Advances In Cost-effective Synthesis: Pioneering Pathways For Sustainable Materials And Chemicals
The relentless pursuit of chemical and material innovation is perpetually balanced against the imperative of economic viability. For decades, sophisticated synthetic methodologies often came with prohibitive costs, limiting their application to high-value sectors like pharmaceuticals. However, a paradigm shift is underway, driven by the urgent need for sustainable manufacturing. The field of cost-effective synthesis is no longer merely about minimizing expense; it is an interdisciplinary frontier focused on developing intelligent, efficient, and scalable processes that minimize environmental impact while maximizing output and functionality. Recent breakthroughs in catalysis, biomass utilization, process intensification, and waste valorization are redefining what is economically and ecologically possible.
Catalytic Innovations: Doing More with Less
At the heart of cost-effective synthesis lies catalysis, and recent years have witnessed remarkable strides in making catalysts more efficient, selective, and durable. Heterogeneous catalysis, where the catalyst is in a different phase from the reactants, remains a cornerstone due to the ease of separation and reuse. Advances here focus on enhancing atom efficiency. For instance, single-atom catalysts (SACs) represent a pinnacle of this principle, where isolated metal atoms are anchored on a support material. This configuration maximizes the utilization of often-expensive precious metals, such as platinum or palladium, achieving unprecedented catalytic activity and selectivity for reactions like CO oxidation and selective hydrogenation (1). By ensuring that every metal atom is a potential active site, SACs dramatically reduce the required metal loading, a significant factor in cost reduction.
Simultaneously, the exploration of non-precious metal catalysts has accelerated. Earth-abundant transition metals like iron, cobalt, and nickel are being engineered into highly active nanostructures. Research by Sun et al. demonstrated that a nitrogen-doped graphene matrix embedded with nickel nanoparticles could rival platinum-based catalysts in the oxygen evolution reaction (OER), a critical yet costly process for water-splitting and metal-air batteries (2). Such developments are crucial for decarbonizing industrial processes and making renewable energy technologies economically competitive.
Harnessing Nature's Blueprint: Biomass as a Feedstock
Perhaps the most transformative trend in cost-effective synthesis is the shift from petroleum-based feedstocks to renewable biomass. Lignocellulosic biomass, derived from non-food plant matter, is an abundant and low-cost carbon source. The challenge has been deconstructing its robust, complex structure into valuable platform chemicals.
Recent technological breakthroughs are overcoming this hurdle. Advanced biocatalysis, employing engineered enzymes and microorganisms, allows for highly selective conversions under mild conditions, saving energy. For example, the synthesis of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural (HMF), a versatile bio-based platform molecule, has been significantly improved. Novel catalytic systems employing biphasic reactors and solid acid catalysts have been developed to convert carbohydrates into HMF with high yield and purity, avoiding the side reactions and purification costs that plagued earlier methods (3). Furthermore, the concept of the "bio-refinery" is gaining traction, where multiple streams of biomass are fractionated and converted into a spectrum of products—fuels, chemicals, and materials—mimicking the efficiency of a petroleum refinery but with a sustainable, cost-effective feedstock base.
Process Intensification and Flow Chemistry
Beyond the chemical reactants themselves, the engineering of the synthesis process is a critical lever for cost reduction. Process intensification, which aims to make manufacturing dramatically more efficient by shrinking equipment size, boosting productivity, and reducing energy consumption, is a key driver. Continuous flow chemistry epitomizes this principle.
Unlike traditional batch reactors, flow systems pass reactants through a contained, often catalyst-packed, tube. This setup offers superior control over reaction parameters (temperature, pressure, residence time), leading to higher selectivity and yield while minimizing by-products. The small reactor volume also enhances safety, allowing for reactions under extreme conditions that would be hazardous in a large batch vessel. A notable advancement is the integration of multiple synthetic steps—telescoping—into a single continuous flow system. This avoids the cost and time associated with isolating and purifying intermediates. Researchers have successfully demonstrated end-to-end synthesis of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) in compact, automated flow systems, reducing the synthetic timeline from days to hours and drastically cutting solvent waste and operational costs (4).
