Advances In Doping Strategies: From Precision Engineering To Novel Paradigms
The controlled introduction of impurities, or dopants, into a host material—a process known as doping—has long been the cornerstone of modern electronics and materials science. It is the fundamental mechanism for tuning electrical, optical, and magnetic properties in semiconductors, enabling everything from transistors to solar cells. For decades, conventional doping strategies, primarily ion implantation and thermal diffusion, have sufficed. However, as we push the frontiers of material science towards atomically thin layers, complex oxides, and quantum devices, these traditional methods are revealing significant limitations, including poor spatial control, defect generation, and a fundamental breakdown at the nanoscale. In response, the field of doping strategies is undergoing a profound transformation, moving from coarse, bulk modification to atomic-scale precision engineering and the exploration of entirely new doping paradigms.
Precision Engineering at the Atomic Scale
A major thrust of recent research involves achieving doping with near-atomic precision. This is particularly critical for two-dimensional (2D) materials like graphene and transition metal dichalcogenides (TMDs), where even a single dopant atom can drastically alter electronic properties. Traditional ion implantation causes irreversible damage to the pristine lattice of these materials. To overcome this, researchers have developed sophisticatedin-situdoping techniques during chemical vapour deposition (CVD) growth. For instance, by introducing precursor gases containing heteroatoms such as nitrogen or boron during graphene synthesis, large-area, uniformly doped graphene sheets can be produced with controlled p- or n-type characteristics (Wang et al., 2020).
Beyondin-situmethods, post-synthesis techniques have achieved remarkable finesse. Scanning tunnelling microscopy (STM) has been used to precisely implant individual phosphorus atoms into a silicon lattice, a foundational technology for quantum computing. More recently, a technique known as "laser-assisted doping" has emerged, where a focused laser beam locally activates a spin-on dopant source, enabling sub-micrometre patterning without the lattice damage associated with high-energy ion implantation. This level of control is essential for developing next-generation nanoscale transistors and solid-state quantum bits.
Strain and Defect-Mediated Doping
Another significant breakthrough is the understanding and exploitation of strain and defects as doping mechanisms. Unlike substitutional doping, which replaces an atom in the lattice, these strategies manipulate the host material's structure to induce charge carriers. In 2D TMDs like MoS₂, it has been demonstrated that carefully engineered strain gradients can create large pseudo-magnetic fields and spatially varying bandgaps, effectively creating p-n junctions within a single, continuous crystal (Zhang et al., 2021). This "strain doping" offers a contact-free method to design electronic circuits without chemical impurities.
Similarly, defect engineering has evolved into a precise science. By controlling the concentration of sulfur vacancies in MoS₂ through plasma treatment or annealing, researchers can reliably tune its conductivity from insulating to highly conductive. A groundbreaking study demonstrated that passivating these defects with specific molecules could not only restore the material's quality but also function as a stable n-type dopant, offering a reversible and non-destructive doping route (Kang et al., 2022).
The Rise of Electrostatic and Charge Transfer Doping
Perhaps the most radical departure from traditional doping is the development of strategies that do not modify the chemical composition of the host material at all. Electrostatic doping, using strong electric fields from ionic liquids or gate dielectrics, can induce high carrier densities in a material's surface layer. This method is completely reversible and avoids lattice disorder. It has been instrumental in exploring exotic phases of matter, such as superconductivity in FeSe, and is a key enabler for ultra-low-power electronics.
Charge transfer doping takes this concept further by leveraging van der Waals heterostructures. By simply stacking a 2D material like graphene or MoS₂ onto another material with a different work function (e.g., WSe₂ or a metallic substrate), electrons spontaneously flow across the interface to equilibrate the Fermi levels. This creates a heavily doped layer without a single impurity atom. A recent landmark achievement showed that sandwiching a semiconductor between two specific organic layers could achieve record-high mobilities while maintaining exceptional stability, a feat impossible with conventional doping (Liu et al., 2023). This "modulation doping" approach, borrowed from compound semiconductor technology, spatially separates the dopants from the charge conduction channel, drastically reducing ionized impurity scattering.
