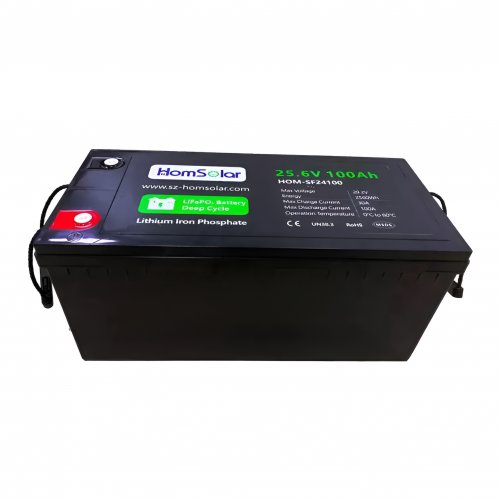
Our line of LiFePO4 (LFP) batteries offer a solution to demanding applications that require a lighter weight, longer life, and higher capacity battery. Features include advanced battery management systems (BMS), Bluetooth® communication and active intelligent monitoring.
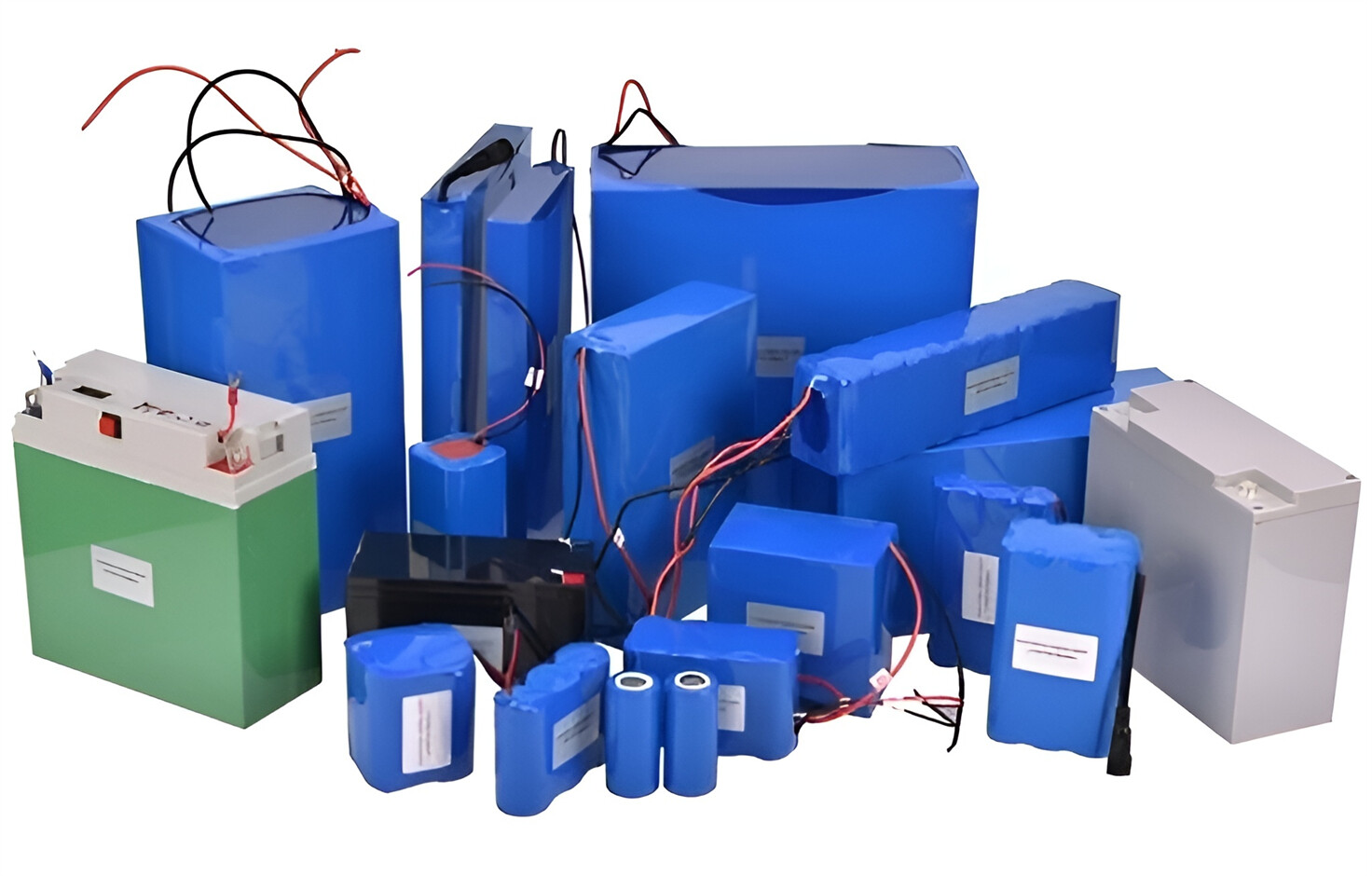

