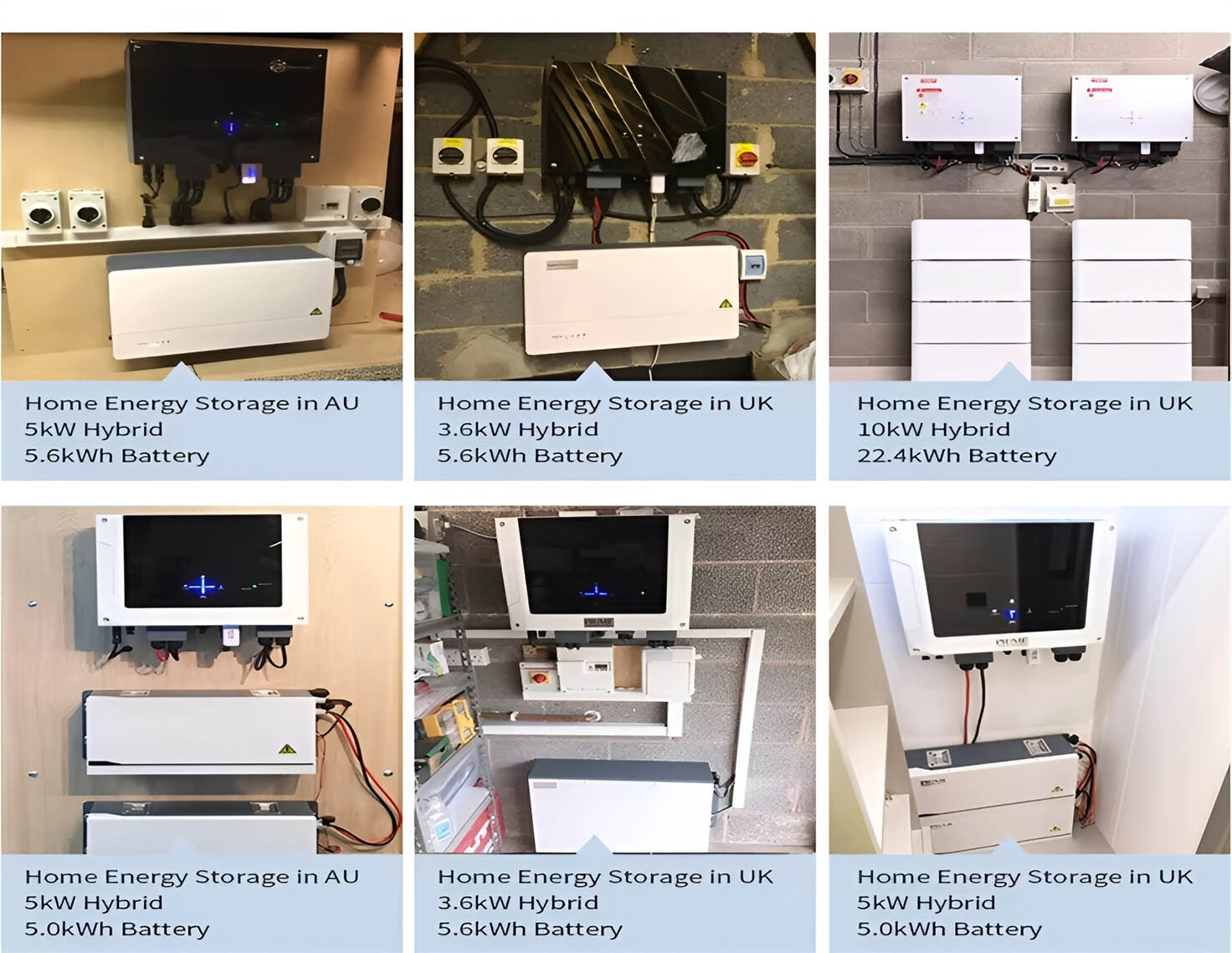
How To Use Safety Precautions: A Comprehensive Guide To Risk Mitigation And Accident Prevention
Introduction Safety precautions are systematic measures implemented to prevent accidents, injuries, and harmful incidents in various environments, from workplaces and laboratories to homes and recreational spaces. They are not merely a list of rules but a proactive mindset and a framework for identifying, assessing, and controlling hazards. Effectively using safety precautions involves understanding their purpose, integrating them into daily routines, and fostering a culture of safety. This guide provides a detailed approach to implementing and utilizing safety precautions to ensure a secure and protected environment.