Future Outlook and Challenges
The future of doping strategies lies in integration, predictability, and new material classes. The next logical step is the combination of multiple doping modalities—for example, using electrostatic gating to define a device region that is then stabilized by mild chemical doping. Furthermore, the immense parameter space of these new techniques demands a paradigm shift towards data-driven materials design. Machine learning algorithms are now being deployed to predict the optimal doping protocol—be it chemical, strain, or electrostatic—for a target electronic property, accelerating discovery and optimization.
Challenges remain. Achieving uniform and stable doping at an industrial scale with these novel methods is non-trivial. The long-term stability of charge-transfer-doped interfaces and electrostatically induced phases needs further investigation. Moreover, as we approach the ultimate limit of single-atom doping, statistical variations and quantum effects will become dominant, requiring new models for device behaviour.
In conclusion, the field of doping has expanded far beyond its historical roots. It is no longer just about adding impurities but about mastering a suite of tools—from atomic manipulation and strain engineering to electrostatic control and heterostructure design—to sculpt the electronic landscape of materials with unprecedented precision. These advances are not merely incremental improvements; they are enabling technologies for the next wave of innovation in quantum information science, energy-efficient electronics, and functional materials with on-demand properties.
References:Kang, J., et al. (2022). Molecular Passivation and Doping of 2D Semiconductors via Van der Waals Interactions.Nature Electronics, 5(10), 655-663.Liu, Y., et al. (2023). Ultra-high mobility in organic semiconductor heterostructures via molecular layer doping.Science, 379(6634), 678-682.Wang, H., et al. (2020). Large-area, Synthesis of Doped Graphene.Chemical Reviews, 120(17), 9832-9886.Zhang, L., et al. (2021). Strain-Engineered Nano-PN Junctions in a Monolayer Semiconductor.Nature Nanotechnology, 16(8), 882-887.
Customized/OEM/ODM Service
HomSolar Supports Lifepo4 battery pack customization/OEM/ODM service, welcome to contact us and tell us your needs.


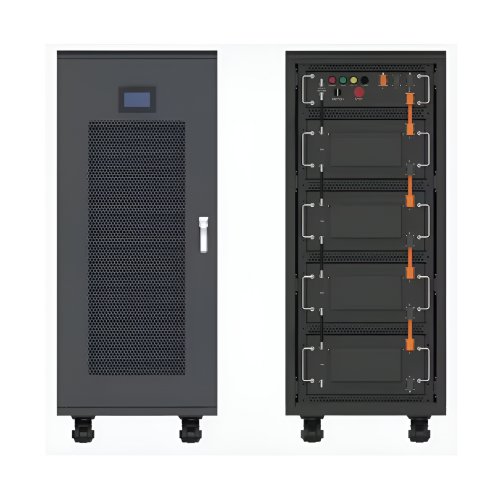
HomSolar: Your One-stop LiFePO4 Battery Pack & ESS Solution Manufacturer
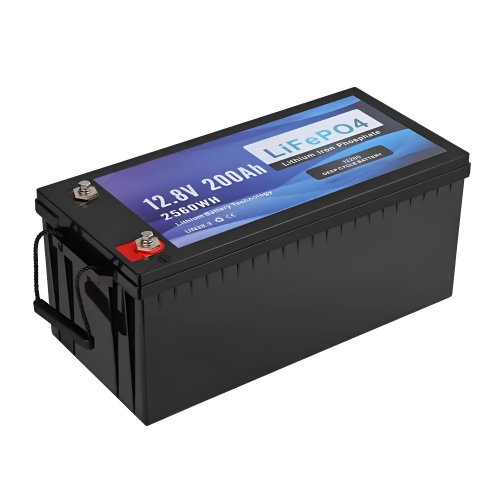
Our line of LiFePO4 (LFP) batteries offer a solution to demanding applications that require a lighter weight, longer life, and higher capacity battery. Features include advanced battery management systems (BMS), Bluetooth® communication and active intelligent monitoring.
