Environmental Impact News: The Corporate Shift From Offsetting To Insetting In Climate Strategy
A significant and strategic evolution is underway in how corporations approach their environmental impact. For years, the dominant model for achieving carbon neutrality has been heavily reliant on carbon offsetting—investing in external environmental projects to compensate for a company’s own emissions. However, a growing chorus of criticism regarding the efficacy and transparency of some offset projects, coupled with intensifying regulatory and consumer pressure, is driving a fundamental re-evaluation. The emerging trend, gaining substantial traction across global supply chains, is a pivot towards "insetting"—a practice focused on directly decarbonizing and regenerating within a company's own value chain.
This shift represents more than a change in terminology; it signals a deeper commitment to tangible, verifiable environmental action. The movement is being fueled by the latest frameworks from standard-setting bodies and the strategic priorities of industry leaders who recognize that long-term resilience is inextricably linked to the health of the ecosystems and communities from which they source.
The Limitations of Offsetting and the Rise of a New Paradigm
The carbon offset market has been a cornerstone of corporate sustainability for over a decade. The premise was straightforward: companies could calculate their emissions and purchase credits from projects like reforestation initiatives or renewable energy installations in developing countries to "offset" their environmental footprint. This allowed for continued business operations while funding climate action elsewhere.
However, this model has faced increasing scrutiny. Recent investigative reports and scientific studies have raised serious questions about the permanence, additionality, and leakage of certain offset projects. For instance, a 2023 study on forest carbon credits suggested that a significant portion may not represent genuine, additional carbon sequestration. Furthermore, critics argue that offsetting can allow companies to postpone the more difficult, capital-intensive work of fundamentally restructuring their own operations and supply chains.
"In the past, offsetting was often seen as a license to pollute," says Dr. Elena Vance, a senior sustainability researcher at the Global Institute for Sustainable Economics. "The market was opaque, and it was difficult for stakeholders to distinguish between high-integrity projects and those with questionable climate benefits. This has eroded trust and pushed companies to seek more direct and accountable solutions."
This erosion of trust is coinciding with a regulatory avalanche. The European Union's Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD) and the newly adopted IFRS Sustainability Disclosure Standards are forcing companies to provide detailed, audited accounts of their environmental footprint, including Scope 3 emissions—those originating from their supply chains. Simply buying offsets no longer satisfies the demand for transparent, embedded climate action.
Insetting: Embedding Sustainability into the Value Chain
Insetting addresses these concerns by focusing investment and innovation internally. The concept, championed by organizations like the International Platform for Insetting (IPI), involves implementing projects that directly reduce greenhouse gas emissions, enhance biodiversity, improve water security, and support socio-economic development within a company's own sphere of influence—from raw material sourcing to manufacturing and logistics.
A prominent example is in the food and agriculture sector. A major chocolate manufacturer, for instance, is no longer just buying offsets for the emissions from its cocoa farms. Instead, it is investing in insetting projects that provide farmers with shade-tree saplings to promote agroforestry, which sequesters carbon in the soil, improves crop resilience to climate change, and boosts biodiversity on the very farms that supply its cocoa. The carbon reduction is achieved within the supply chain, and the company simultaneously de-risks its raw material supply.
Similarly, in the fashion industry, a leading apparel brand has launched a program to transition its cotton farmers to regenerative agricultural practices. This insetting initiative reduces the carbon footprint of the cotton (a Scope 3 emission), reduces water usage, and improves soil health, creating a more resilient and sustainable raw material base. The environmental benefit is intrinsic to the product itself.
"With insetting, the value is multi-layered," explains Michael Thorne, a supply chain sustainability consultant. "You are not just ticking a box for a carbon accountant. You are building soil health, which secures your agricultural yields for the future. You are conserving water, which mitigates operational risk in water-stressed regions. You are investing in the communities you depend on, which strengthens your social license to operate. The business case is profoundly strategic."
Industry Dynamics and Future Outlook
The transition to insetting is not without its challenges. It is often more complex and resource-intensive than purchasing offsets. It requires deep collaboration with suppliers, significant upfront investment, and robust monitoring and verification systems to track progress. Technology, however, is playing a pivotal role in overcoming these hurdles. Satellite imaging, IoT sensors, and blockchain-based traceability platforms are enabling companies to monitor land-use changes, carbon sequestration, and supply chain conditions with unprecedented accuracy, providing the data needed to validate insetting claims.
