How To Use Safety Precautions: A Comprehensive Guide For Workplace And Home Security
Introduction
Safety precautions are not merely a set of rules; they are a proactive mindset and a systematic approach to identifying, evaluating, and mitigating risks in any environment. Whether in a high-stakes industrial workplace or within the comfort of your own home, the correct application of safety precautions is fundamental to preventing accidents, injuries, and damage. This guide provides a detailed framework for understanding and implementing these critical measures effectively.
Understanding the Fundamentals
Before diving into specific steps, it's crucial to grasp the core principles that underpin all safety precautions. These are often summarized as the "Hierarchy of Controls," a model used to prioritize the most effective protective measures:
1. Elimination: Physically remove the hazard. This is the most effective precaution. For example, removing a tripping hazard from a walkway. 2. Substitution: Replace the hazard with a safer alternative. For instance, using a non-toxic cleaning chemical instead of a corrosive one. 3. Engineering Controls: Isolate people from the hazard. This includes machine guards, ventilation systems, and sound-dampening enclosures. 4. Administrative Controls: Change the way people work. This involves training, procedures, warning signs, and work schedules that reduce exposure to a hazard. 5. Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Protect the worker with equipment. This is the last line of defense and includes items like safety glasses, gloves, hard hats, and respirators.
A robust safety plan utilizes a combination of these controls, always aiming for the highest level of protection possible.
Step-by-Step Implementation Guide
Step 1: Conduct a Risk Assessment You cannot protect against a risk you haven't identified. Begin by thoroughly inspecting your environment.Workplace: Walk through all areas, including storage rooms, maintenance closets, and outdoor spaces. Look for potential hazards such as slippery floors, exposed wiring, unguarded machinery, poor lighting, and chemical storage issues.Home: Check for frayed electrical cords, clutter on stairs, loose rugs, malfunctioning smoke detectors, and the security of heavy furniture that could tip over.Document: Create a list of all identified hazards. For each, note who might be harmed and how.
Step 2: Develop a Safety Plan Based on your assessment, develop a clear, written plan.Apply the Hierarchy of Controls: For each hazard, decide on the best control method. Can the hazard be eliminated? If not, can it be substituted? If engineering controls are needed, what are they?Establish Procedures: Write simple, clear Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) for tasks that involve risk. For example, a "Lockout/Tagout" procedure for repairing equipment.Emergency Preparedness: Create and communicate plans for fires, chemical spills, medical emergencies, or natural disasters. Include evacuation routes and assembly points.
Step 3: Procure and Maintain Safety Equipment Ensure you have the right tools for the job.PPE: Provide appropriate, well-fitting PPE for all relevant tasks. This is not optional; it is essential.Engineering Controls: Install necessary guards, ventilation, and safety mechanisms on equipment.Emergency Equipment: Ensure fire extinguishers, first-aid kits, eye wash stations, and emergency showers are fully stocked, accessible, and regularly inspected.
Step 4: Training and Communication A plan is useless if people don't know about it or understand it.Formal Training: Conduct mandatory training sessions on general safety principles, specific hazard controls, and emergency procedures.Clear Signage: Use universally understood symbols and clear language on warning signs. Mark hazardous areas, designate PPE zones, and highlight emergency exits.Ongoing Dialogue: Foster a culture where safety is discussed openly. Encourage employees or family members to report hazards or near-misses without fear of blame.
Step 5: Continuous Monitoring and Review Safety is not a one-time project but an ongoing process.Regular Audits: Schedule periodic re-inspections of the workplace or home to identify new hazards.Investigate Incidents: If an accident or near-miss occurs, investigate it thoroughly to understand the root cause and prevent recurrence.Update Plans: Revise your safety plan and procedures as processes change, new equipment is introduced, or after an incident.
Practical Tips and Best PracticesErgonomics Matters: In both office and home settings, poor ergonomics is a major source of injury. Adjust chairs, monitors, and workstations to promote a neutral body posture.The 3-Point Contact Rule: Always maintain three points of contact (two hands and one foot, or two feet and one hand) when climbing ladders or into vehicles to prevent falls.Housekeeping is a Safety Function: A clean, organized space is a safe space. Immediate cleanup of spills and proper storage of materials prevents countless accidents.Plan Your Lift: To avoid back injuries, bend at the knees, not the waist. Keep the load close to your body and ask for help with heavy or awkward objects.Know Your Exits: In any new building you enter, make a mental note of the two closest emergency exits.