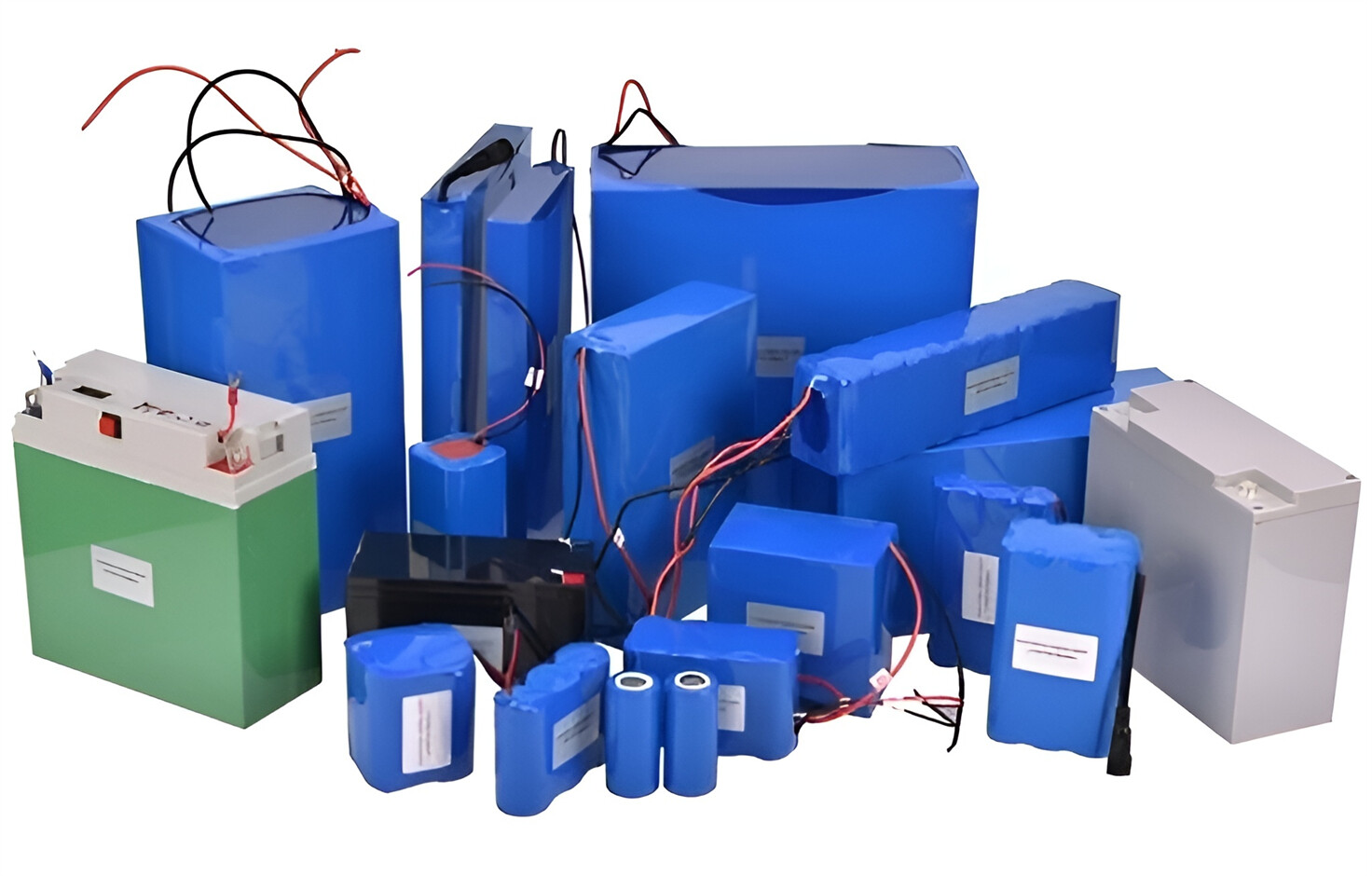

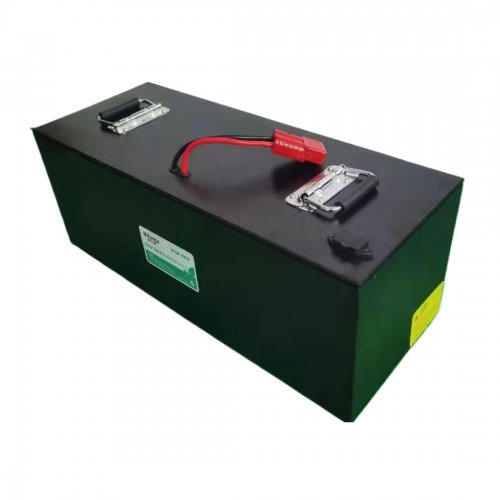
Customised Lithium Iron Phosphate Battery Casing
ABS plastic housing, aluminium housing, stainless steel housing and iron housing are available, and can also be designed and customised according to your needs.

