Advances In Electrolyte Additives: Forging High-energy And Long-lived Batteries
The relentless pursuit of higher energy density and enhanced safety in lithium-ion batteries (LIBs) and next-generation systems, such as lithium-metal (Li metal) and solid-state batteries (SSBs), has placed unprecedented focus on the electrolyte. While the bulk composition of the electrolyte is crucial, it is the minor, yet sophisticated, incorporation of electrolyte additives that has emerged as a pivotal strategy for engineering stable electrode-electrolyte interfaces. These additives, typically constituting less than 5% of the total electrolyte weight, function as "chemical surgeons," selectively modifying interfacial chemistry to suppress parasitic reactions, enhance cycle life, and improve safety. Recent research has transcended traditional additive design, moving from single-function molecules to multi-functional, synergistic systems that address the complex failure modes of advanced battery chemistries.
Latest Research and Technological Breakthroughs
A primary frontier in additive research is the stabilization of high-capacity anodes. For silicon (Si)-based anodes, which suffer from severe volume expansion (>300%) and continuous solid electrolyte interphase (SEI) breakdown, fluoroethylene carbonate (FEC) remains a benchmark. However, its efficacy is limited by its consumption rate and potential to generate HF at high voltages. Recent breakthroughs involve novel co-additive systems. For instance, the combination of FEC with lithium bis(oxalato)borate (LiBOB) has been shown to create a more resilient and flexible SEI. The LiBOB-derived borate-rich outer layer complements the FEC-derived polycarbonate inner layer, resulting in a hierarchical SEI that effectively accommodates Si particle strain and minimizes irreversible lithium loss. A 2023 study by Chen et al. demonstrated that this dual-additive system enabled a SiOx-C||NMC811 full cell to retain 80% capacity after 800 cycles, a significant improvement over cells with FEC alone.
The ultimate anode challenge lies with metallic lithium. Here, the formation of a stable, uniform solid electrolyte interphase (SEI) is critical to suppress dendrite growth. Lithium nitrate (LiNO3) is a well-known promoter of beneficial Li3N-rich SEI layers in ether-based electrolytes, but its poor solubility in commercial carbonate electrolytes has been a major hurdle. A landmark technological breakthrough has been the development of soluble nitrate analogs. Molecules like potassium (K) or cesium (Cs) nitrate, with their "cation-solvent interaction" mechanism, have shown enhanced solubility and can be reduced prior to Li+ to form a protective layer. More recently, organic nitrate compounds, such as S-(trifluoromethyl)sulfonyl- O- nitrate (TFSN), have been synthesized. TFSN not only decomposes to form a robust LiF/Li3N-rich SEI but also scavenges harmful HF, offering dual functionality. Work by Zhang and colleagues inNature Energyshowcased that a carbonate electrolyte with 0.5 wt% TFSN enabled a Li||NMC811 cell to achieve a Coulombic efficiency of 99.6% and stable cycling for over 200 cycles.
On the cathode side, the push towards high-voltage cathodes like LiNi0.8Mn0.1Co0.1O2 (NMC811) and Li-rich layered oxides is plagued by transition metal (TM) dissolution, oxygen release, and subsequent catalytic decomposition of the electrolyte. Additives that form a protective cathode electrolyte interphase (CEI) are paramount. Tris(trimethylsilyl) phosphite (TTSPi) has gained prominence as a multi-functional additive. It effectively scavenges HF, suppresses PF5-induced solvent decomposition, and forms a thin, uniform CEI comprising LiF, LixPOyFz, and silyl species. This CEI layer acts as a physical barrier, inhibiting TM dissolution and mitigating oxygen release at high states of charge. Furthermore, the integration of TTSPi with anode-protecting additives like FEC creates a holistic electrolyte formulation that protects both electrodes simultaneously, a strategy now being adopted by leading battery manufacturers.