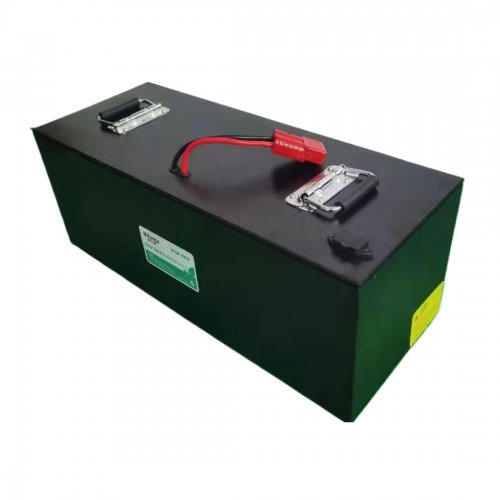
Customised Lithium Iron Phosphate Battery Casing
ABS plastic housing, aluminium housing, stainless steel housing and iron housing are available, and can also be designed and customised according to your needs.

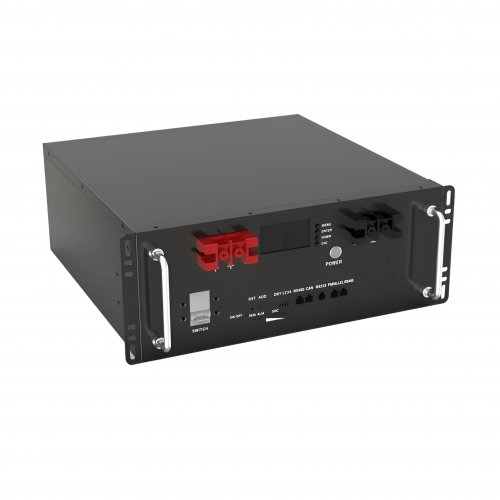
HomSolar Smart BMS
Intelligent Battery Management System for HomSolar Energy Storage