Understanding the Fundamentals Before diving into specific steps, it's crucial to grasp the core principles behind safety precautions. They are built on a hierarchy of controls, a system that prioritizes the most effective methods of risk reduction: 1. Elimination: Physically removing the hazard is the most effective precaution. 2. Substitution: Replacing the hazard with a safer alternative. 3. Engineering Controls: Isolating people from the hazard through physical means (e.g., machine guards, ventilation systems). 4. Administrative Controls: Changing the way people work through procedures, training, and signage. 5. Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Protecting the worker with equipment like gloves, goggles, and helmets. PPE is the last line of defense.
A robust safety plan utilizes a combination of these controls.
Step-by-Step Guide to Implementing Safety Precautions
Step 1: Hazard Identification and Risk Assessment The first and most critical step is to conduct a thorough inspection of your environment.Action: Walk through the area and systematically identify anything with the potential to cause harm. Look for physical hazards (slippery floors, exposed wiring, moving machinery), chemical hazards (toxic substances, flammables), biological hazards (bacteria, viruses), and ergonomic hazards (poor posture, repetitive strain).Technique: Use a checklist to ensure no area is overlooked. Consider routine tasks, non-routine tasks (like maintenance), and emergency situations. For each identified hazard, assess the risk by considering its severity and likelihood.
Step 2: Develop and Document Procedures Based on your risk assessment, develop clear and concise safety procedures.Action: Create Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) for tasks involving identified hazards. These documents should provide step-by-step instructions on how to perform the task safely.Technique: Involve employees or users in this process. Those who perform the tasks daily have invaluable insights into practical risks and solutions. Ensure the language is simple, direct, and accessible to everyone.
Step 3: Procure and Maintain Safety Equipment Ensure all necessary safety equipment is available, functional, and well-maintained.Action: This includes engineering controls (fire extinguishers, safety interlocks, fume hoods) and PPE (safety glasses, hard hats, respirators).Technique: Establish a regular inspection and maintenance schedule. Assign responsibility to specific individuals for checking equipment. For PPE, ensure it is the correct type for the hazard, fits the user properly, and is stored in a clean, accessible location.
Step 4: Training and Communication Precautions are useless if people are unaware of them or do not understand their importance.Action: Conduct comprehensive training sessions for all individuals entering the environment. Training must cover identified hazards, safety procedures, the correct use of safety equipment, and emergency protocols.Technique: Move beyond passive lectures. Use hands-on demonstrations, workshops, and realistic drills. Post clear safety signage and warnings at the point of hazard. Safety should be a constant topic of conversation, not a once-a-year event.
Step 5: Continuous Monitoring and Improvement Safety is not a static goal but a dynamic process that requires ongoing attention.Action: Regularly audit and inspect the environment for new or recurring hazards. Encourage the reporting of near-misses and potential hazards without fear of blame.Technique: Hold regular safety meetings to discuss concerns, review incidents, and update procedures as necessary. Investigate all accidents and near-misses to identify root causes and prevent recurrence.
Practical Operational Advice and Key ConsiderationsThe "What If" Mindset: Cultivate a habit of always asking "what if?" before starting a task. What if the tool slips? What if the chemical spills? This proactive thinking is the bedrock of personal safety.Housekeeping: A clean and organized workspace is a safe workspace. Clutter, spills, and obstructions are major contributors to trips, falls, and other accidents. Make good housekeeping a non-negotiable standard.Right to Refuse Unsafe Work: Empower everyone with the unequivocal right to stop any task they believe to be dangerously unsafe. This must be supported by management without retaliation.PPE is a Last Resort: Never rely solely on PPE. Always ask if the hazard can be eliminated, substituted, or controlled through engineering means first. PPE can fail, be worn incorrectly, or create a false sense of security.Emergency Preparedness: Knowing routine precautions is not enough. Ensure everyone knows exactly what to do in an emergency: the location of exits, assembly points, first aid kits, and eyewash stations, and how to sound the alarm.Mental and Physical State: An often-overlooked precaution is being aware of one's own condition. Fatigue, stress, distraction, and impairment significantly increase the risk of an accident. Do not engage in high-risk activities if you are not alert and focused.
Conclusion Using safety precautions effectively is an active and continuous commitment to preservation and care. It transforms safety from a abstract concept into a tangible set of actions woven into the fabric of every activity. By diligently following the steps of identification, planning, equipping, training, and reviewing, you create a resilient shield against harm. Remember, the ultimate goal of any safety precaution is to ensure that everyone goes home healthy and safe at the end of the day. It is a goal worth unwavering attention and effort.