Waste Valorization: Turning Trash into Treasure
The ultimate expression of cost-effectiveness is creating value from waste streams. The synthesis of functional materials from industrial or agricultural waste is an area of explosive growth. For instance, the conversion of carbon dioxide, a major greenhouse gas, into chemicals and fuels is a holy grail of sustainable synthesis. Recent breakthroughs in electrocatalysis and photocatalysis are making this a reality. Novel metal-organic framework (MOF)-derived catalysts and molecularly engineered semiconductors are demonstrating efficient and selective conversion of CO2 to CO, formic acid, or even ethylene, turning a liability into a feedstock (5).
Similarly, chitin from seafood waste is being transformed into nitrogen-containing chemicals, silica from rice husk is being used to synthesize high-value silicates and adsorbents, and waste plastics are being chemically broken down into their original monomers for repolymerization—a circular approach to synthesis. These strategies not only reduce raw material costs but also address pressing waste management issues.
Future Outlook and Challenges
The future of cost-effective synthesis is intelligent and integrated. The integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning for reaction prediction and optimization is poised to accelerate discovery. AI algorithms can analyze vast datasets to suggest novel catalytic combinations or optimal reaction pathways, drastically reducing the time and resources spent on experimental trial-and-error.
Furthermore, the convergence of biotechnology, electrochemistry, and advanced materials science will open new avenues. Electrosynthesis, driven by renewable electricity, offers a pathway to conduct redox reactions without expensive and wasteful chemical oxidants or reductants. The development of robust and selective electrodes will be crucial for its widespread, cost-effective adoption.
However, challenges remain. Scaling up laboratory breakthroughs to industrial production consistently presents hurdles related to catalyst stability, reactor fouling, and process control. The economic viability of many biomass and waste-valorization routes is still sensitive to fluctuating energy prices and policy frameworks. Lifecycle assessment (LCA) will become an indispensable tool to validate the true economic and environmental cost-effectiveness of these new synthetic pathways.
In conclusion, the advances in cost-effective synthesis are fundamentally reshaping the landscape of chemical manufacturing. By leveraging smarter catalysts, sustainable feedstocks, intensified processes, and waste streams, researchers are building a new paradigm where economic advantage is inextricably linked to ecological responsibility. This progress is not merely about making things cheaper; it is about forging a viable and resilient foundation for the materials and chemicals that will support a sustainable future.
References
1. Yang, X. F., et al. "Single-Atom Catalysts: A New Frontier in Heterogeneous Catalysis."Accounts of Chemical Research46.8 (2013): 1740-1748. 2. Sun, Y., et al. "Nitrogen-Doped Graphene Encapsulated Nickel Nanoparticles as an Efficient Electrocatalyst for Oxygen Evolution Reaction."Advanced Energy Materials7.6 (2017): 1601499. 3. van Putten, R. J., et al. "Hydroxymethylfurfural, A Versatile Platform Chemical Made from Renewable Resources."Chemical Reviews113.3 (2013): 1499-1597. 4. Bogdan, A. R., & Dombrowski, A. W. "Emerging Trends in Flow Chemistry and Applications to the Pharmaceutical Industry."Journal of Medicinal Chemistry62.14 (2019): 6422-6468. 5. De Luna, P., et al. "What would it take for renewably powered electrosynthesis to displace petrochemical processes?"Science364.6438 (2019): eaav3506.
