Advances In Scalable Synthesis: Bridging Laboratory Innovation And Industrial Production
The pursuit of scalable synthesis represents one of the most critical and challenging frontiers in modern chemistry and materials science. It marks the crucial transition from a promising laboratory discovery to a commercially viable and socially impactful technology. For decades, a pervasive "valley of death" has separated ingenious bench-scale syntheses from their widespread application, often due to issues of cost, safety, reproducibility, and energy consumption. Recent years, however, have witnessed a paradigm shift, driven by interdisciplinary approaches that integrate novel reactor design, advanced automation, and data-driven methodologies to overcome these traditional barriers.
The Paradigm of Continuous Flow Chemistry
A cornerstone of modern scalable synthesis is the move from traditional batch processing to continuous flow chemistry. Unlike a batch reactor, where reactions occur in a single, large vessel, flow systems pump reagents through narrow tubing or microstructured reactors. This fundamental shift in engineering offers profound advantages for scalability. A landmark achievement in this area has been the continuous-flow synthesis of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs). Researchers from MIT demonstrated a refrigerator-sized, reconfigurable flow system capable of producing multiple APIs, including diazepam and diphenhydramine, with yields and purities matching or exceeding batch methods. The system integrated multiple synthetic steps, including reaction, work-up, and purification, in a single, streamlined process. This approach not only reduces the physical footprint but also enhances safety by minimizing the inventory of hazardous intermediates at any given time.
The scalability of flow chemistry is further amplified by its synergy with photoredox catalysis and electrochemistry. Photochemical reactions in batch are notoriously difficult to scale due to the rapid attenuation of light penetration. In flow, however, the high surface-area-to-volume ratio ensures uniform irradiation of the entire reaction volume. For instance, the Noël group at Eindhoven University of Technology has pioneered the scale-up of photochemical [2+2] cycloadditions and other transformations, achieving kilogram-per-day outputs in compact reactor setups. Similarly, electrochemical synthesis in flow elegantly addresses the issue of electrode surface area, enabling efficient electron transfer on a large scale. This has opened new, sustainable pathways for oxidation and reduction reactions without the need for stoichiometric oxidants or reductants, a significant advance for green chemistry.
Automation and Artificial Intelligence in Synthesis Design
Beyond novel reactors, the very process of designing and optimizing synthetic routes is being revolutionized by automation and artificial intelligence (AI). High-throughput experimentation (HTE) platforms, equipped with robotic liquid handlers and automated analytics, can now screen thousands of reaction conditions in the time it once took to test a dozen. This data-rich approach is invaluable for identifying the optimal parameters for a scalable process rapidly.
The integration of AI and machine learning is the logical next step. By training algorithms on vast datasets of successful reactions, researchers can now predict viable synthetic routes and anticipate potential bottlenecks before any wet chemistry begins. For example, the development of natural language processing models capable of extracting synthetic procedures from the scientific literature has created massive, structured reaction databases. Companies and academic groups are using these databases to train predictive models that suggest optimal solvents, catalysts, and conditions for a target molecule. A notable example is the work by Jensen and colleagues, who coupled a robotic flow chemistry platform with a Bayesian optimization algorithm to autonomously discover and scale-up a complex palladium-catalyzed cross-coupling reaction, achieving high yield with minimal human intervention. This closed-loop "self-optimizing" system represents a glimpse into the future of chemical manufacturing, where AI-driven platforms can adapt and perfect a synthesis for scale with unprecedented efficiency.
Advanced Materials and Nanotechnology at Scale
The challenge of scalability is perhaps most acute in the field of nanomaterials and advanced materials, where precise control over size, shape, and composition is paramount. Breakthroughs in this area are crucial for the commercialization of technologies ranging from perovskite solar cells to metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) and graphene.
For MOFs, renowned for their exceptionally high surface areas but often synthesized slowly under solvothermal conditions, continuous flow methods have been a game-changer. The Farha group at Northwestern University demonstrated a continuous flow synthesis of several robust MOFs, including UiO-66, achieving production rates of kilograms per day while maintaining the high crystallinity and porosity achieved in lab-scale batches. This breakthrough paves the way for the widespread use of MOFs in gas storage, separation, and catalysis.
