Advances In Carbon Coating: From Enhanced Battery Anodes To Next-generation Functional Surfaces
The application of ultrathin, conformal carbon layers—collectively known as carbon coating—has long been a cornerstone strategy in materials science for enhancing the performance and durability of various functional materials. Historically employed to improve electrical conductivity and chemical stability, recent years have witnessed a paradigm shift in carbon coating technologies. Driven by the demands of renewable energy, advanced electronics, and environmental sustainability, research has progressed from simple, bulk coating methods to sophisticated, atomic-level engineering. This article explores the latest breakthroughs in synthesis techniques, novel applications beyond traditional batteries, and the future trajectory of this dynamic field.
Recent Breakthroughs in Synthesis and Precision Engineering
The most significant advancements lie in the development of precise, controllable, and versatile coating methodologies. While traditional approaches like solid-state carbonization using sucrose or pitch remain in use for mass production, the frontier has moved towards vapor-phase and solution-based techniques that offer unparalleled control.
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) and its variants, particularly Atomic Layer Deposition (ALD)-assisted carbon coating, have emerged as powerful tools. Researchers have successfully demonstrated the coating of complex nanostructures, such as silicon nanoparticles for lithium-ion batteries and sulfur cathodes for lithium-sulfur systems, with graphitic carbon layers of sub-10 nanometer thickness. A recent study by Lee et al. (2023) showcased a plasma-enhanced CVD process that enabled a conformal, few-layer graphene coating on porous silicon microparticles, effectively accommodating their large volume expansion during cycling and leading to a dramatic improvement in cycle life. The key innovation was the in-situ formation of a covalent Si-C bond at the interface, which drastically enhanced mechanical adhesion and interfacial ion transport.
Simultaneously, solution-processable precursors are gaining traction for their scalability and ability to coat temperature-sensitive materials. The use of poly-dopamine and other bio-inspired polymers as carbon precursors allows for a uniform coating on virtually any substrate through a simple dip-coating process. After carbonization, these layers form a robust, N-doped carbon shell that enhances electrochemical activity. Furthermore, the exploration of new carbon allotropes for coating is underway. For instance, the direct assembly of graphene oxide sheets into a compact, dense coating via electrophoretic deposition or spray-coating, followed by reduction, creates a highly conductive and mechanically strong barrier layer. This "graphene-wrapping" technique has been successfully applied to cathode materials like LiFePO4 and LiMn2O4, effectively suppressing metal ion dissolution and improving high-rate performance.
Expanding Applications: Beyond Conventional Battery Anodes
While enhancing silicon and lithium metal anodes remains a primary focus, the scope of carbon coating has dramatically expanded.
1. Energy Storage and Conversion: In sodium-ion and potassium-ion batteries, which are emerging as cost-effective alternatives to lithium-ion, carbon coating is indispensable. Many promising electrode materials, such as Prussian blue analogues and polyanionic compounds, suffer from poor intrinsic electronic conductivity. A uniform carbon coating transforms their performance, making them viable for commercial applications. Beyond batteries, carbon coating is revolutionizing supercapacitors. Coating transition metal oxides (e.g., MnO2) with a porous carbon layer creates a core-shell structure that combines the high pseudocapacitance of the core with the excellent electrical conductivity and cycling stability of the carbon shell, enabling ultra-high power densities.
2. Catalysis and Environmental Remediation: Carbon coating has found a new life in electrocatalysis. Coating non-precious metal catalysts (e.g., Fe-N-C complexes) or metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) with a graphitic carbon layer protects the active sites from aggregation and corrosion in harsh acidic or alkaline environments. This significantly boosts the stability of catalysts for the oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) in fuel cells. A notable breakthrough was reported by Zhang et al. (2022), who encapsulated cobalt nanoparticles in a nitrogen-doped carbon nanotube shell. This architecture not only provided exceptional ORR activity rivaling platinum but also demonstrated remarkable resistance to poisoning, a critical hurdle for commercial fuel cells. In photocatalysis, carbon-coated semiconductors exhibit reduced charge recombination and enhanced light absorption, improving the efficiency of water splitting and CO2 reduction processes.