Critical Considerations and WarningsComplacency is the Enemy: Familiarity with a task can lead to shortcuts and ignoring safety rules. Consistently reinforce the importance of following procedures every time.PPE is a Last Resort, Not a First Option: Never rely solely on PPE. It can fail, be worn incorrectly, or not provide adequate protection against a severe hazard. Always implement higher-level controls first.Understand Chemical Safety: Always consult Safety Data Sheets (SDS) for any chemical product. They provide critical information on hazards, proper handling, storage, and emergency measures.Never Bypass Safety Mechanisms: Machine guards, emergency stop buttons, and electrical panel locks are there for a reason. Tampering with them dramatically increases the risk of severe injury.Listen to Your Instincts: If a situation feels unsafe, it probably is. Stop the task and reassess the hazards and controls before proceeding.
Conclusion
Effectively using safety precautions is an active and continuous responsibility. It requires vigilance, commitment, and participation from everyone involved. By systematically following these steps—assessing risks, planning, equipping, training, and reviewing—you build a resilient defense against the unforeseen. Ultimately, integrating these precautions into your daily routine transforms them from a checklist into a culture, ensuring that everyone can work and live in a secure and protected environment.
Customized/OEM/ODM Service
HomSolar Supports Lifepo4 battery pack customization/OEM/ODM service, welcome to contact us and tell us your needs.


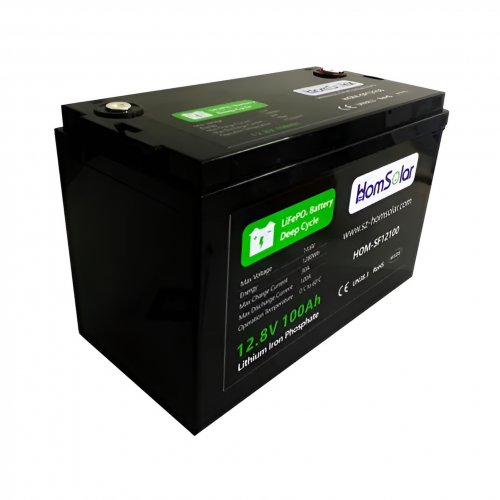
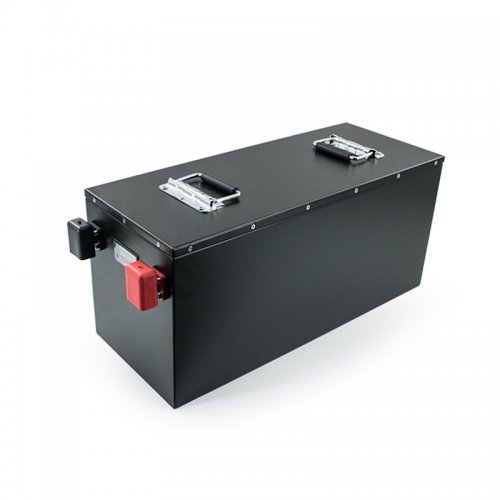
HomSolar: Your One-stop LiFePO4 Battery Pack & ESS Solution Manufacturer
Our line of LiFePO4 (LFP) batteries offer a solution to demanding applications that require a lighter weight, longer life, and higher capacity battery. Features include advanced battery management systems (BMS), Bluetooth® communication and active intelligent monitoring.

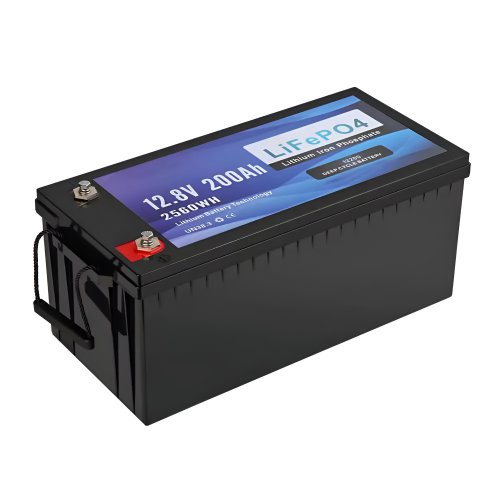
Customised Lithium Iron Phosphate Battery Casing
ABS plastic housing, aluminium housing, stainless steel housing and iron housing are available, and can also be designed and customised according to your needs.