In the realm of two-dimensional materials, researchers have made significant strides in scaling up the production of graphene. While mechanical exfoliation with sticky tape yielded the first samples, chemical vapor deposition (CVD) on metal foils has emerged as the most promising scalable route. Recent progress has focused on developing roll-to-roll CVD processes and electrochemical methods that allow for the continuous production and transfer of high-quality graphene films onto flexible substrates, a critical step for applications in flexible electronics and coatings.
Future Outlook and Challenges
The future of scalable synthesis is bright and will be defined by several converging trends. The concept of "distributed manufacturing" is gaining traction, where compact, automated flow reactors could produce chemicals on-demand and on-site, reducing supply chain dependencies and waste. The integration of real-time analytics, such as inline IR and UV spectroscopy, with feedback control loops will further enhance the robustness of continuous processes, ensuring consistent product quality.
Sustainability will remain a central driver. The push towards bio-based feedstocks and the integration of enzymatic catalysis with continuous processing will create more environmentally friendly synthetic pathways. Furthermore, the application of scalable electrosynthesis using renewable electricity is poised to decarbonize segments of the chemical industry.
However, significant challenges persist. The initial capital investment for advanced flow and automation systems can be high, necessitating clear economic benefits for adoption. The handling of solids and highly viscous materials in continuous flow remains a technical hurdle. Finally, the cultural and educational shift required for chemists to think natively in terms of process intensification and scale from the outset of their research is an ongoing process.
In conclusion, the field of scalable synthesis is undergoing a profound transformation. The synergistic combination of continuous flow engineering, intelligent automation, and data science is systematically dismantling the barriers between laboratory discovery and global impact. As these technologies mature and become more accessible, they promise to accelerate the delivery of new medicines, materials, and sustainable technologies to society, heralding a new era of efficient and intelligent chemical production.