The trend is also creating new alliances and financing models. Collective Impact Coalitions, where competing companies within an industry collaborate to transform a shared supply chain, are emerging. For example, several competing consumer goods companies are jointly funding large-scale insetting projects in key commodity-producing regions.
Looking ahead, experts predict that the carbon market will not disappear but will evolve. High-quality offsets will likely be reserved for neutralizing the final, hardest-to-abate emissions after a company has exhausted all possible insetting and direct reduction efforts.
"The future of corporate climate action is a hierarchy: first, reduce your direct emissions and energy use. Second, implement insetting projects to decarbonize and regenerate your value chain. Finally, for what remains, purchase only the most verified and high-integrity offsets," concludes Dr. Vance. "The era of using offsets as a primary strategy is closing. The era of embedded, value-chain-centric action is just beginning. This is not merely a trend; it is a fundamental recalibration of corporate responsibility in the face of the climate and biodiversity crises."
This strategic shift from offsetting to insetting marks a more mature, integrated, and ultimately more impactful approach to managing corporate environmental footprints, positioning it as one of the most significant developments in sustainable business practice today.
Customized/OEM/ODM Service
HomSolar Supports Lifepo4 battery pack customization/OEM/ODM service, welcome to contact us and tell us your needs.


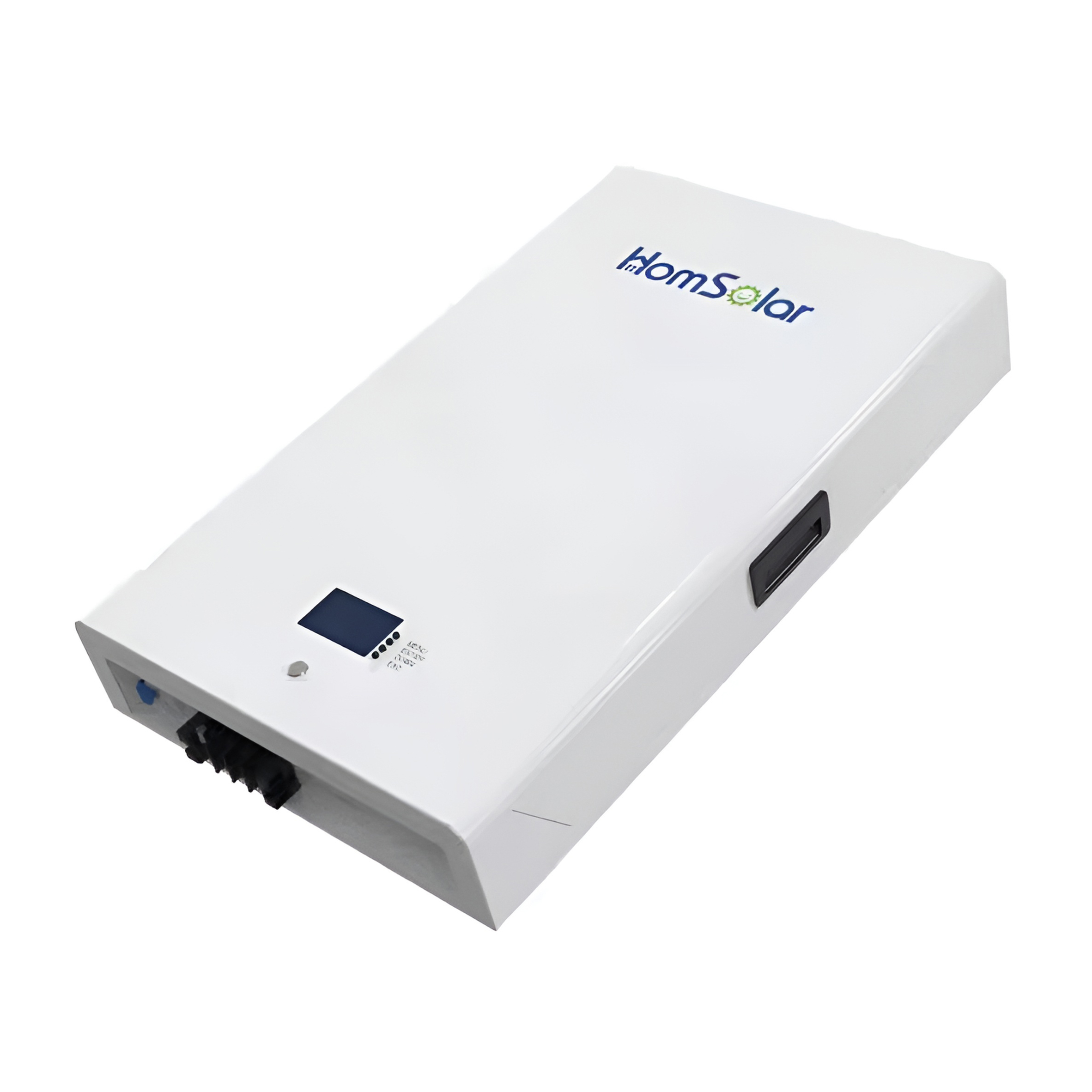
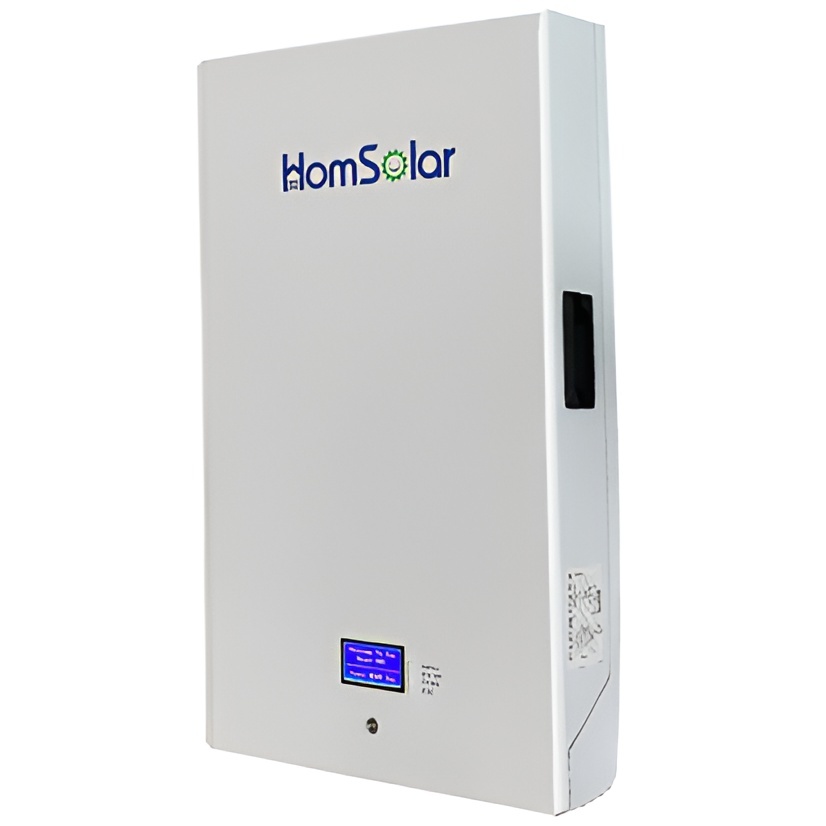
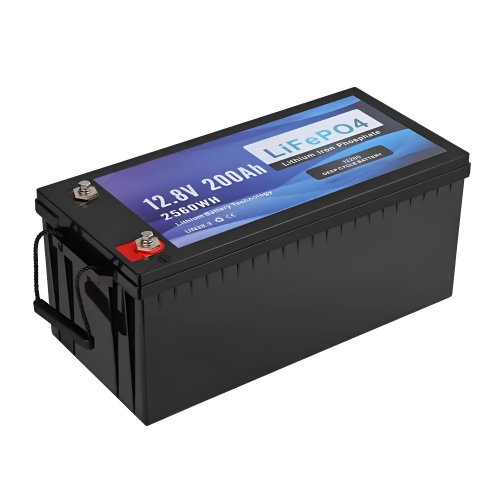
HomSolar: Your One-stop LiFePO4 Battery Pack & ESS Solution Manufacturer
Our line of LiFePO4 (LFP) batteries offer a solution to demanding applications that require a lighter weight, longer life, and higher capacity battery. Features include advanced battery management systems (BMS), Bluetooth® communication and active intelligent monitoring.