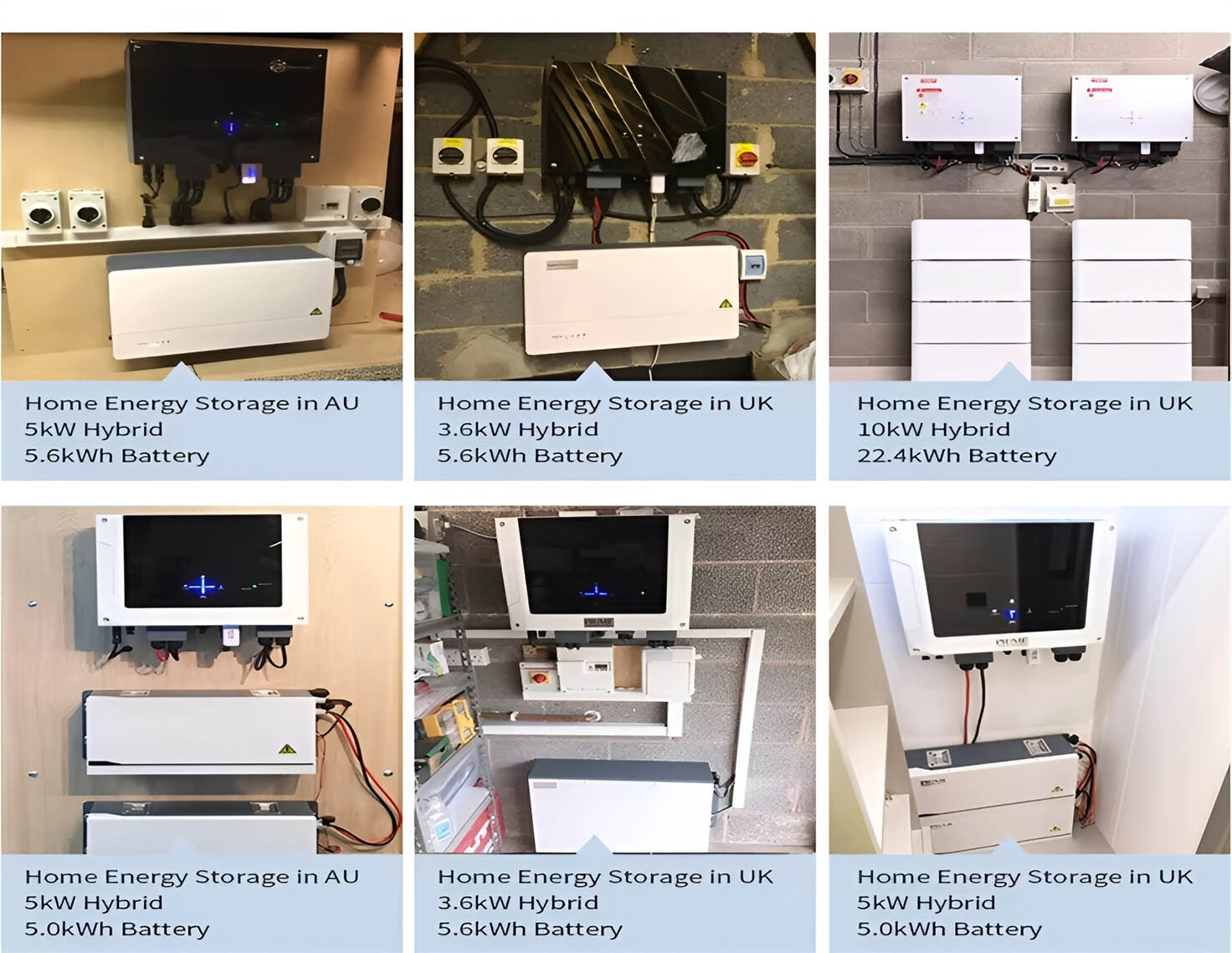
Customized/OEM/ODM Service
HomSolar Supports Lifepo4 battery pack customization/OEM/ODM service, welcome to contact us and tell us your needs.


HomSolar: Your One-stop LiFePO4 Battery Pack & ESS Solution Manufacturer
Our line of LiFePO4 (LFP) batteries offer a solution to demanding applications that require a lighter weight, longer life, and higher capacity battery. Features include advanced battery management systems (BMS), Bluetooth® communication and active intelligent monitoring.