System. Bluetooth, temperature sensor, LCD display, CAN interface, UART interface also available.


Terminals & Plugs Can Be Customized
A wide range of terminals and plugs can be customised to suit the application needs of your battery products.

Well-designed Solutions for Energy Storage Systems
We will design the perfect energy storage system solution according to your needs, so that you can easily solve the specific industry applications of battery products.

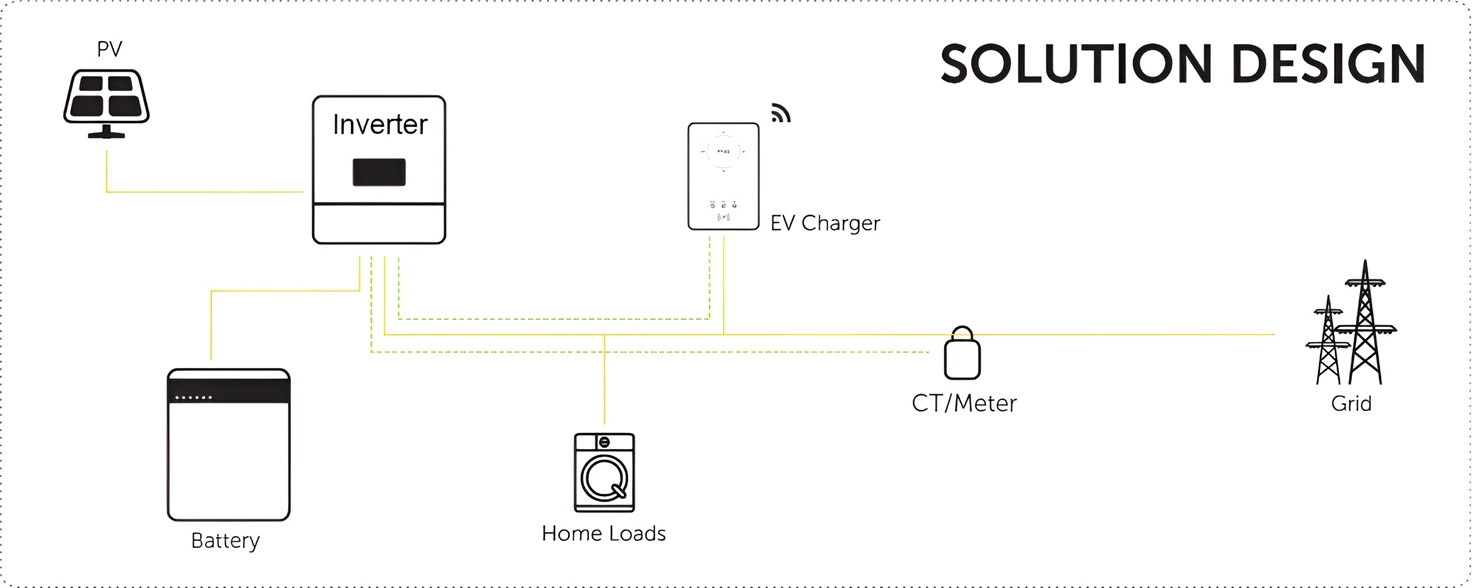
About Our Battery Cells
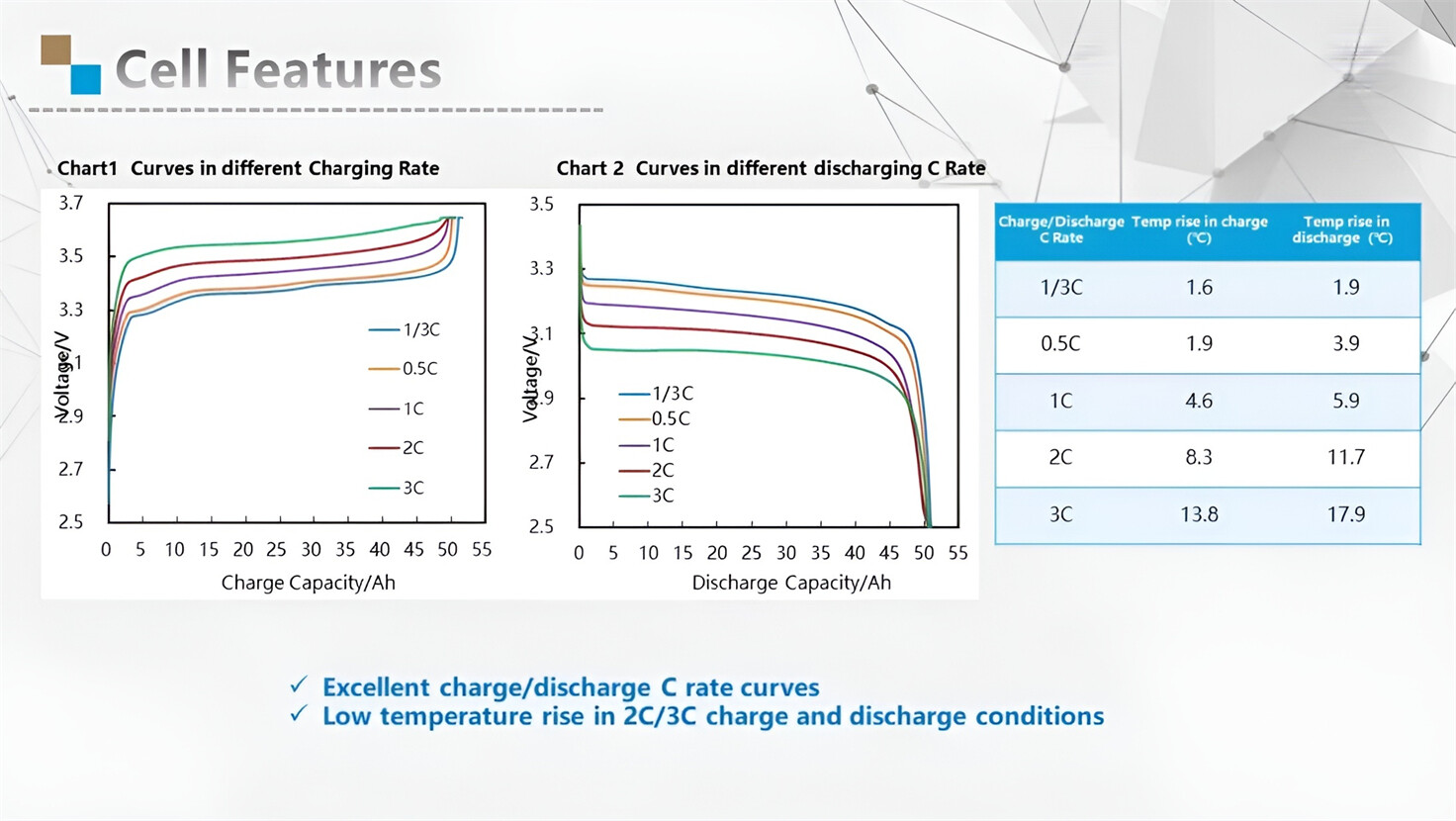
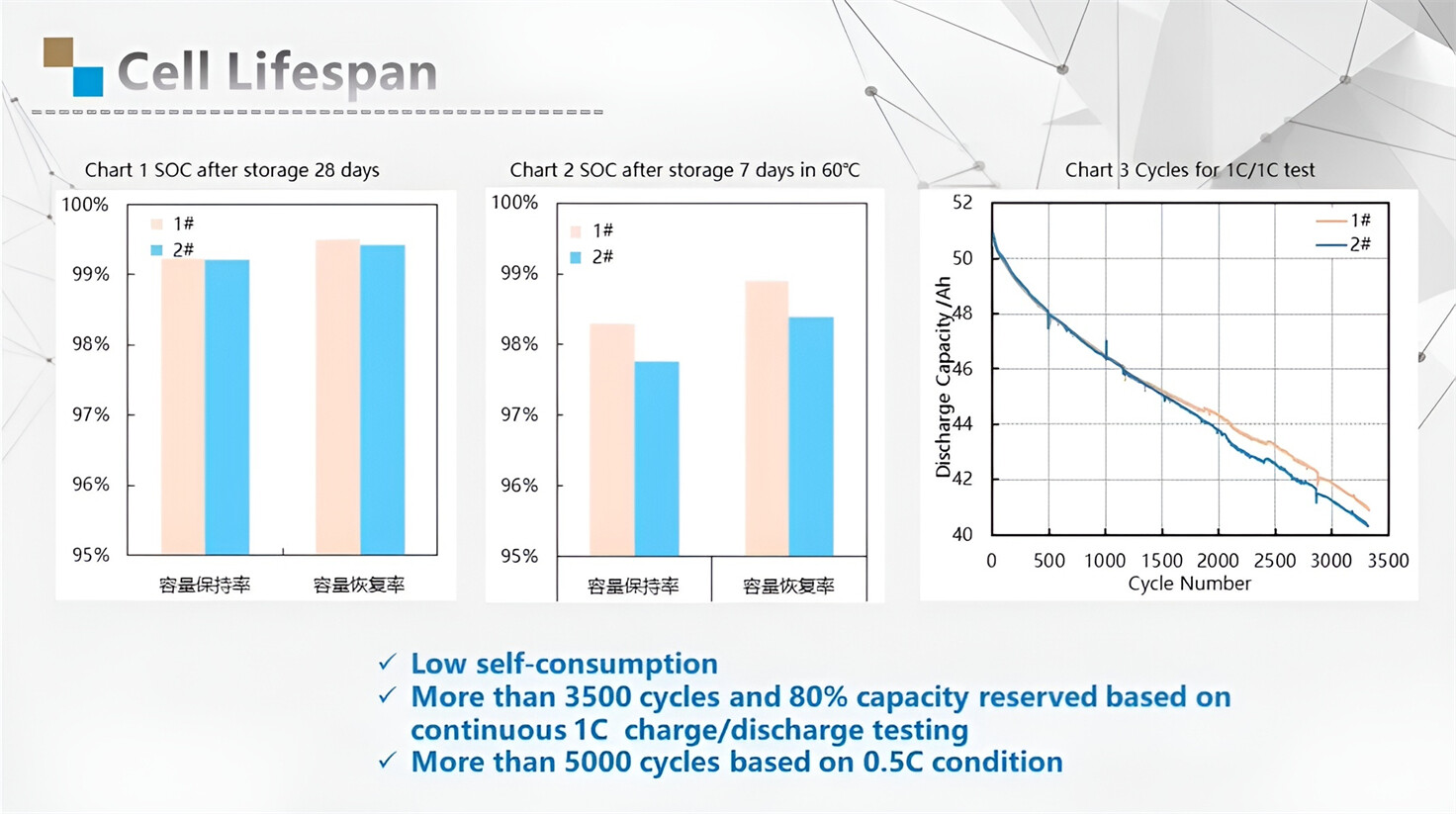
Our energy storage system products use brand new grade A LiFePO4 cells with a battery lifespan of more than 4,000 charge/discharge cycles.