References:
1. Adamo, A., et al. (2016). On-demand continuous-flow production of pharmaceuticals in a compact, reconfigurable system.Science, 352(6281), 61-67. 2. Noël, T., & Su, Y. (2021). Scale-up of Photoredox Catalysis in Continuous-Flow Microreactors.Nature Protocols, 16(7), 3487-3515. 3. Coley, C. W., et al. (2019). A robotic platform for flow synthesis of organic compounds informed by AI planning.Science, 365(6453), eaax1566. 4. Rubio-Martinez, M., et al. (2017). Continuous-flow synthesis of metal-organic frameworks.Science Advances, 3(8), e1700508. 5. Bae, S., et al. (2010). Roll-to-roll production of 30-inch graphene films for transparent electrodes.Nature Nanotechnology, 5(8), 574-578.
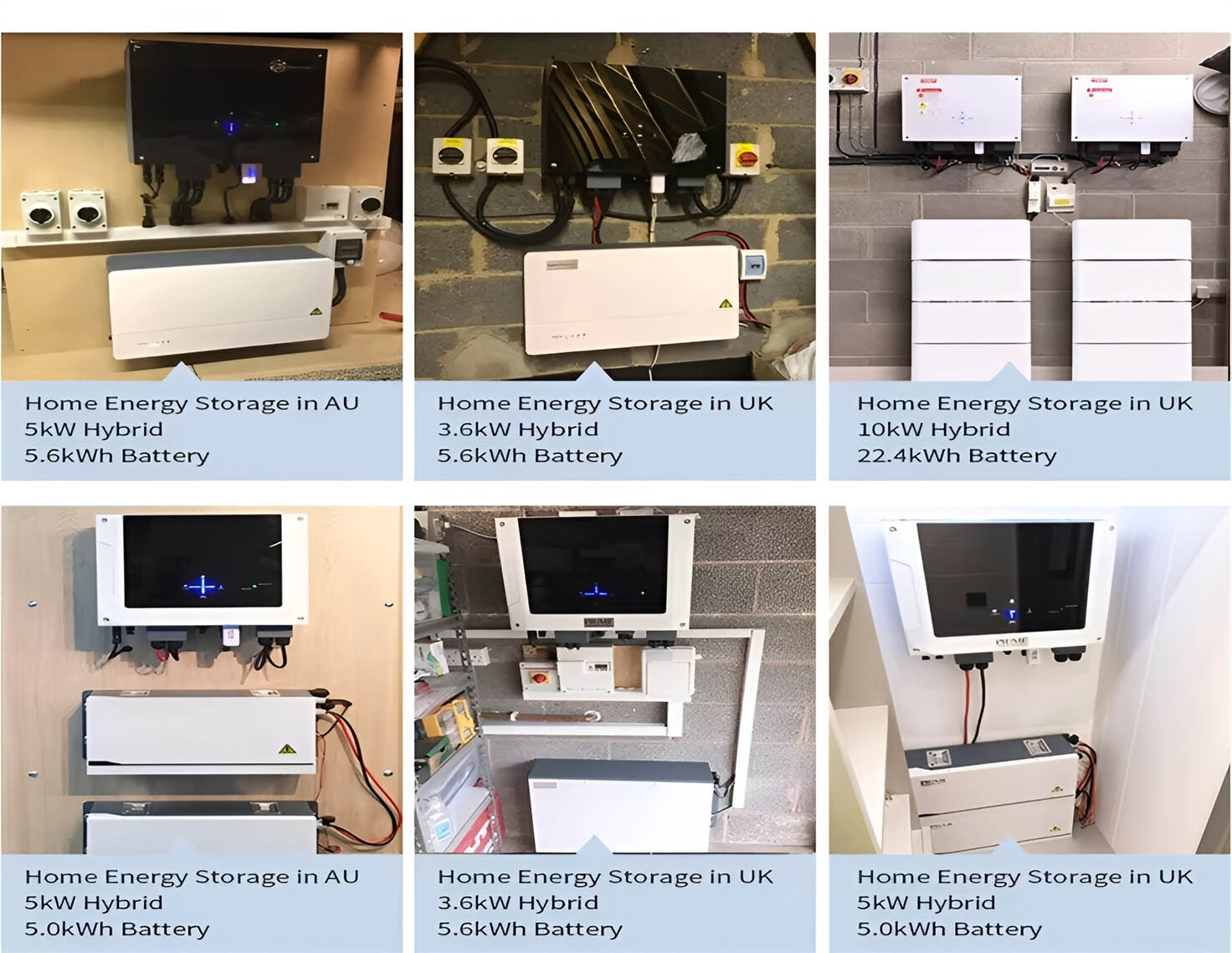
Customized/OEM/ODM Service
HomSolar Supports Lifepo4 battery pack customization/OEM/ODM service, welcome to contact us and tell us your needs.


HomSolar: Your One-stop LiFePO4 Battery Pack & ESS Solution Manufacturer
Our line of LiFePO4 (LFP) batteries offer a solution to demanding applications that require a lighter weight, longer life, and higher capacity battery. Features include advanced battery management systems (BMS), Bluetooth® communication and active intelligent monitoring.

Customised Lithium Iron Phosphate Battery Casing
ABS plastic housing, aluminium housing, stainless steel housing and iron housing are available, and can also be designed and customised according to your needs.

HomSolar Smart BMS
Intelligent Battery Management System for HomSolar Energy Storage System. Bluetooth, temperature sensor, LCD display, CAN interface, UART interface also available.


Terminals & Plugs Can Be Customized
A wide range of terminals and plugs can be customised to suit the application needs of your battery products.

Well-designed Solutions for Energy Storage Systems
We will design the perfect energy storage system solution according to your needs, so that you can easily solve the specific industry applications of battery products.