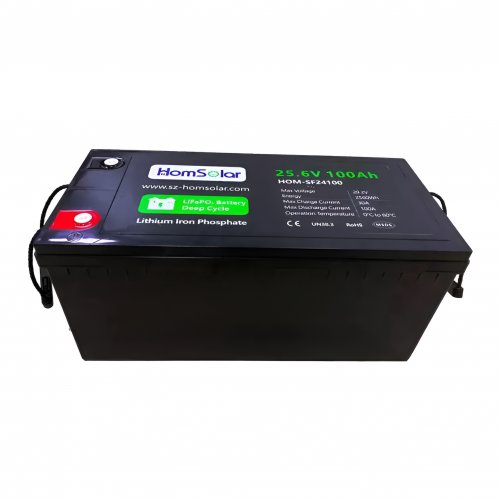
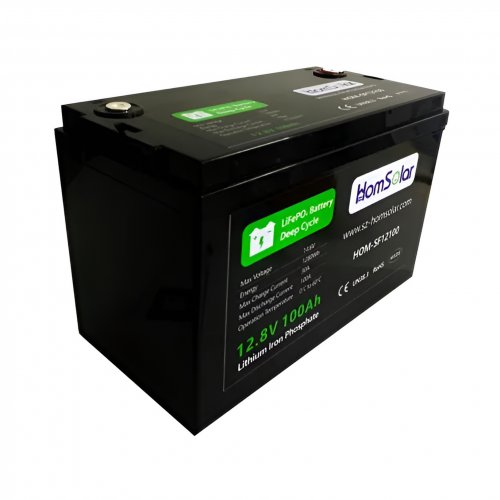
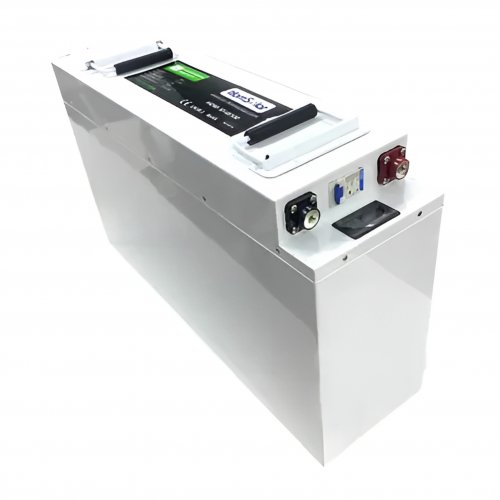
Customised Lithium Iron Phosphate Battery Casing
ABS plastic housing, aluminium housing, stainless steel housing and iron housing are available, and can also be designed and customised according to your needs.

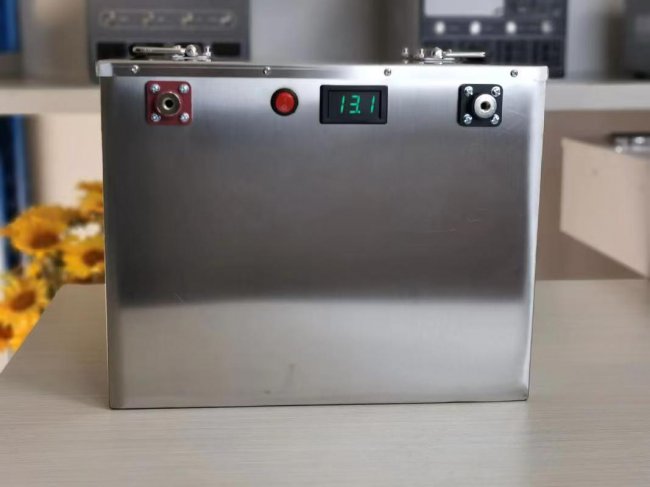
HomSolar Smart BMS
Intelligent Battery Management System for HomSolar Energy Storage System. Bluetooth, temperature sensor, LCD display, CAN interface, UART interface also available.


Terminals & Plugs Can Be Customized
A wide range of terminals and plugs can be customised to suit the application needs of your battery products.

Well-designed Solutions for Energy Storage Systems
We will design the perfect energy storage system solution according to your needs, so that you can easily solve the specific industry applications of battery products.