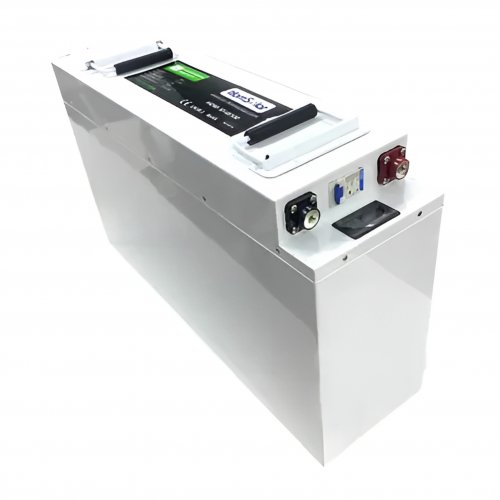
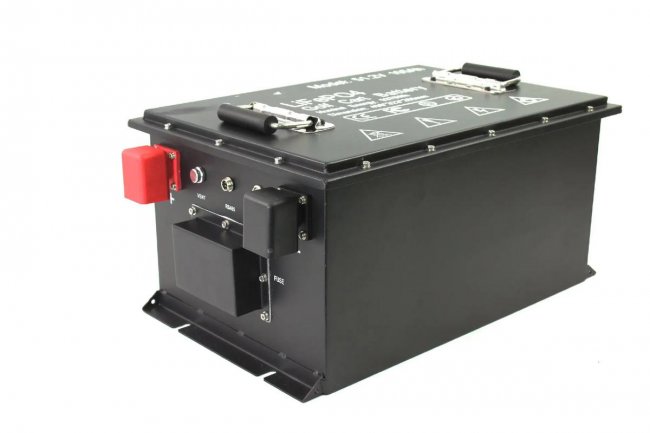
HomSolar Smart BMS
Intelligent Battery Management System for HomSolar Energy Storage System. Bluetooth, temperature sensor, LCD display, CAN interface, UART interface also available.


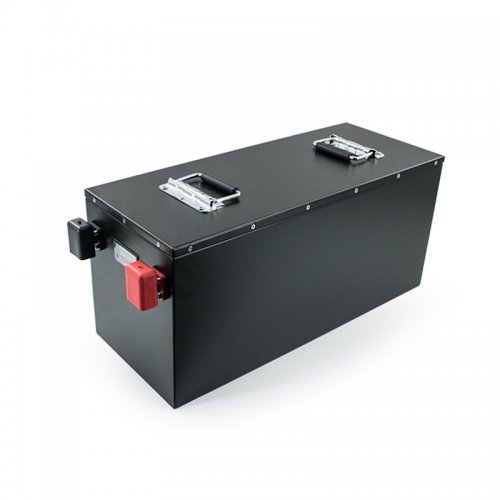
Terminals & Plugs Can Be Customized
A wide range of terminals and plugs can be customised to suit the application needs of your battery products.

Well-designed Solutions for Energy Storage Systems
We will design the perfect energy storage system solution according to your needs, so that you can easily solve the specific industry applications of battery products.