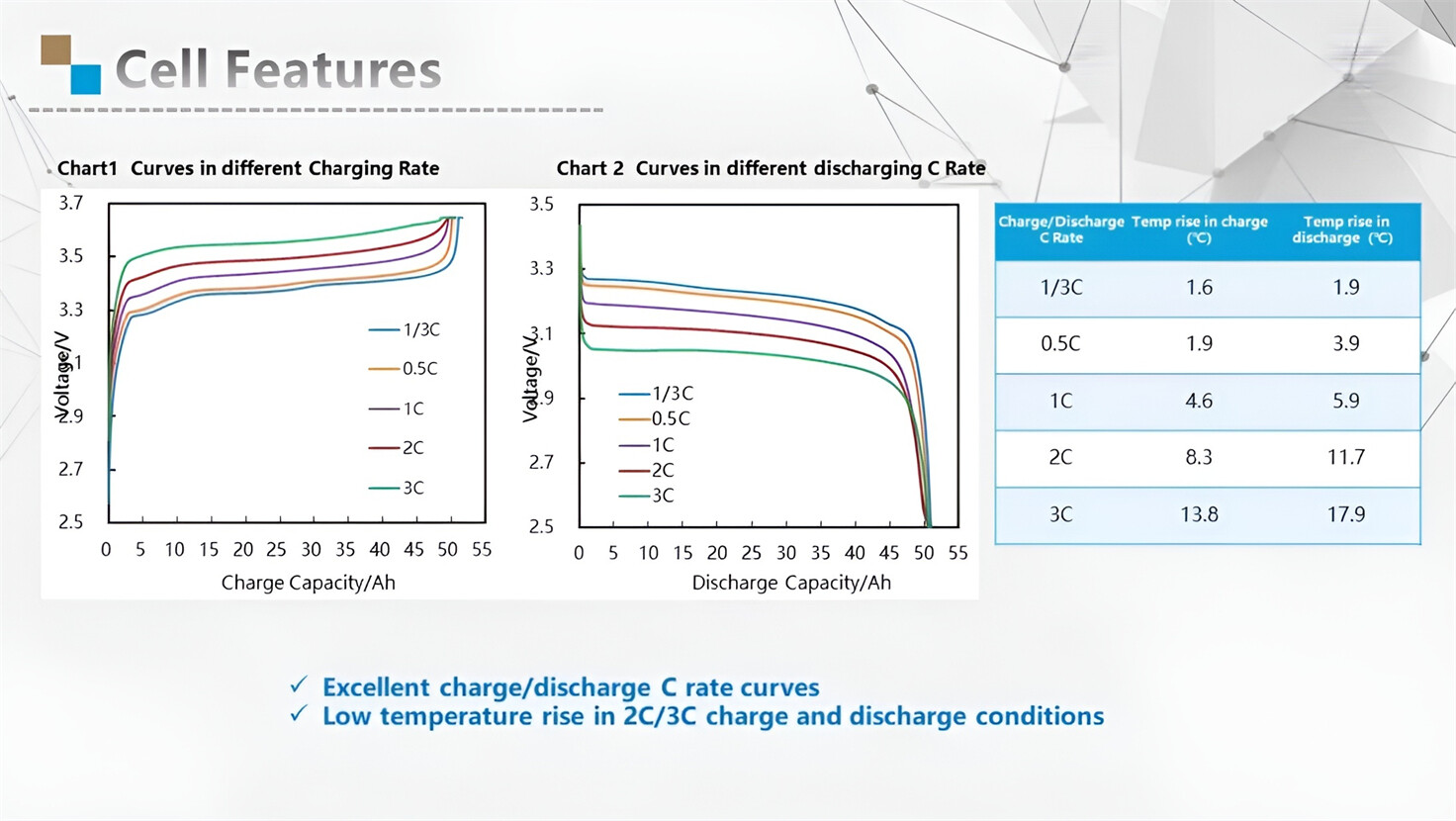
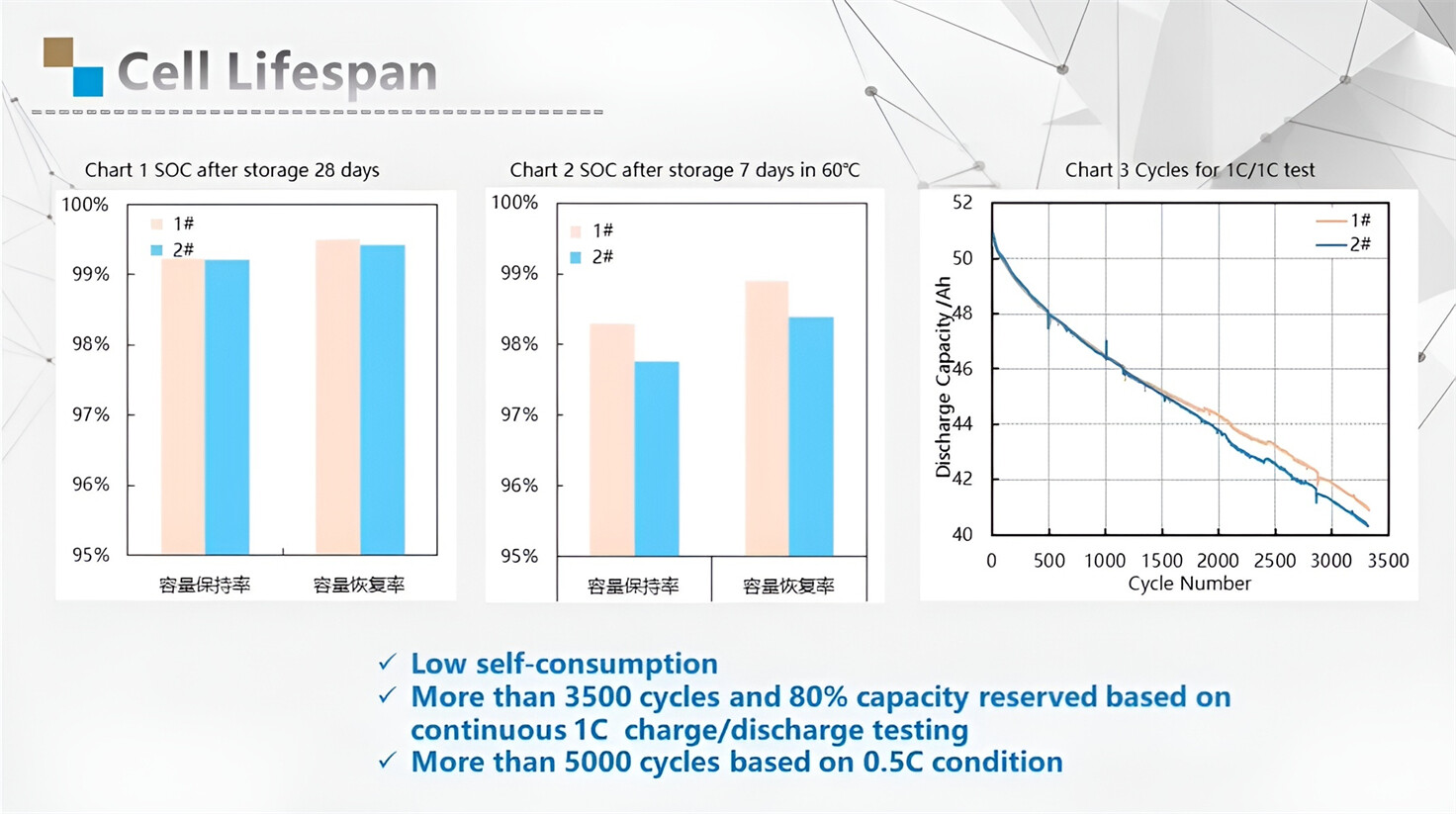
About Our Battery Cells
Our energy storage system products use brand new grade A LiFePO4 cells with a battery lifespan of more than 4,000 charge/discharge cycles.