Customized/OEM/ODM Service
HomSolar Supports Lifepo4 battery pack customization/OEM/ODM service, welcome to contact us and tell us your needs.


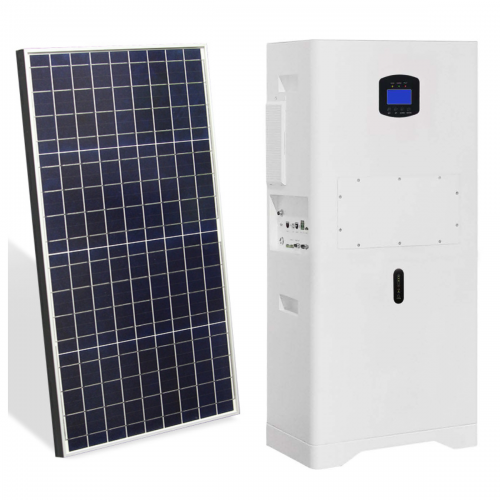
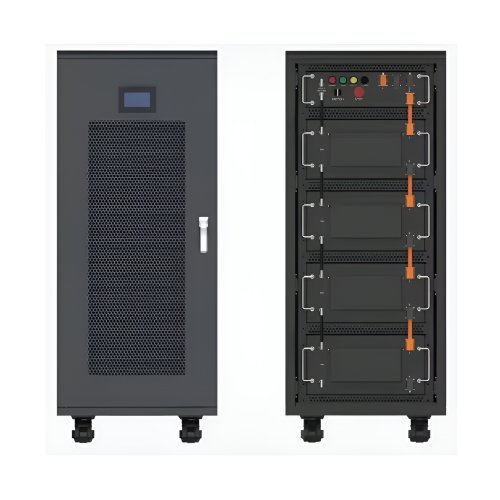
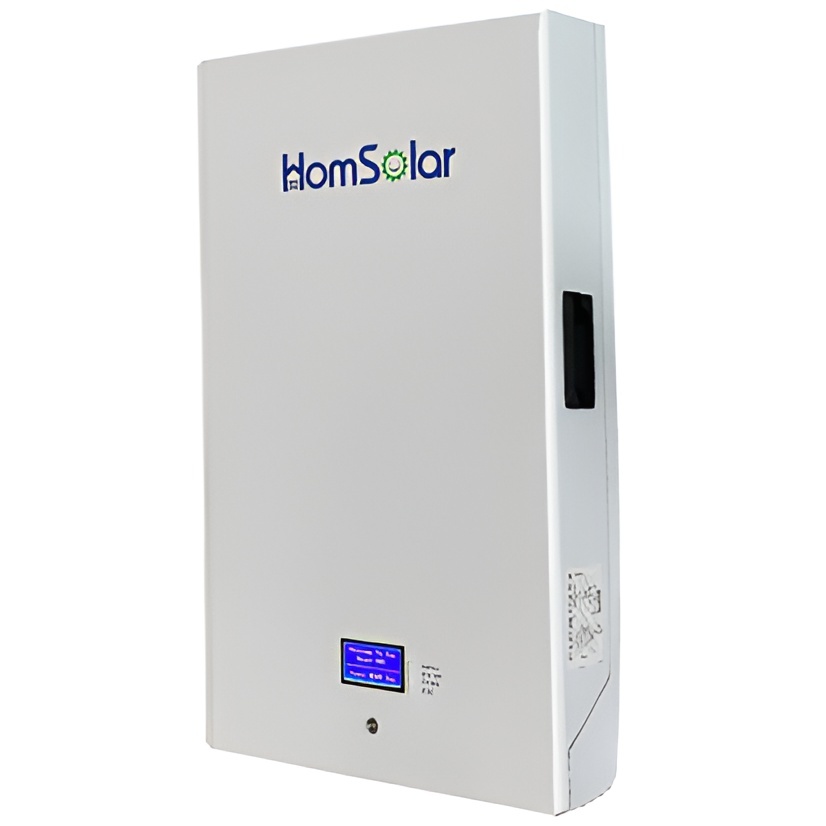
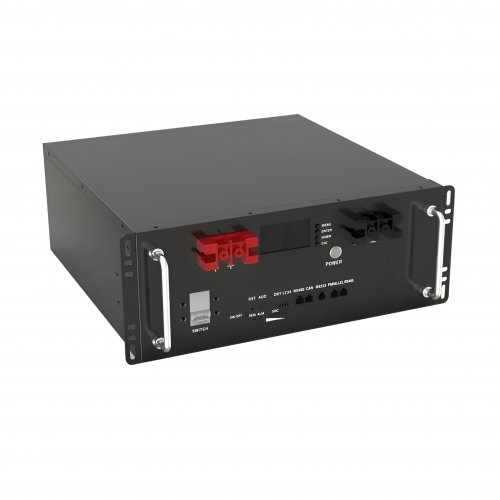
HomSolar: Your One-stop LiFePO4 Battery Pack & ESS Solution Manufacturer
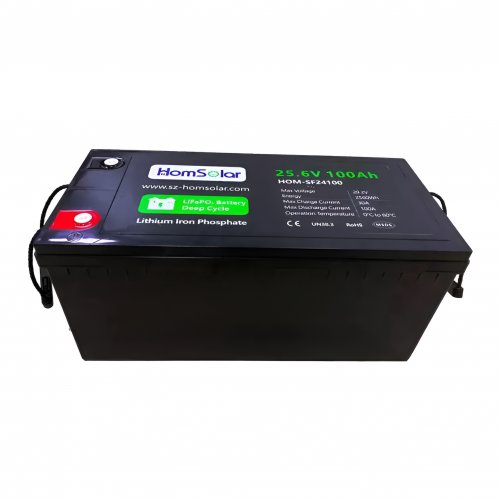
Our line of LiFePO4 (LFP) batteries offer a solution to demanding applications that require