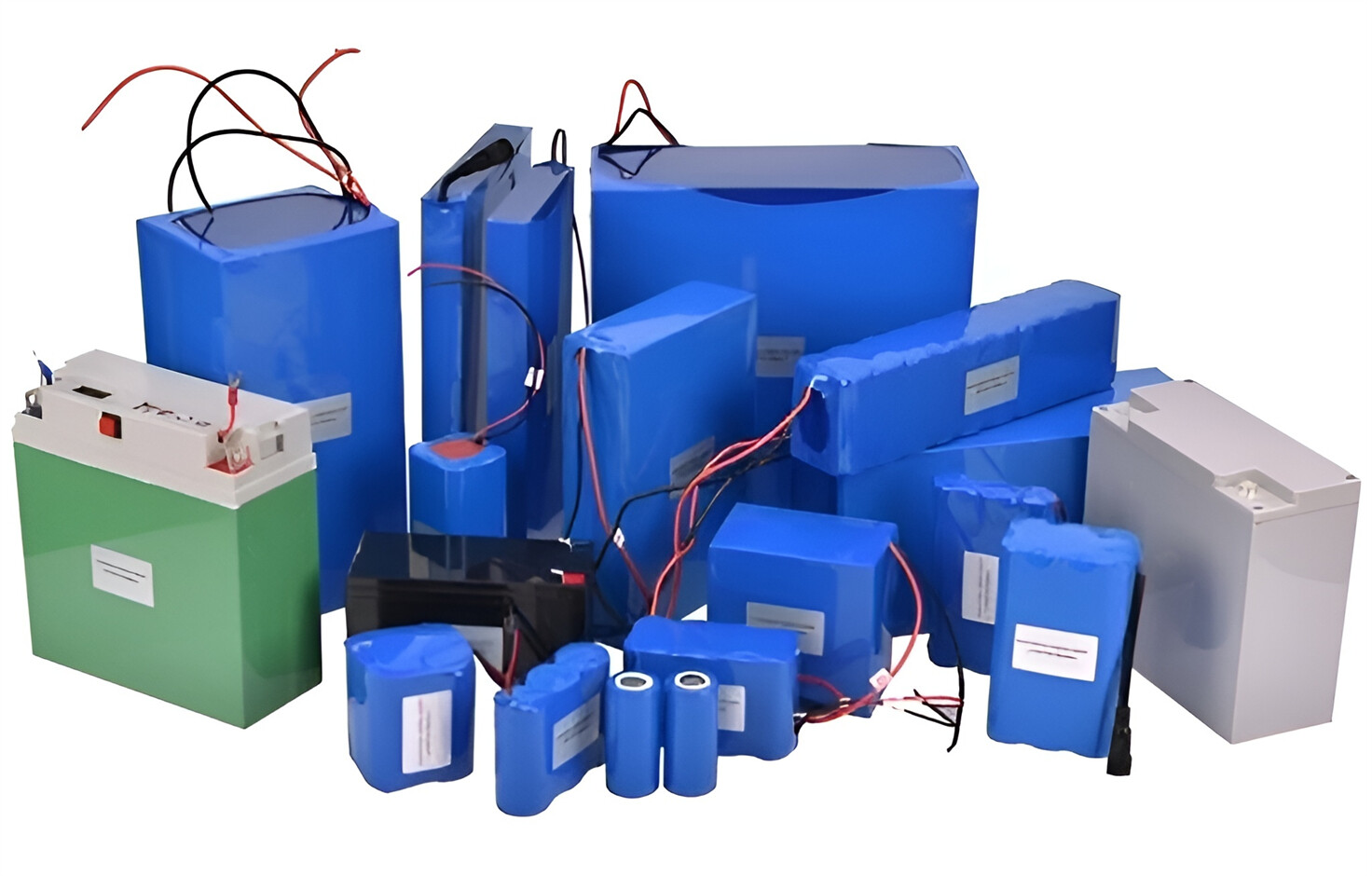

Customised Lithium Iron Phosphate Battery Casing
ABS plastic housing, aluminium housing, stainless steel housing and iron housing are available, and can also be designed and customised according to your needs.