The advent of solid-state batteries (SSBs) introduces a new set of challenges, particularly at the solid-solid interfaces. While not "additives" in the liquid sense, interfacial engineering principles remain. For ceramic electrolytes like LLZO, Al2O3 or SiO2 nano-coatings on the cathode particles serve an analogous purpose—they prevent detrimental side reactions and reduce interfacial resistance. In polymer-based SSBs, small amounts of plasticizers or Li-salts with specific anions can be added to the polymer matrix to enhance ion transport and interfacial stability, blurring the line between additive and bulk component.
Future Outlook
The future trajectory of electrolyte additive development is poised to become even more intelligent and targeted. Several key directions are emerging:
1. AI-Driven Discovery and Multi-Scale Modeling: The traditional trial-and-error approach is being superseded by high-throughput computational screening and machine learning. By simulating the molecular orbital energy levels (HOMO/LUMO) and reduction/oxidation potentials of thousands of candidate molecules, researchers can rapidly identify promising additives for specific electrode materials. Thisin-silicodesign, coupled with molecular dynamics simulations of interface formation, will dramatically accelerate the development cycle.
2. Multi-Functional and Synergistic Systems: The era of the "magic bullet" single additive is fading. The future lies in meticulously designed "cocktails" where each component performs a specific, non-overlapping function—one for anode SEI, one for cathode CEI, one for HF scavenging, and one for overcharge protection. Understanding the complex interplay and potential synergies or antagonisms between these components will be a central research theme.
3. Additives for Sustainability and Recycling: As sustainability concerns grow, future additives will need to be evaluated not only for performance but also for their environmental impact and recyclability. The design of biodegradable or less toxic additives, and the development of recycling processes that can efficiently separate and remove these additives from spent electrolytes, will become increasingly important.
4. In-Operando Diagnostics and Dynamic Additives: The ultimate goal is to achieve dynamic, self-healing interfaces. This could involve additives that are catalytically regenerated during cycling or that release passivating agents only when triggered by specific conditions, such as a local voltage spike or temperature increase. Advancedin-situandoperandocharacterization techniques (e.g., synchrotron X-ray, NMR) are crucial to unravel the real-time decomposition pathways and interfacial evolution of these smart additives.
In conclusion, electrolyte additives have evolved from simple film-forming agents into sophisticated molecular tools for precise interfacial control. The latest breakthroughs in multi-functional molecules, synergistic co-additives, and soluble nitrate analogs are directly enabling the commercialization of high-energy-density batteries based on silicon and lithium metal anodes. Looking ahead, the integration of artificial intelligence, a deeper fundamental understanding of interfacial dynamics, and a focus on sustainability will propel this field forward, ensuring that electrolyte additives remain a cornerstone of battery innovation for years to come.
References (Illustrative):Chen, X., et al. (2023). A Hierarchical SEI Enabled by FEC/LiBOB Dual Additives for High-Performance Silicon Anodes.Advanced Energy Materials, 13(15), 2203671.Zhang, Z., et al. (2022). A sustainable solid electrolyte interphase for high-energy-density lithium metal batteries.Nature Energy, 7(10), 940-950.Li, W., et al. (2021). Tris(trimethylsilyl)phosphite as a multifunctional electrolyte additive for high-voltage LiNi0.8Mn0.1Co0.1O2 cathodes.Journal of Power Sources, 482, 228947.Yu, Z., et al. (2020). Rational solvent molecule tuning for high-performance lithium metal battery electrolytes.Nature Energy, 5(7), 526-533.
Customized/OEM/ODM Service
HomSolar Supports Lifepo4 battery pack customization/OEM/ODM service, welcome to contact us and tell us your needs.