a lighter weight, longer life, and higher capacity battery. Features include advanced battery management systems (BMS), Bluetooth® communication and active intelligent monitoring.

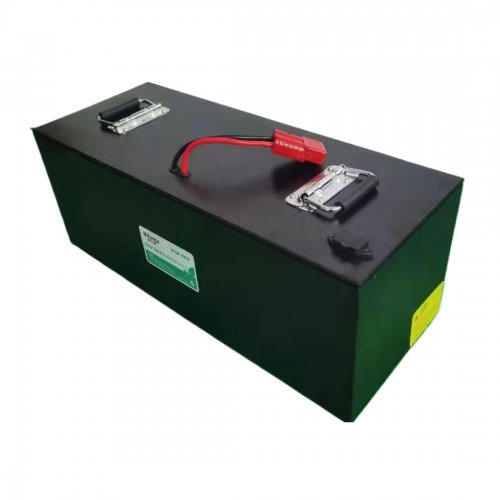
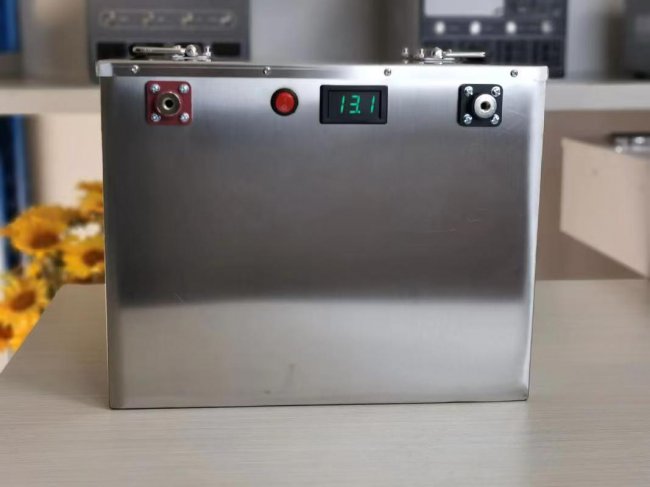
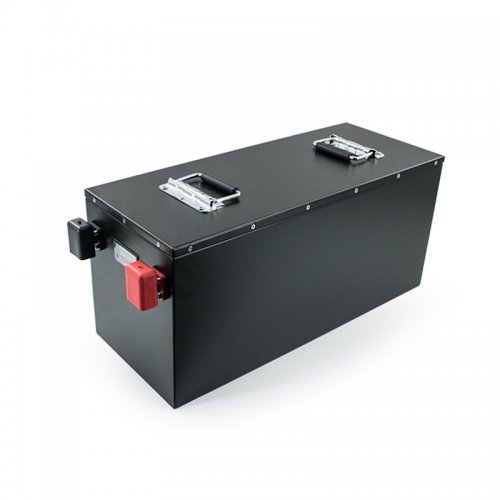
Customised Lithium Iron Phosphate Battery Casing
ABS plastic housing, aluminium housing, stainless steel housing and iron housing are available, and can also be designed and customised according to your needs.