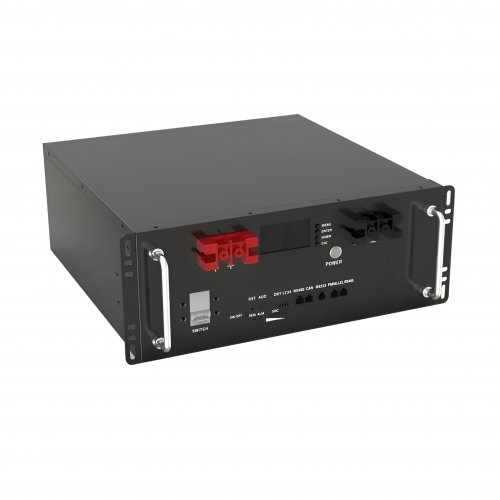
HomSolar Smart BMS
Intelligent Battery Management System for HomSolar Energy Storage System. Bluetooth, temperature sensor, LCD display, CAN interface, UART interface also available.


Terminals & Plugs Can Be Customized
A wide range of terminals and plugs can be customised to suit the application needs of your battery products.

Well-designed Solutions for Energy Storage Systems
We will design the perfect energy storage system solution according to your needs, so that you can easily solve the specific industry applications of battery products.

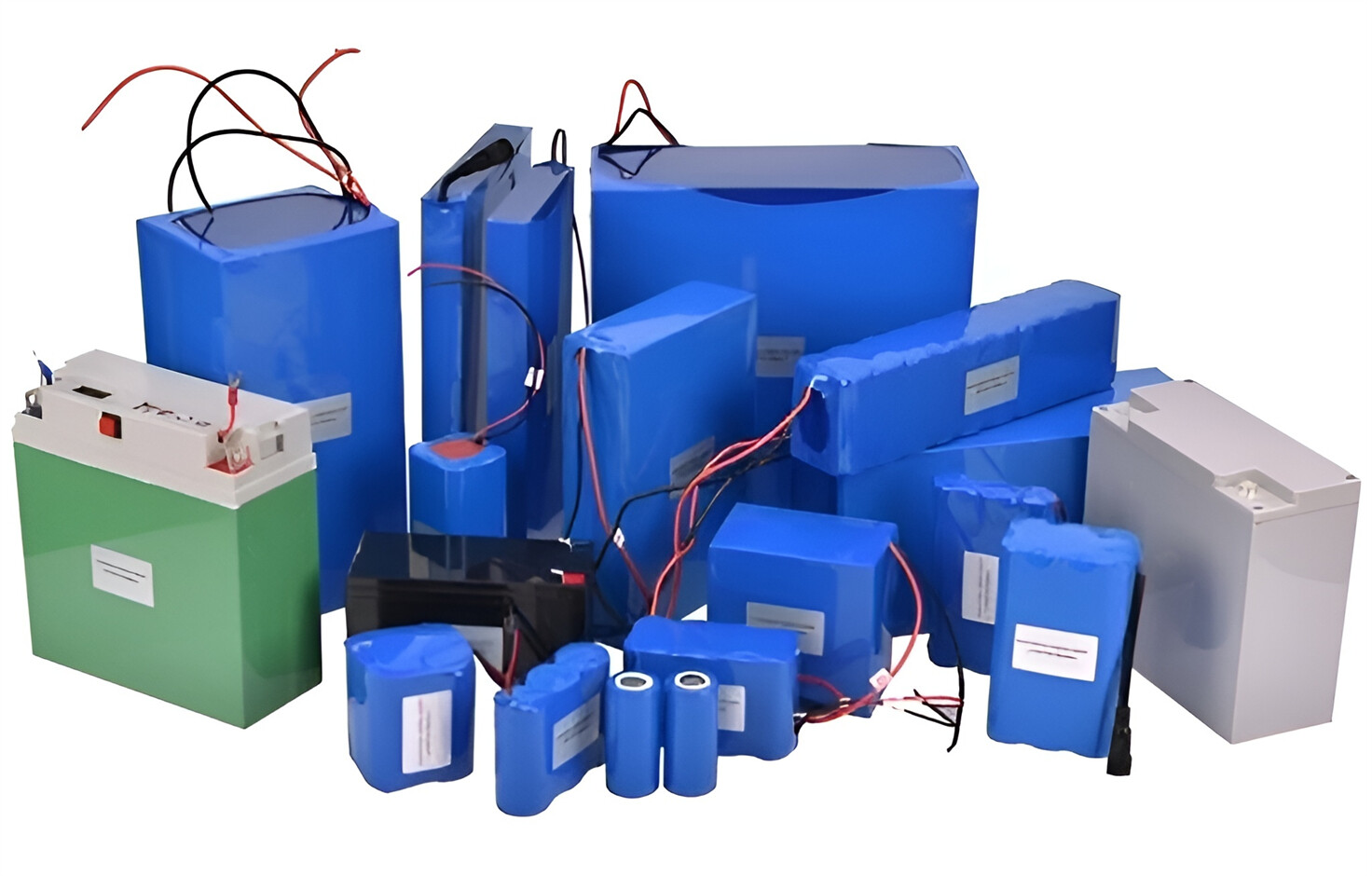
About Our Battery Cells
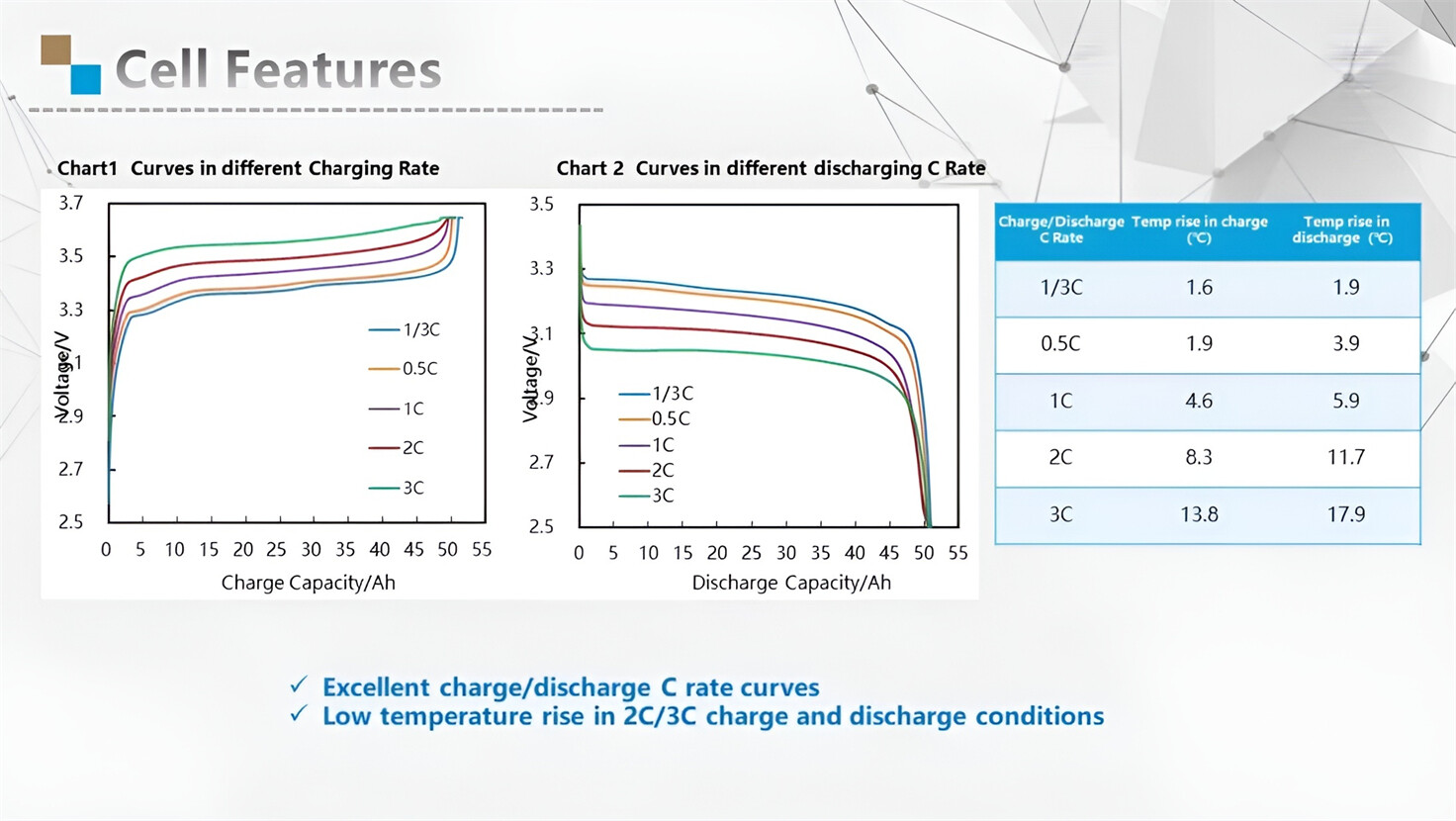
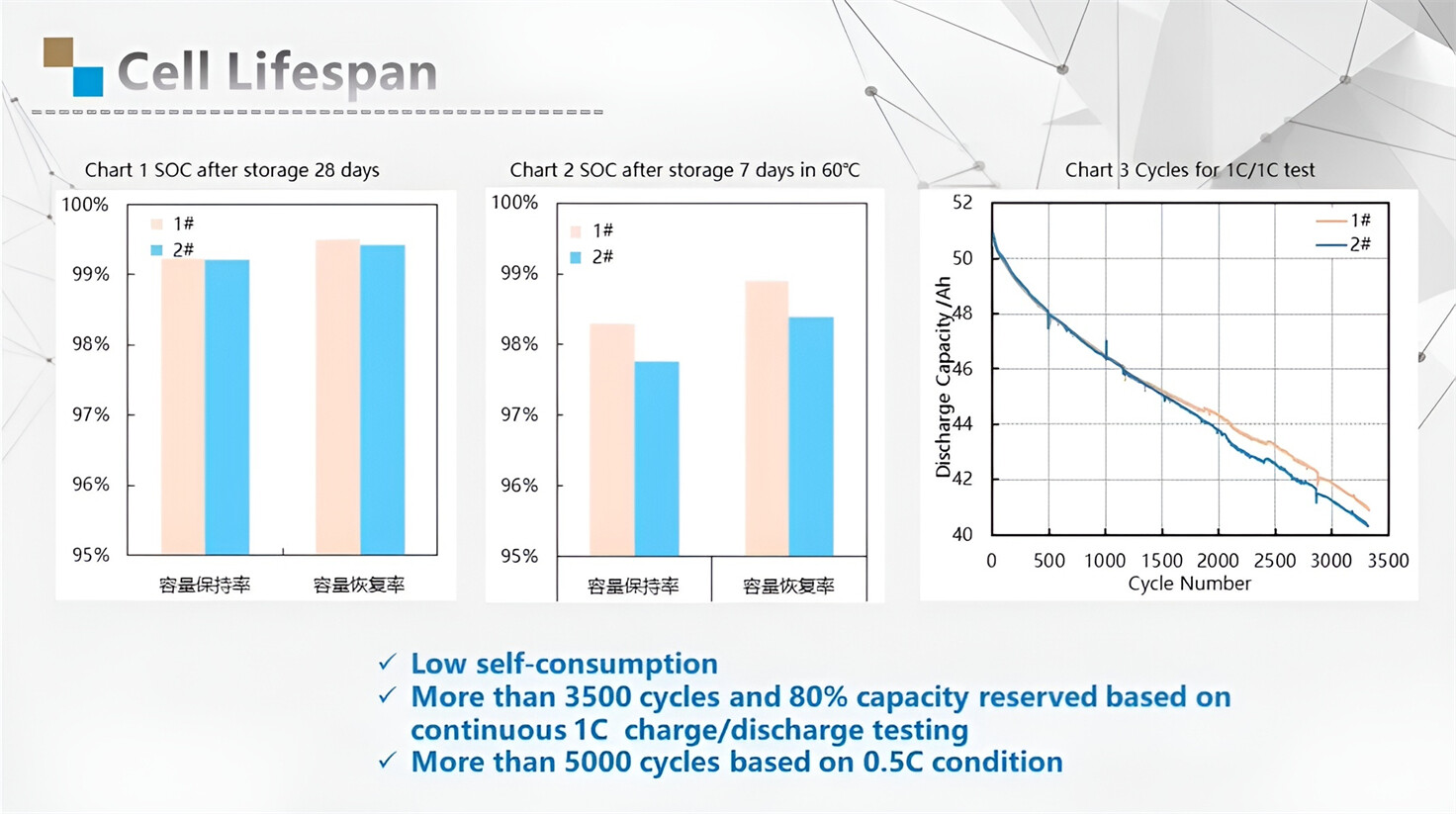
Our energy storage system products use brand new grade A LiFePO4 cells with a battery lifespan of more than 4,000 charge/discharge cycles.