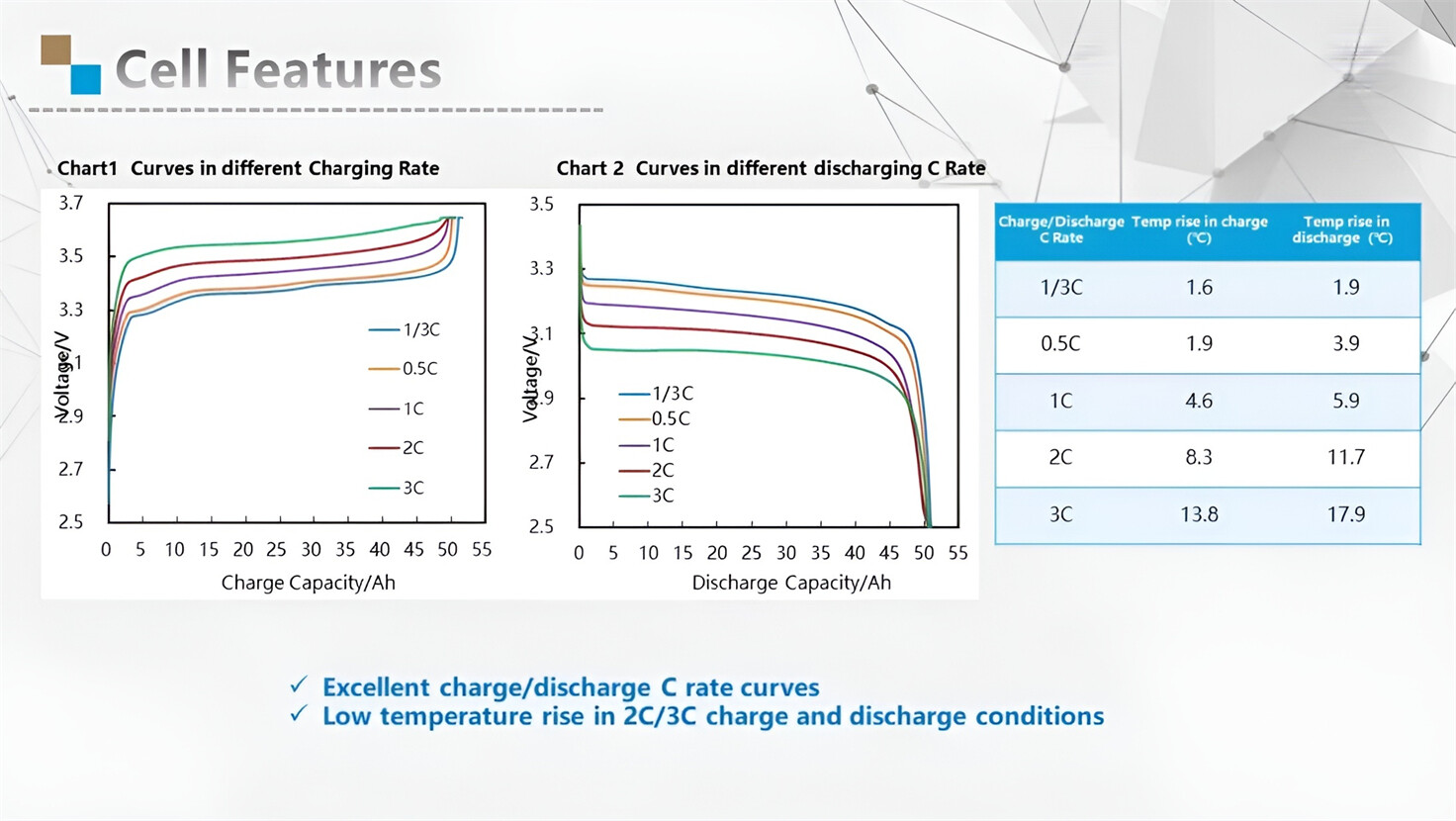
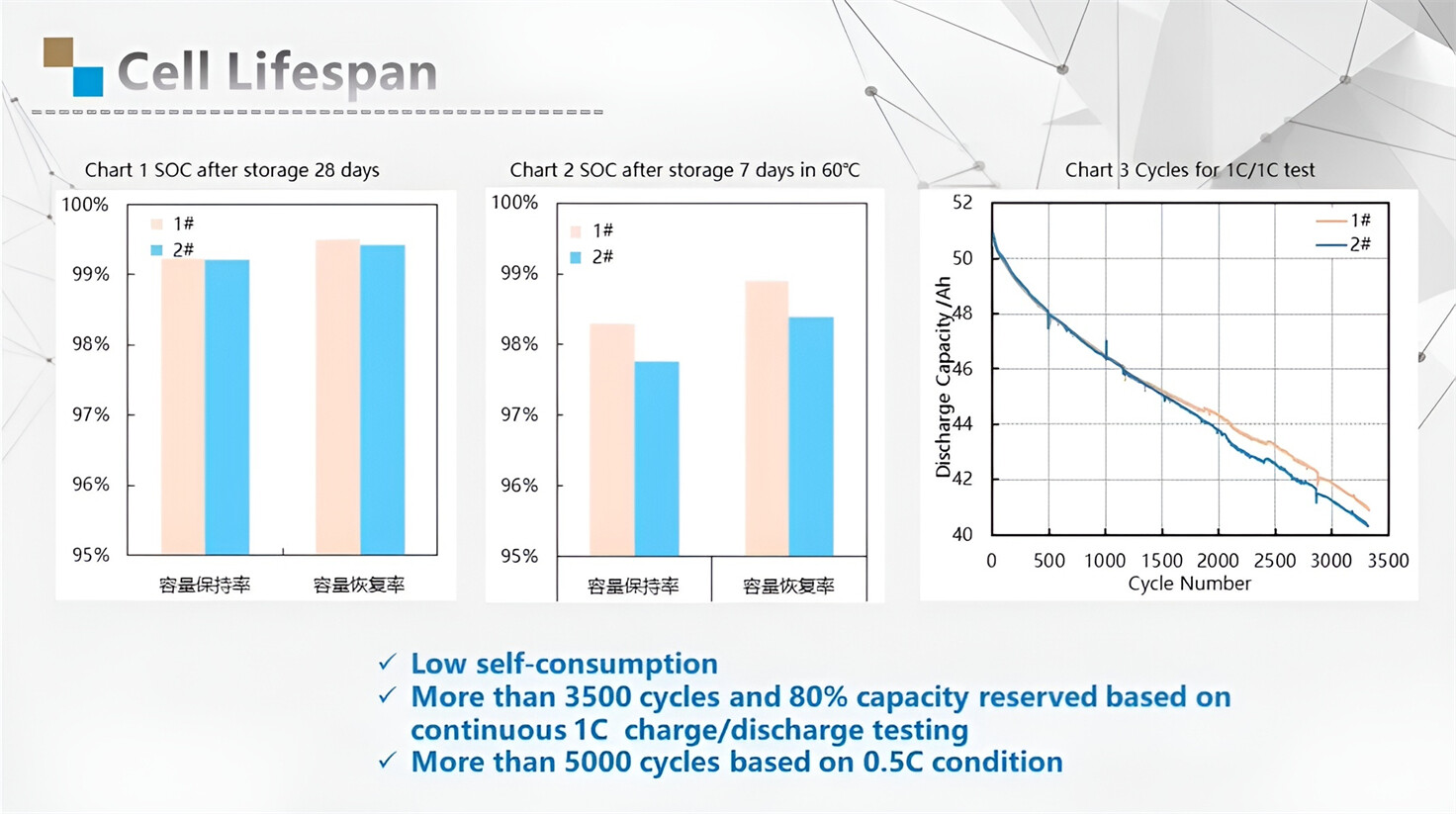
About Our Battery Cells
Our energy storage system products use brand new grade A LiFePO4 cells with a battery lifespan of more than 4,000 charge/discharge cycles.