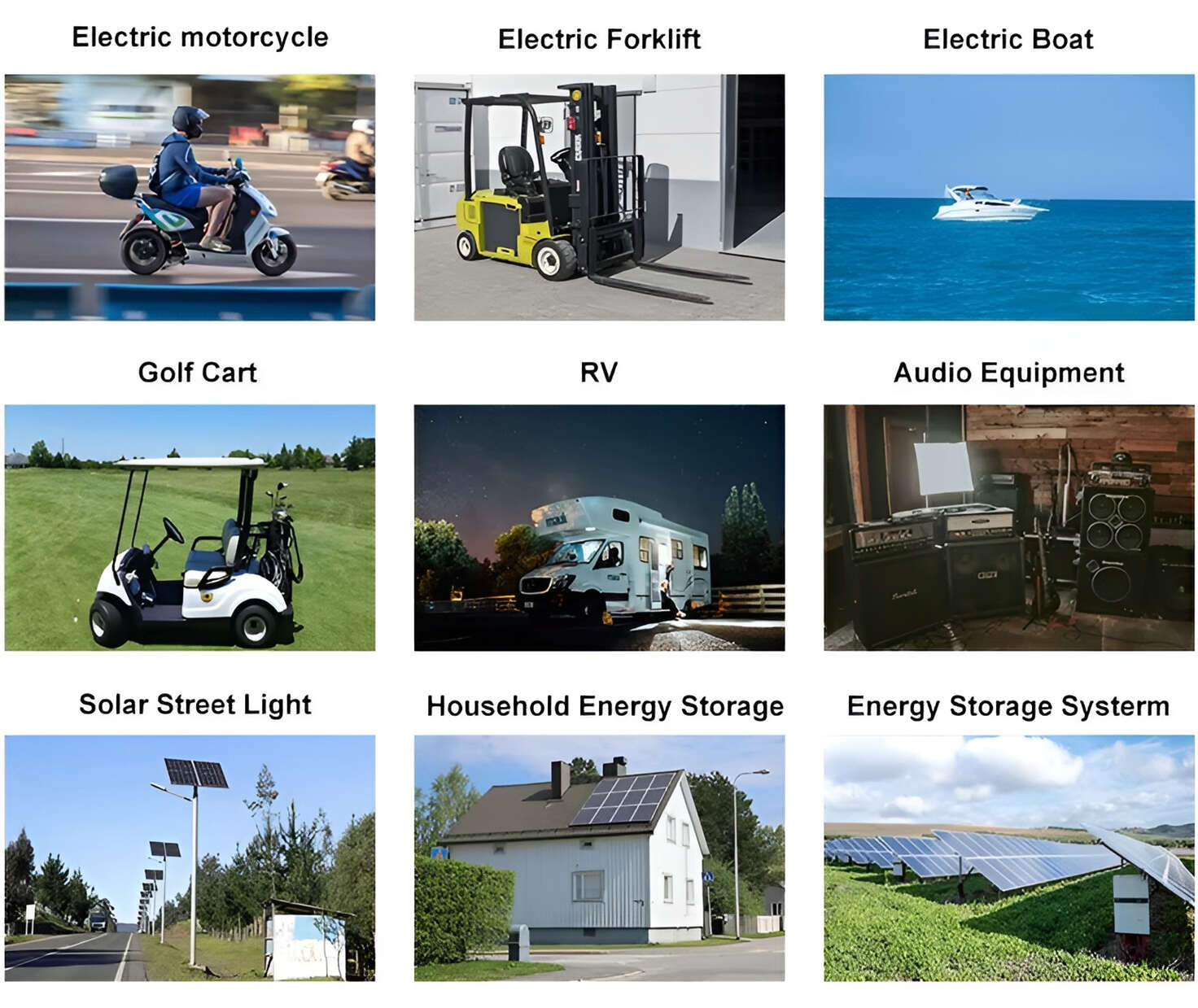
Applications in Different Industries
We supply customized & OEM battery pack, assemble cells with wiring, fuse and plastic cover, all the cell wires connected to PCB plug or built BMS.
Applications: E-bike, Electric Scooter, Golf Carts, RV, Electric Wheelchair, Electric Tools, Robot Cleaner, Robot Sweeper, Solar Energy Storage System, Emergency Light, Solar Power Light, Medical Equipment, UPS Backup Power Supply.
We can provide you with customized services. We have the ability to provide a vertical supply chain, from single cells to pack/module and to a complete power solution with BMS, etc.

HomSolar (Shenzhen) Technology Co., Ltd
