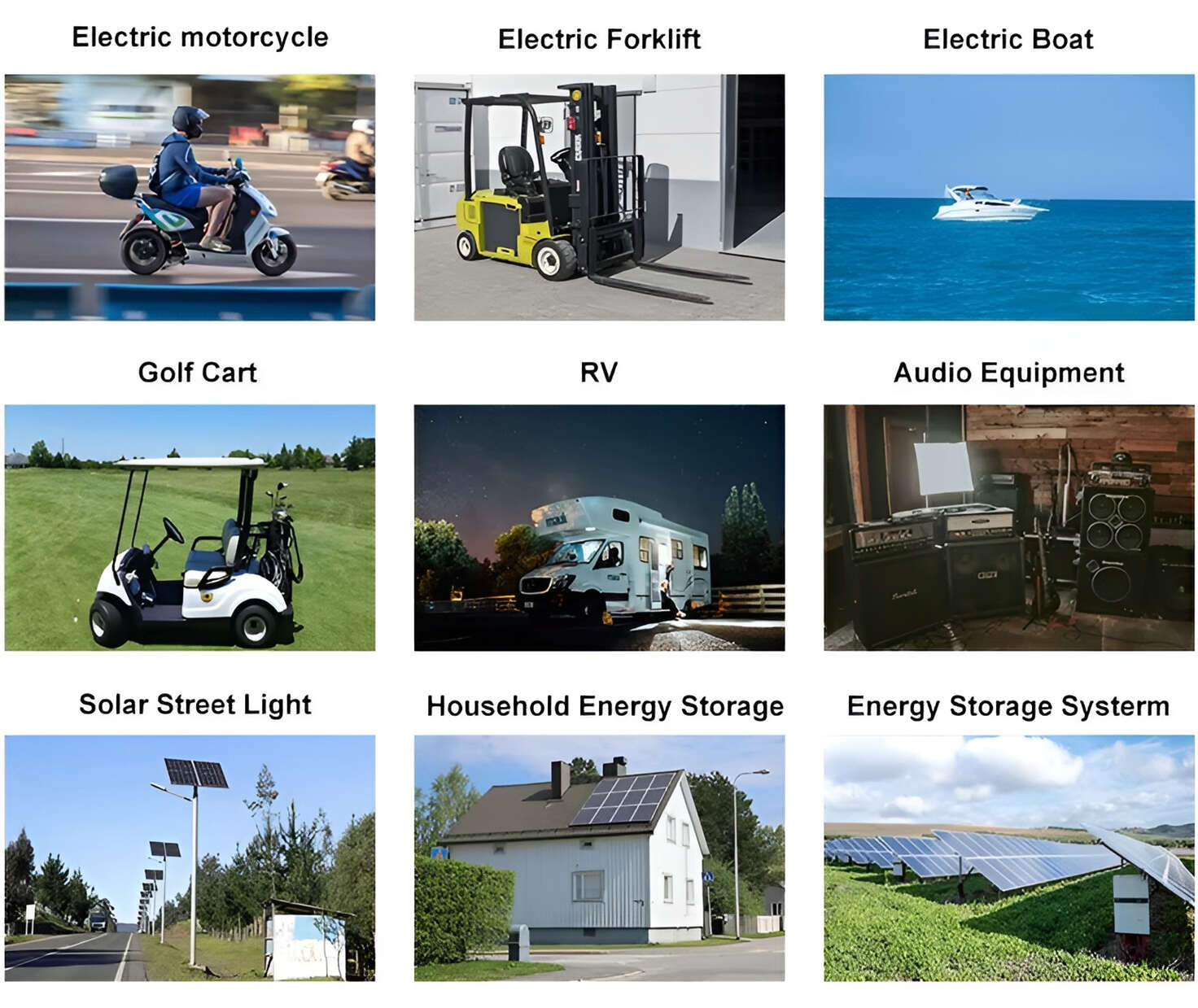
Applications in Different Industries
We supply customized & OEM battery pack, assemble cells with wiring, fuse and plastic cover, all the cell wires connected to PCB plug or built BMS.
Applications: E-bike, Electric Scooter, Golf Carts, RV, Electric Wheelchair, Electric Tools, Robot Cleaner, Robot Sweeper, Solar Energy Storage System, Emergency Light, Solar Power Light, Medical Equipment, UPS Backup Power Supply.
We can provide you with customized services. We have the ability to provide a vertical supply chain, from single cells to pack/module and to a complete power solution with BMS, etc.

HomSolar (Shenzhen) Technology Co., Ltd
