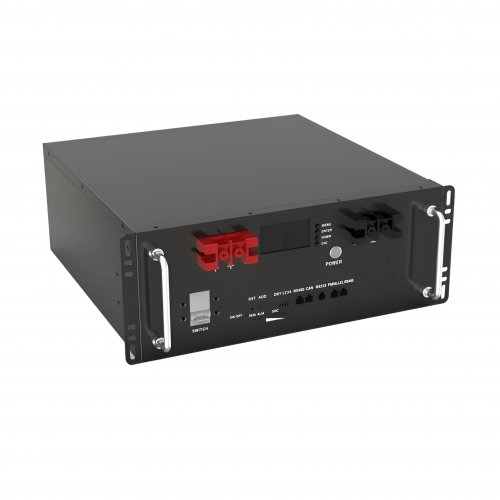
HomSolar Smart BMS
Intelligent Battery Management System for HomSolar Energy Storage System. Bluetooth, temperature sensor, LCD display, CAN interface, UART interface also available.


Terminals & Plugs Can Be Customized
A wide range of terminals and plugs can be customised to suit the application needs of your battery products.

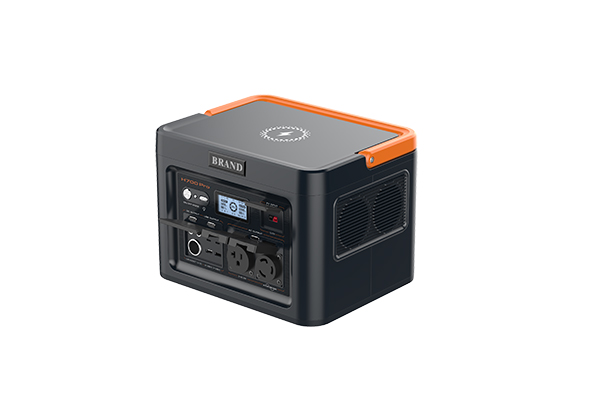
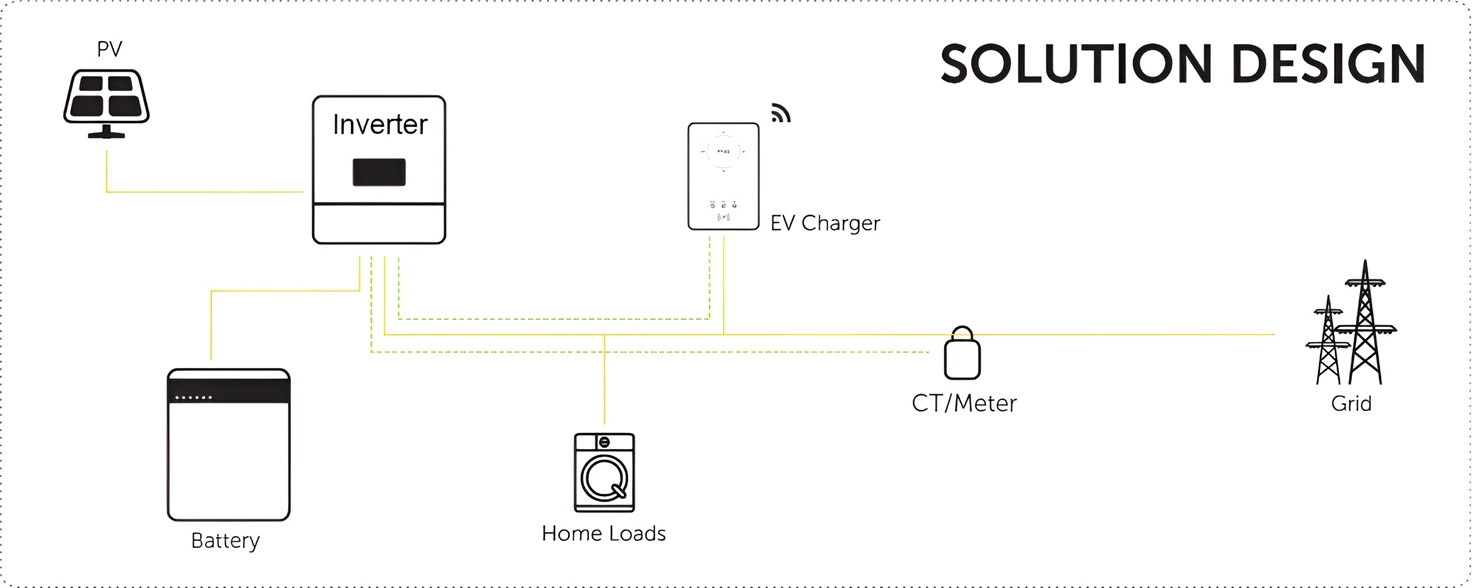
Well-designed Solutions for Energy Storage Systems
We will design the perfect energy storage system solution according to your needs, so that you can easily solve the specific industry applications of battery products.