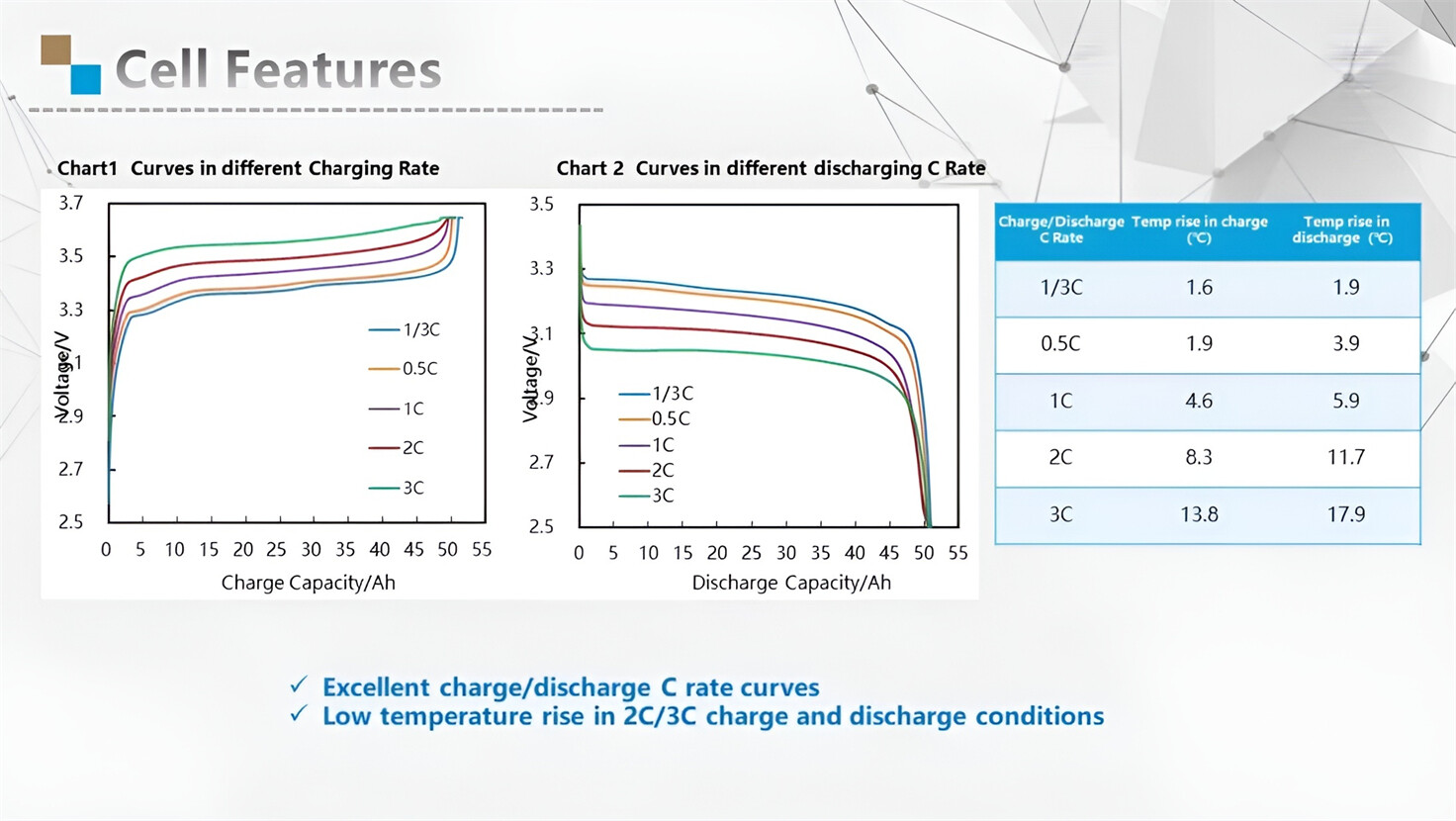
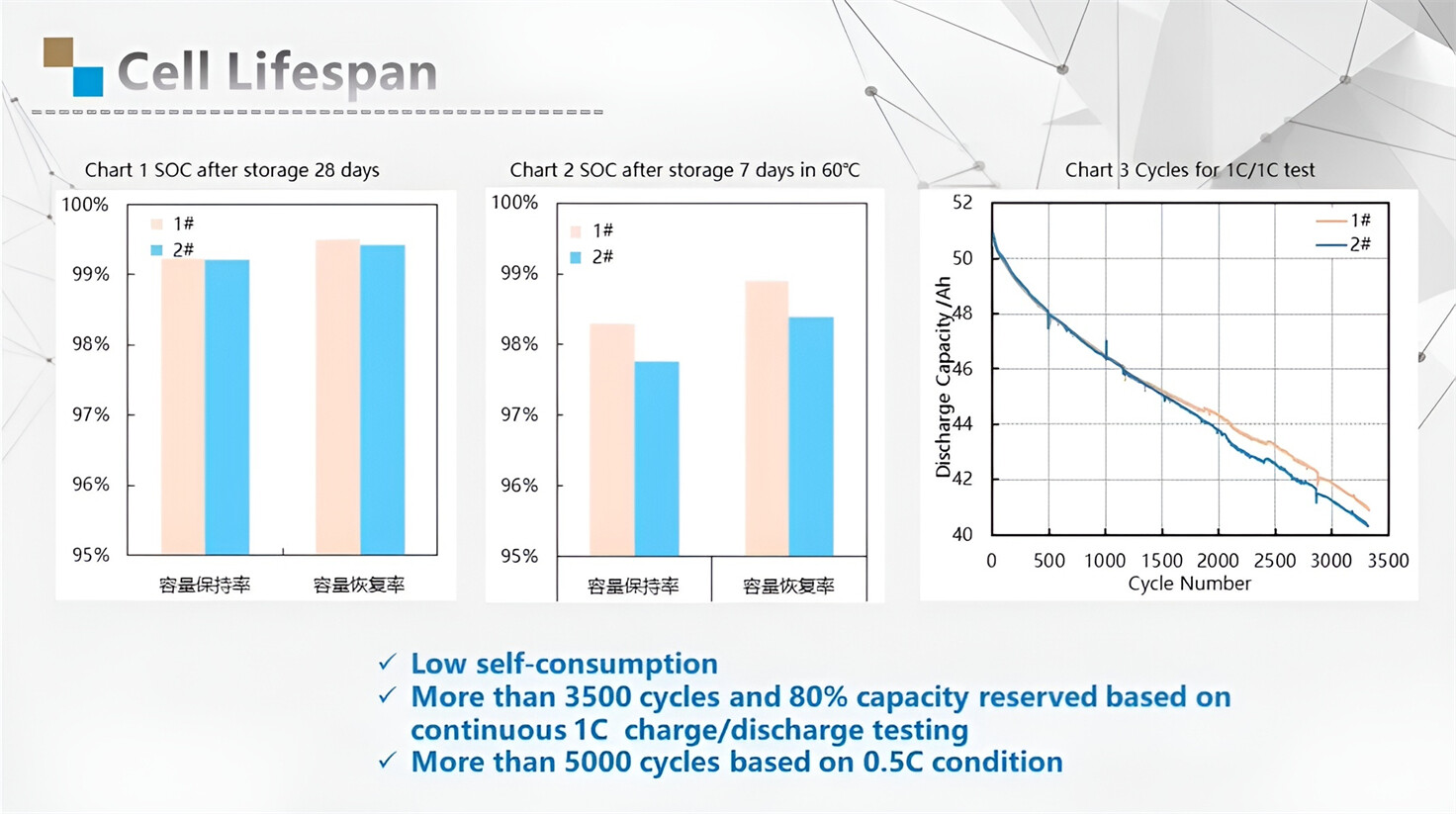
About Our Battery Cells
Our energy storage system products use brand new grade A LiFePO4 cells with a battery lifespan of more than 4,000 charge/discharge cycles.

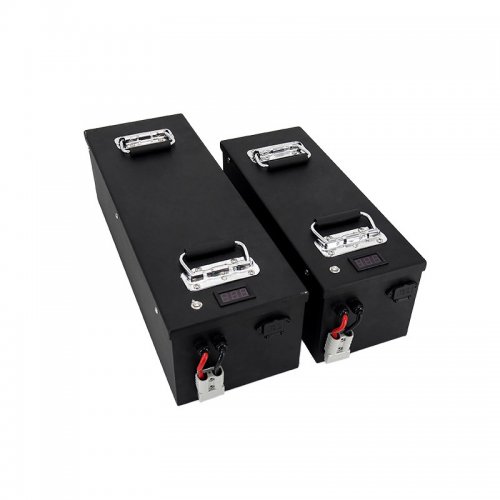
Applications in Different Industries
We supply customized & OEM battery pack, assemble cells with wiring, fuse and plastic cover, all the cell wires connected to PCB plug or built BMS.
Applications: E-bike, Electric Scooter, Golf Carts, RV, Electric Wheelchair, Electric Tools, Robot Cleaner, Robot Sweeper, Solar Energy Storage System, Emergency Light, Solar Power Light, Medical Equipment, UPS Backup Power Supply.
We can provide you with customized services. We have the ability to provide a vertical supply chain, from single cells to pack/module and to a complete power solution with BMS, etc.

HomSolar (Shenzhen) Technology Co., Ltd
