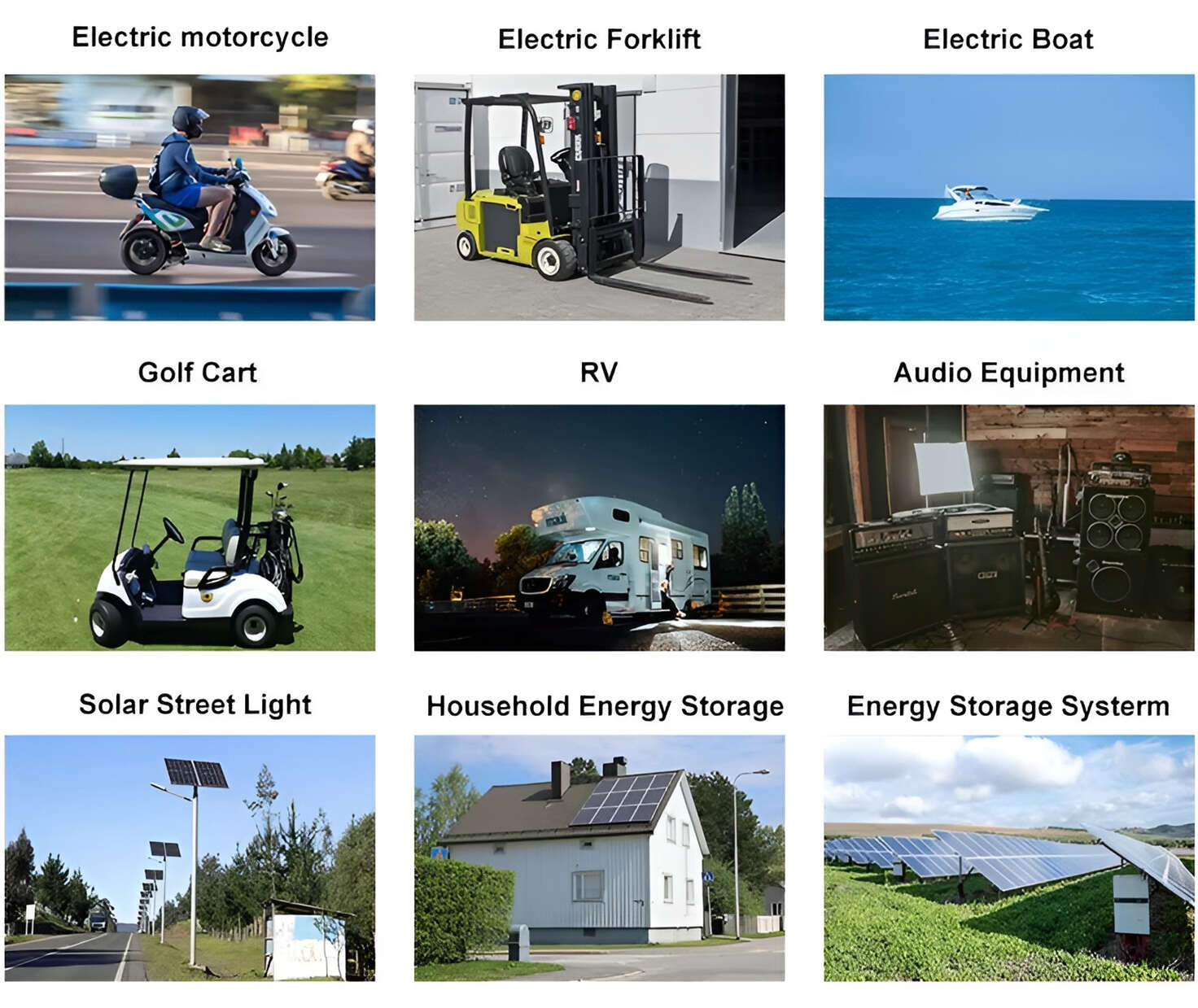
Applications in Different Industries
We supply customized & OEM battery pack, assemble cells with wiring, fuse and plastic cover, all the cell wires connected to PCB plug or built BMS.
Applications: E-bike, Electric Scooter, Golf Carts, RV, Electric Wheelchair, Electric Tools, Robot Cleaner, Robot Sweeper, Solar Energy Storage System, Emergency Light, Solar Power Light, Medical Equipment, UPS Backup Power Supply.
We can provide you with customized services. We have the ability to provide a vertical supply chain, from single cells to pack/module and to a complete power solution with BMS, etc.

HomSolar (Shenzhen) Technology Co., Ltd
