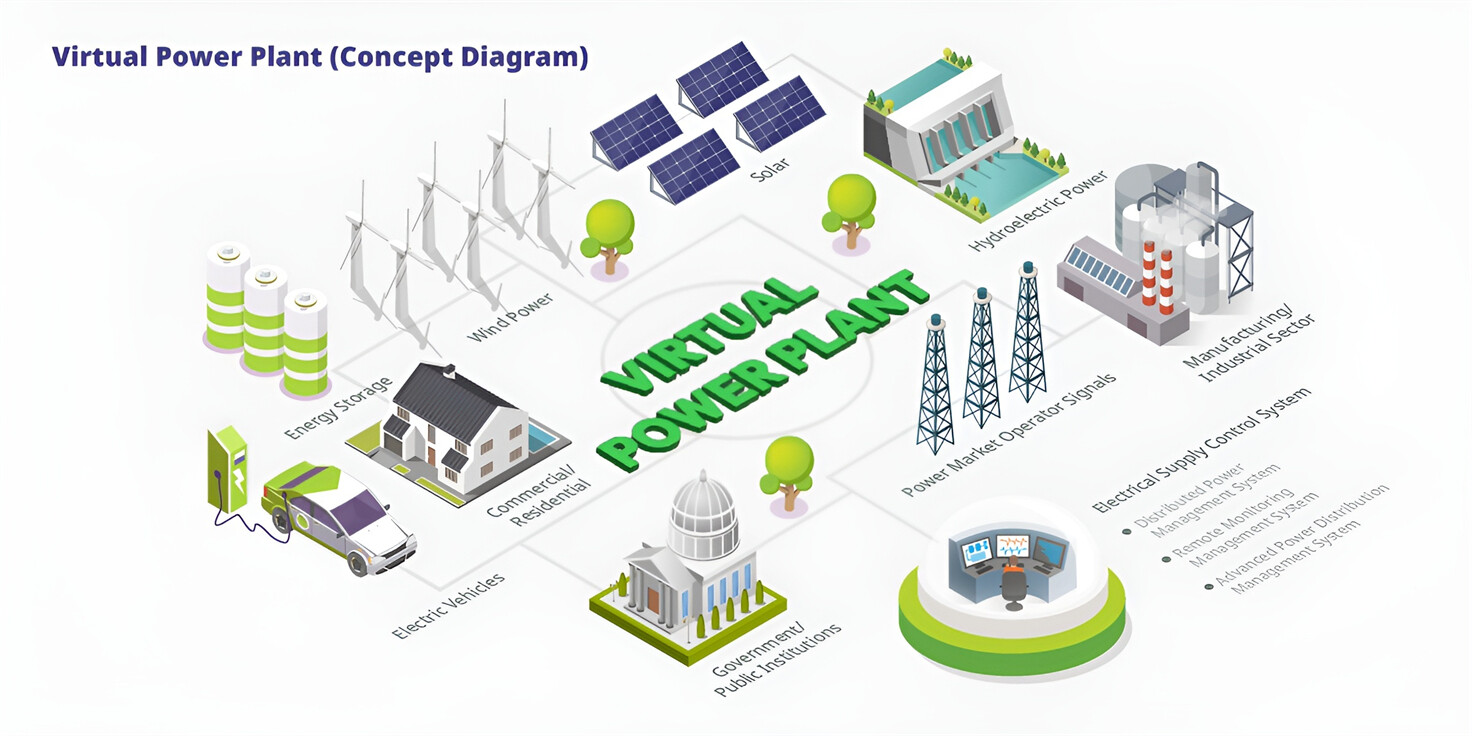
About Our Battery Cells
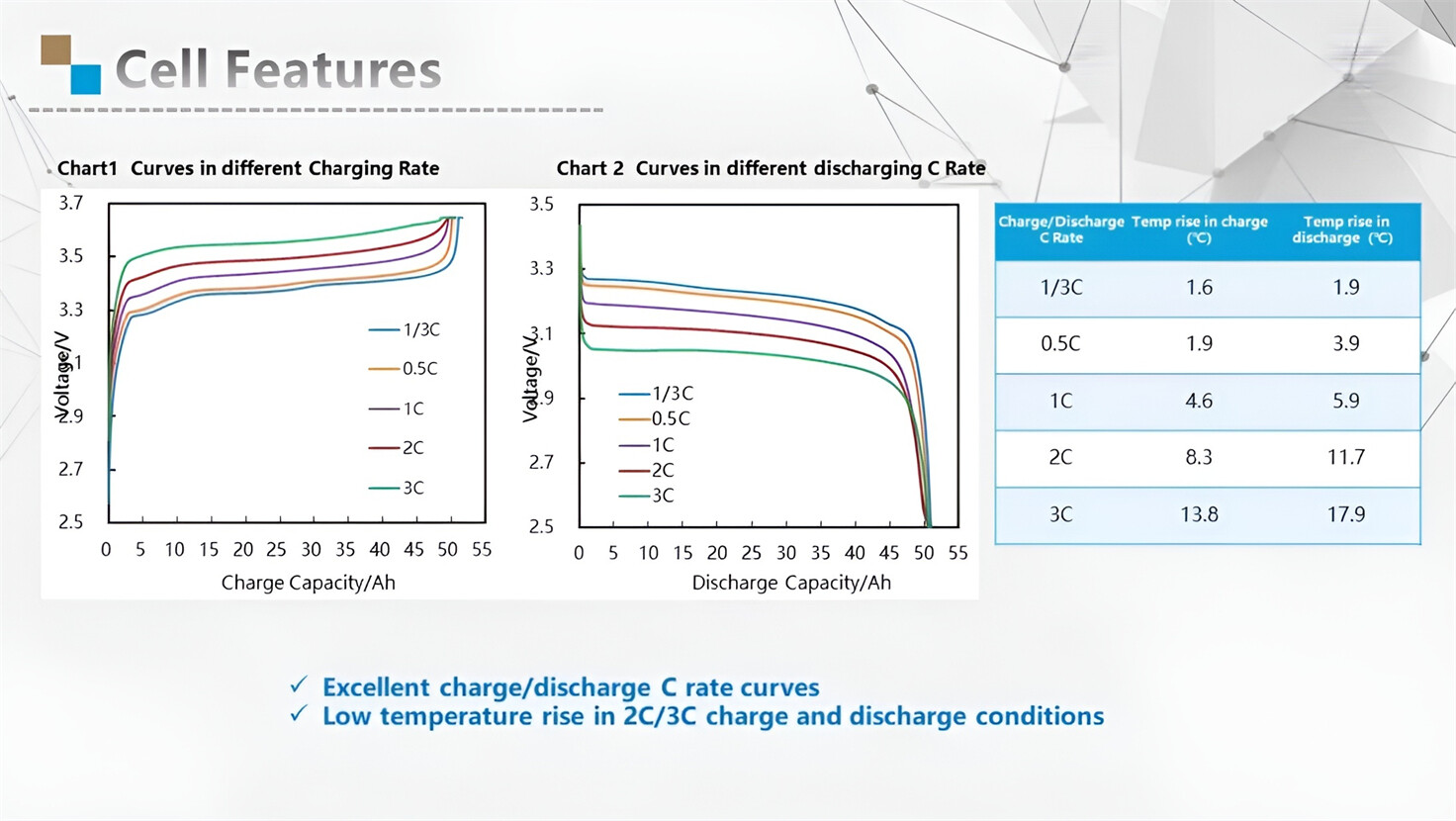
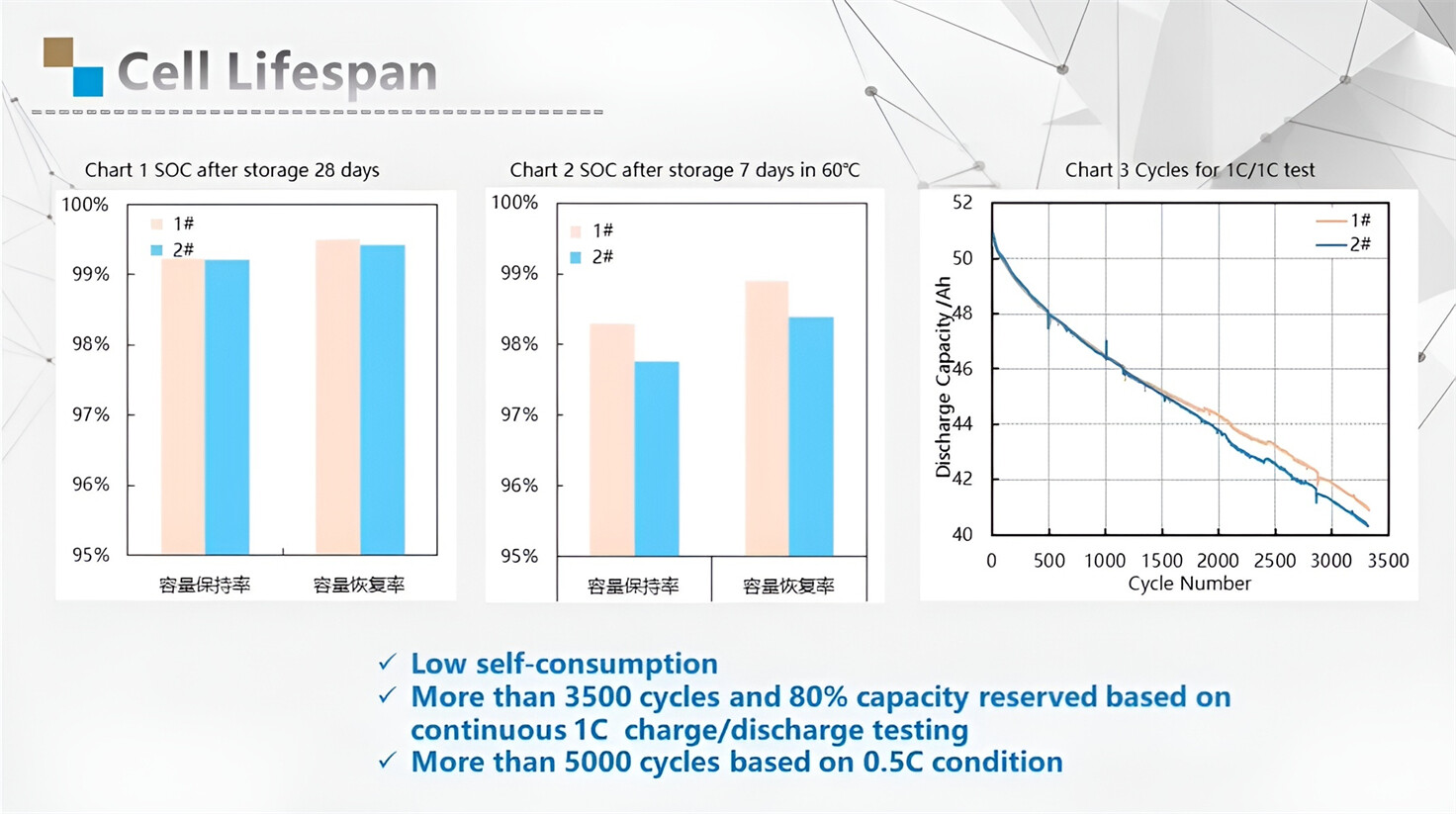
Our energy storage system products use brand new grade A LiFePO4 cells with a battery lifespan of more than 4,000 charge/discharge cycles.

Applications in Different Industries
We supply customized & OEM battery pack, assemble cells with wiring, fuse and plastic cover, all the cell wires connected to PCB plug or built BMS.
Applications: E-bike, Electric Scooter, Golf Carts, RV, Electric Wheelchair, Electric Tools, Robot Cleaner, Robot Sweeper, Solar Energy Storage System, Emergency Light, Solar Power Light, Medical Equipment, UPS Backup Power Supply.
We can provide you with customized services. We have the ability to provide a vertical supply chain, from single cells to pack/module and to a complete power solution with BMS, etc.

HomSolar (Shenzhen) Technology Co., Ltd
