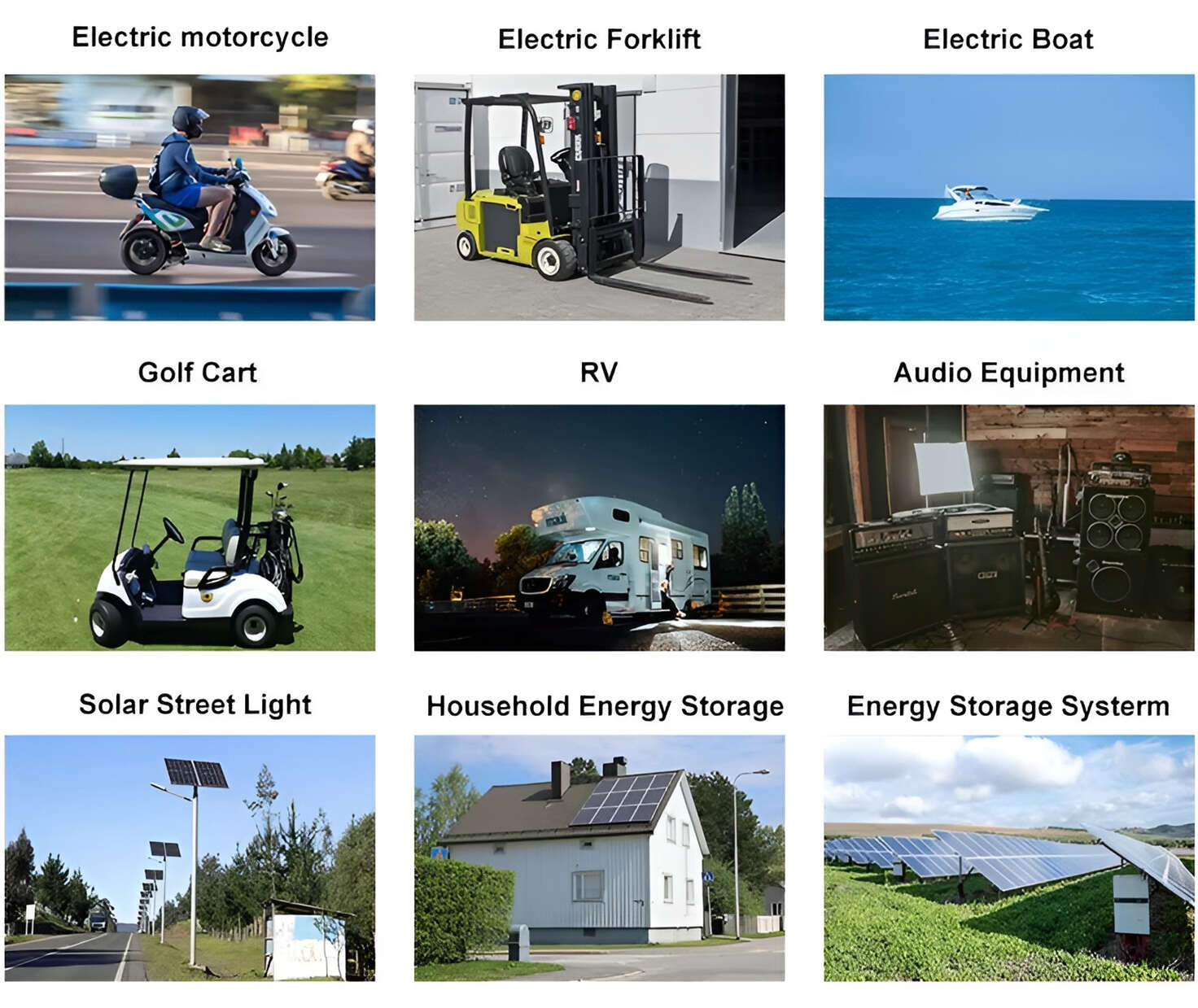
Applications in Different Industries
We supply customized & OEM battery pack, assemble cells with wiring, fuse and plastic cover, all the cell wires connected to PCB plug or built BMS.
Applications: E-bike, Electric Scooter, Golf Carts, RV, Electric Wheelchair, Electric Tools, Robot Cleaner, Robot Sweeper, Solar Energy Storage System, Emergency Light, Solar Power Light, Medical Equipment, UPS Backup Power Supply.
We can provide you with customized services. We have the ability to provide a vertical supply chain, from single cells to pack/module and to a complete power solution with BMS, etc.

HomSolar (Shenzhen) Technology Co., Ltd
