HomSolar: Your One-stop LiFePO4 Battery Pack & ESS Solution Manufacturer
Our line of LiFePO4 (LFP) batteries offer a solution to demanding applications that require a lighter weight, longer life, and higher capacity battery. Features include advanced battery management systems (BMS), Bluetooth® communication and active intelligent monitoring.

Customised Lithium Iron Phosphate Battery Casing
ABS plastic housing, aluminium housing, stainless steel housing and iron housing are available, and can also be designed and customised according to your needs.

HomSolar Smart BMS
Intelligent Battery Management System for HomSolar Energy Storage System. Bluetooth, temperature sensor, LCD display, CAN interface, UART interface also available.


Terminals & Plugs Can Be Customized
A wide range of terminals and plugs can be customised to suit the application needs of your battery products.

Well-designed Solutions for Energy Storage Systems
We will design the perfect energy storage system solution according to your needs, so that you can easily solve the specific industry applications of battery products.

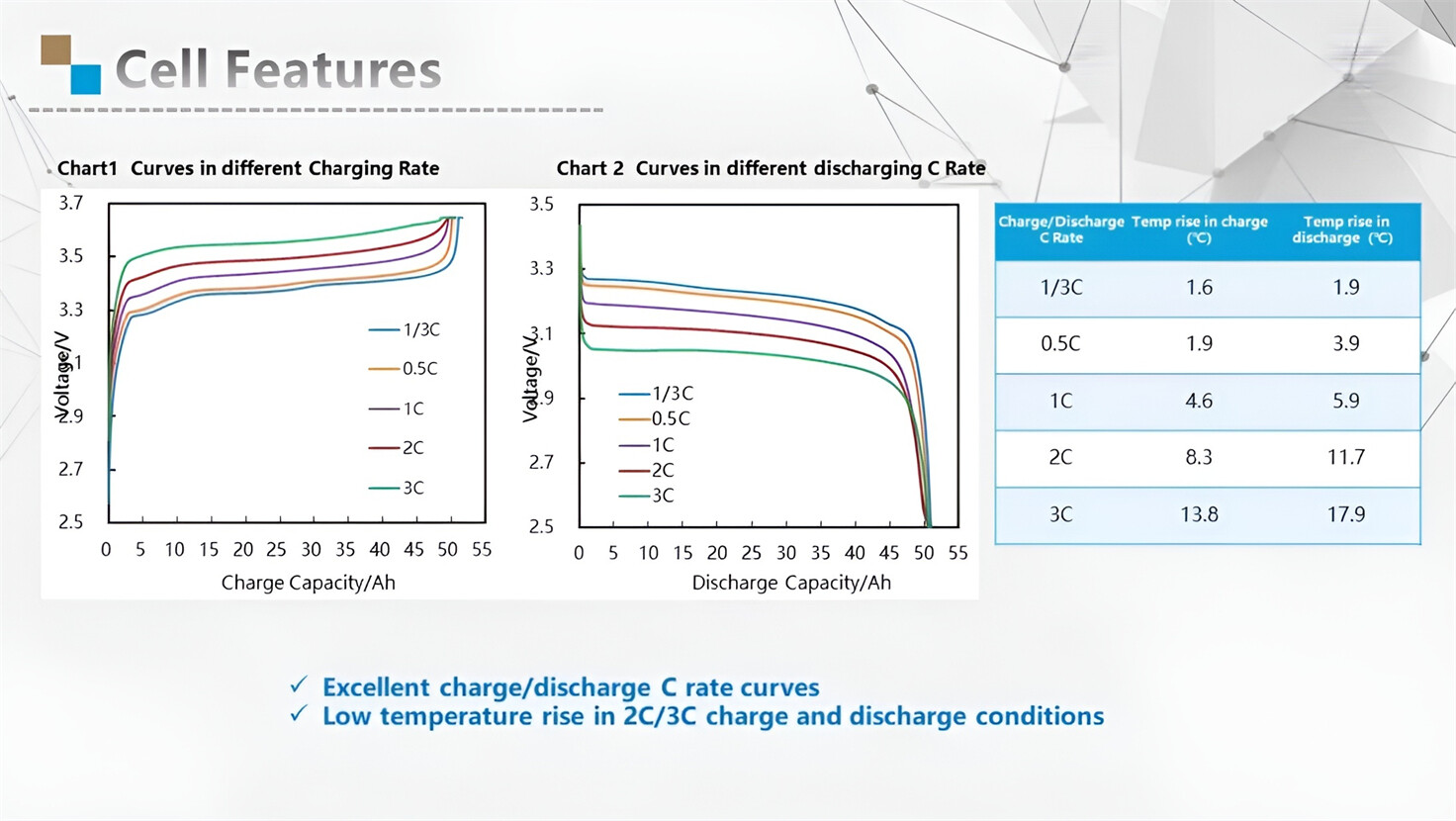
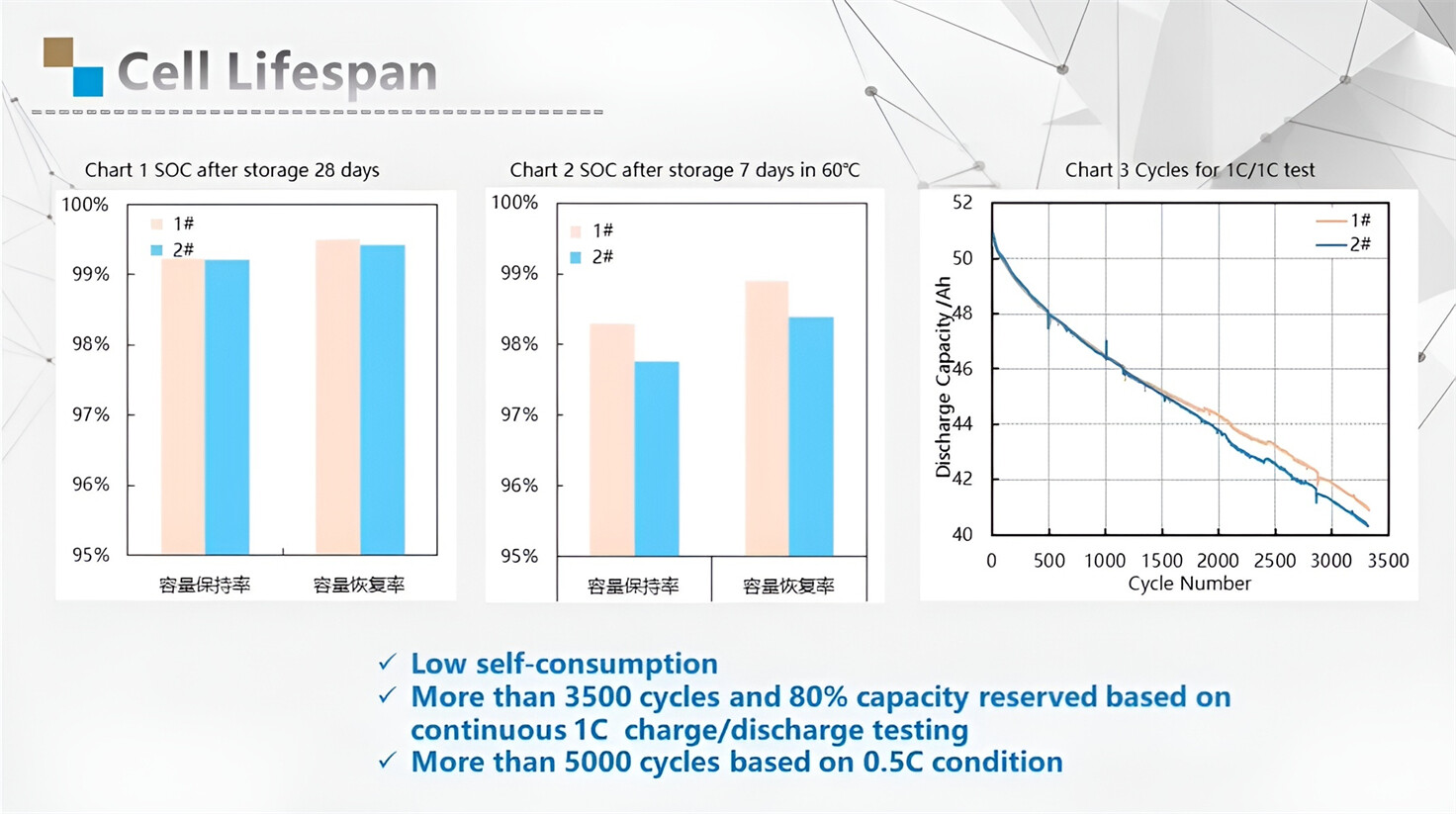
About Our Battery Cells
Our energy storage system products use brand new grade A LiFePO4 cells with a battery lifespan of more than 4,000 charge/discharge cycles.

Applications in Different Industries
We supply customized & OEM battery pack, assemble cells with wiring, fuse and plastic cover, all the cell wires connected to PCB plug or built BMS.
Applications: E-bike, Electric Scooter, Golf Carts, RV, Electric Wheelchair, Electric Tools, Robot Cleaner, Robot Sweeper, Solar Energy Storage System, Emergency Light, Solar Power Light, Medical Equipment, UPS Backup Power Supply.
We can provide you with customized services. We have the ability to provide a vertical supply chain, from single cells to pack/module and to a complete power solution with BMS, etc.

HomSolar (Shenzhen) Technology Co., Ltd
