HomSolar Smart BMS
Intelligent Battery Management System for HomSolar Energy Storage System. Bluetooth, temperature sensor, LCD display, CAN interface, UART interface also available.


Terminals & Plugs Can Be Customized
A wide range of terminals and plugs can be customised to suit the application needs of your battery products.

Well-designed Solutions for Energy Storage Systems
We will design the perfect energy storage system solution according to your needs, so that you can easily solve the specific industry applications of battery products.

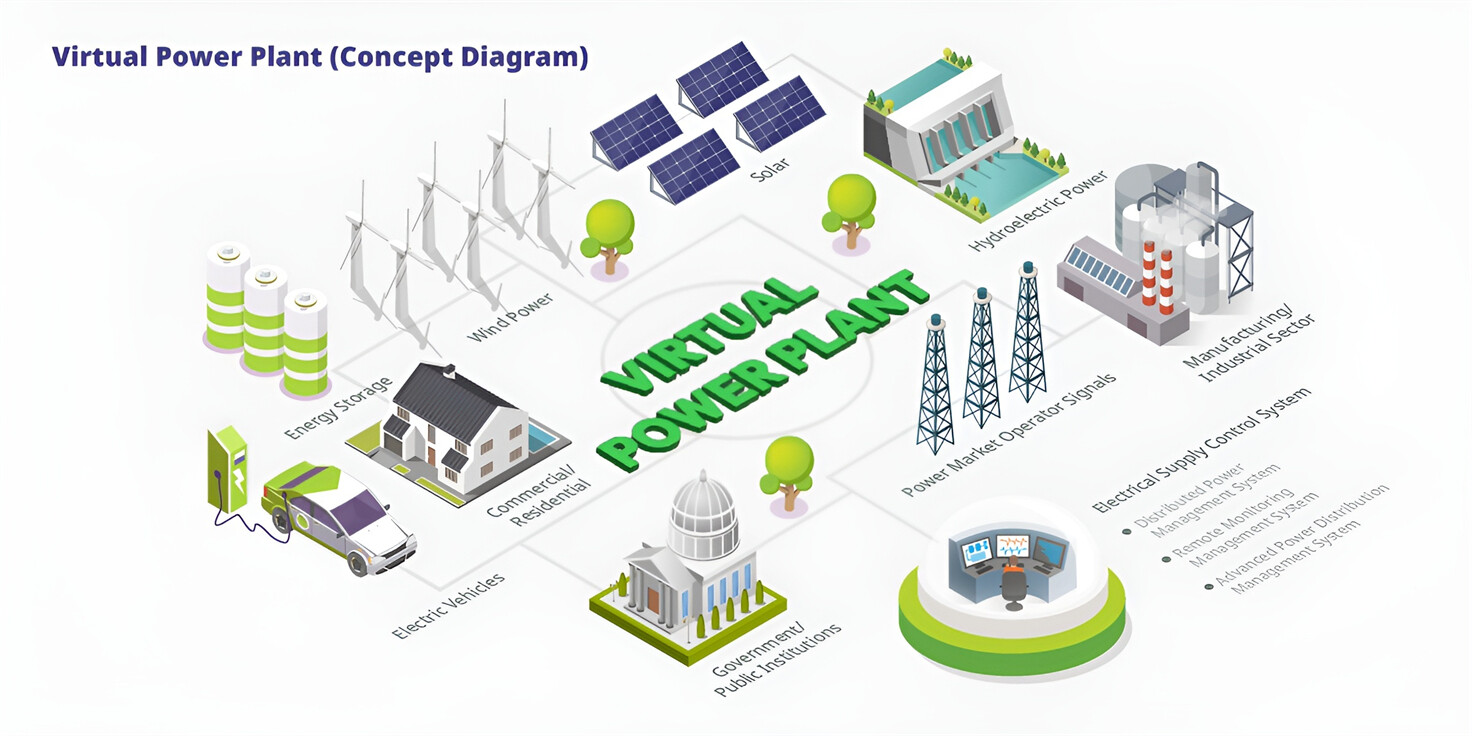
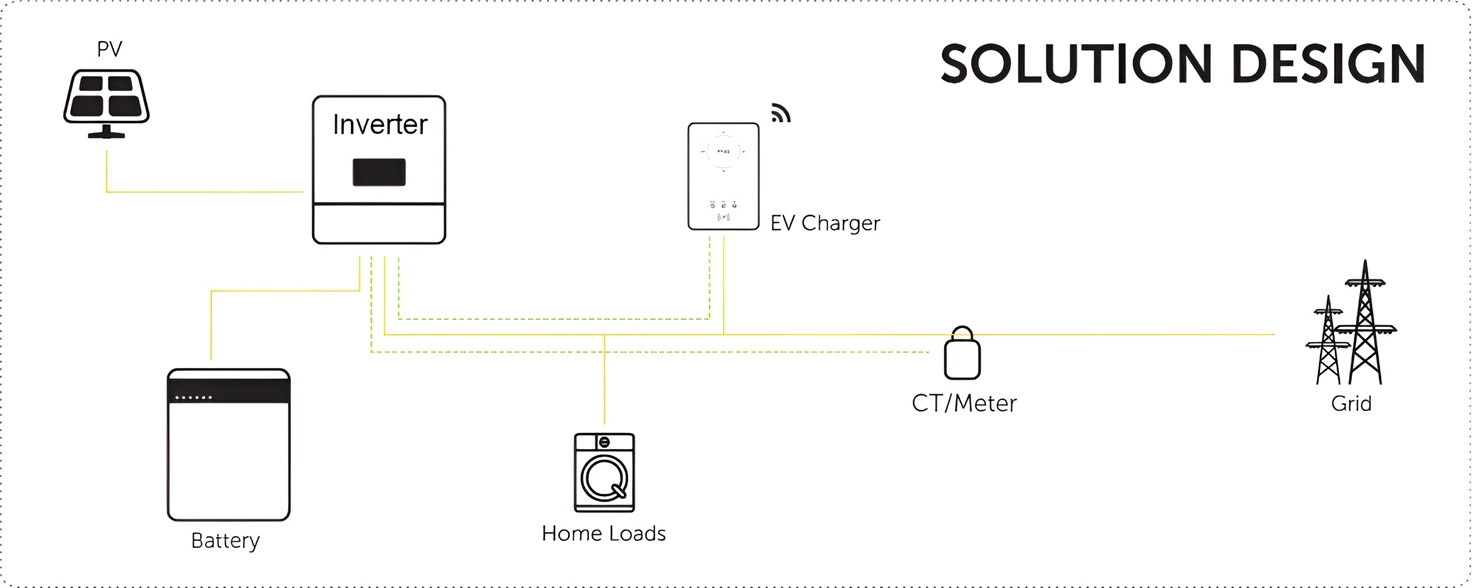
About Our Battery Cells
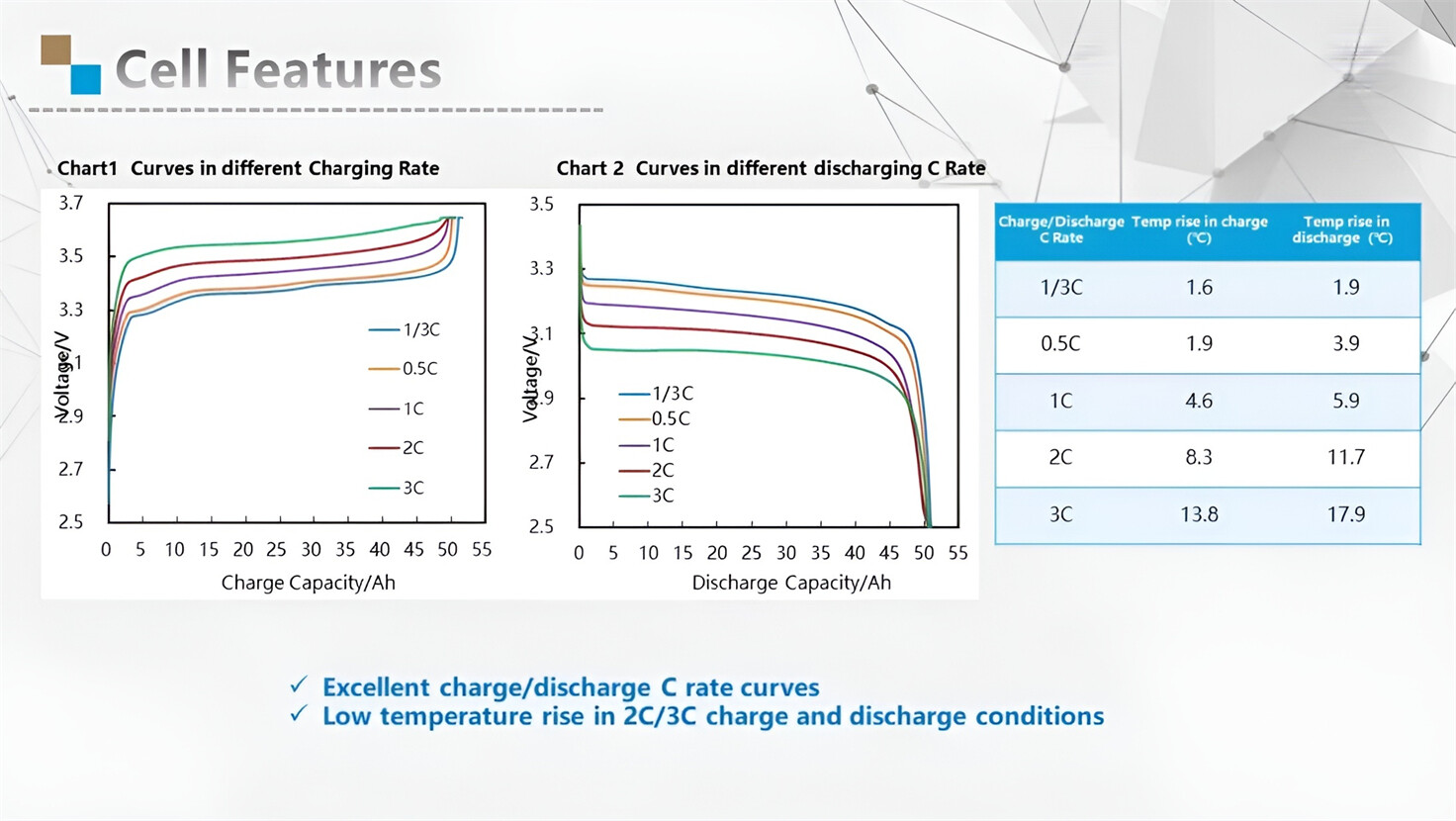
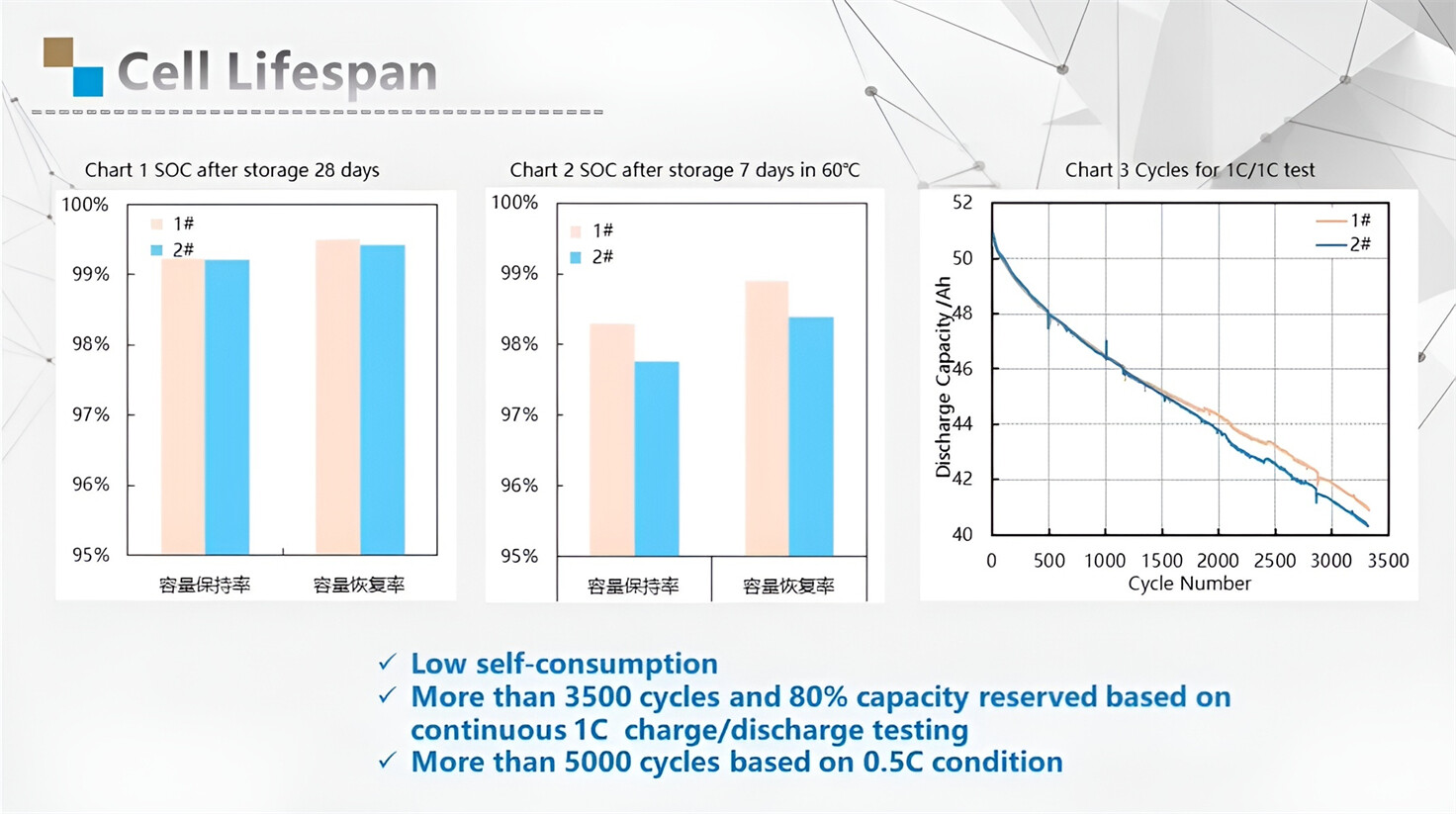
Our energy storage system products use brand new grade A LiFePO4 cells with a battery lifespan of more than 4,000 charge/discharge cycles.

Applications in Different Industries
We supply customized & OEM battery pack, assemble cells with wiring, fuse and plastic cover, all the cell wires connected to PCB plug or built BMS.
Applications: E-bike, Electric Scooter, Golf Carts, RV, Electric Wheelchair, Electric Tools, Robot Cleaner, Robot Sweeper, Solar Energy Storage System, Emergency Light, Solar Power Light, Medical Equipment, UPS Backup Power Supply.
We can provide you with customized services. We have the ability to provide a vertical supply chain, from single cells to pack/module and to a complete power solution with BMS, etc.

HomSolar (Shenzhen) Technology Co., Ltd
