3. Advanced Functional Materials: The role of carbon coating in tribology and corrosion protection is being redefined. Applying a dense, amorphous carbon (diamond-like carbon) coating to mechanical components drastically reduces friction and wear, extending the lifetime of machinery. In the biomedical field, carbon-coated implants, particularly those with a diamond-like carbon film, exhibit superior biocompatibility, reduced biofilm formation, and enhanced resistance to bodily fluid corrosion compared to uncoated metallic surfaces.
Future Outlook and Challenges
The future of carbon coating research is poised to become even more interdisciplinary and intelligent. Several key directions are emerging:Multi-Functional and Graded Coatings: The next generation of coatings will not be monolithic. Researchers are designing graded or multi-layered coatings where the composition, density, and crystallinity vary from the substrate to the surface. For example, a soft, amorphous carbon layer adjacent to a volume-changing silicon particle could provide stress relief, while a outer graphitic layer ensures high electronic conductivity.In-situ and Operando Characterization: Understanding the dynamic evolution of the coating-substrate interface during operation (e.g., during battery cycling) is crucial. The integration of in-situ TEM, XPS, and Raman spectroscopy will provide unprecedented insights into failure mechanisms, guiding the design of more resilient interfaces.AI-Guided Materials Design: Machine learning and computational screening are beginning to play a role in predicting the optimal combination of precursor, coating thickness, and carbonization temperature for a specific substrate and application. This data-driven approach will accelerate the discovery of novel coating formulations and protocols.Sustainability of Precursors: As the scale of application grows, the environmental impact of carbon precursors will come under scrutiny. Future research will increasingly focus on deriving carbon sources from sustainable biomass or recycled materials, aligning materials synthesis with circular economy principles.
The primary challenges that remain include achieving perfect conformality on ultra-high-aspect-ratio structures, scaling up the most precise vapor-phase techniques cost-effectively, and fundamentally understanding and controlling the interfacial chemistry between the carbon layer and diverse substrates.
In conclusion, carbon coating has evolved from a simple performance-enhancing treatment into a sophisticated materials engineering discipline. The latest advances in precision synthesis and the exploration of novel applications in energy, catalysis, and biomedicine underscore its enduring relevance. As research continues to push the boundaries of interfacial control and multi-functionality, carbon coating will undoubtedly remain a vital tool in the development of next-generation technologies for a sustainable future.
References:
1. Lee, K., et al. (2023). "Conformal Graphene Caging via Interfacial Carbide Bonding for Ultrastable Silicon Anodes."Advanced Energy Materials, 13(15), 2203650. 2. Zhang, H., et al. (2022). "Cobalt Nanoparticles Encapsulated in Nitrogen-Doped Carbon Nanotubes as a Robust Bifunctional Electrocatalyst for Zn-Air Batteries."Nature Communications, 13, 1455. 3. Wang, J., et al. (2021). "Multi-layer Carbon Coating of LiFePO4 Cathodes for High-Performance Lithium-Ion Batteries: An In-depth Study of Interface Properties."Energy Storage Materials, 42, 58-67. 4. Chen, Y., et al. (2023). "Biomass-Derived Carbon Coating for Sustainable and Stable Sodium-Ion Battery Cathodes."ACS Nano, 17(4), 3894-3905.
Customized/OEM/ODM Service
HomSolar Supports Lifepo4 battery pack customization/OEM/ODM service, welcome to contact us and tell us your needs.


HomSolar: Your One-stop LiFePO4 Battery Pack & ESS Solution Manufacturer
Our line of LiFePO4 (LFP) batteries offer a solution to demanding applications that require a lighter weight, longer life, and higher capacity battery. Features include advanced battery management systems (BMS), Bluetooth® communication and active intelligent monitoring.

Customised Lithium Iron Phosphate Battery Casing
ABS plastic housing, aluminium housing, stainless steel housing and iron housing are available, and can also be designed and customised according to your needs.

HomSolar Smart BMS
Intelligent Battery Management System for HomSolar Energy Storage System. Bluetooth, temperature sensor, LCD display, CAN interface, UART interface also available.


Terminals & Plugs Can Be Customized
A wide range of terminals and plugs can be customised to suit the application needs of your battery products.

Well-designed Solutions for Energy Storage Systems
We will design the perfect energy storage system solution according to your needs, so that you can easily solve the specific industry applications of battery products.

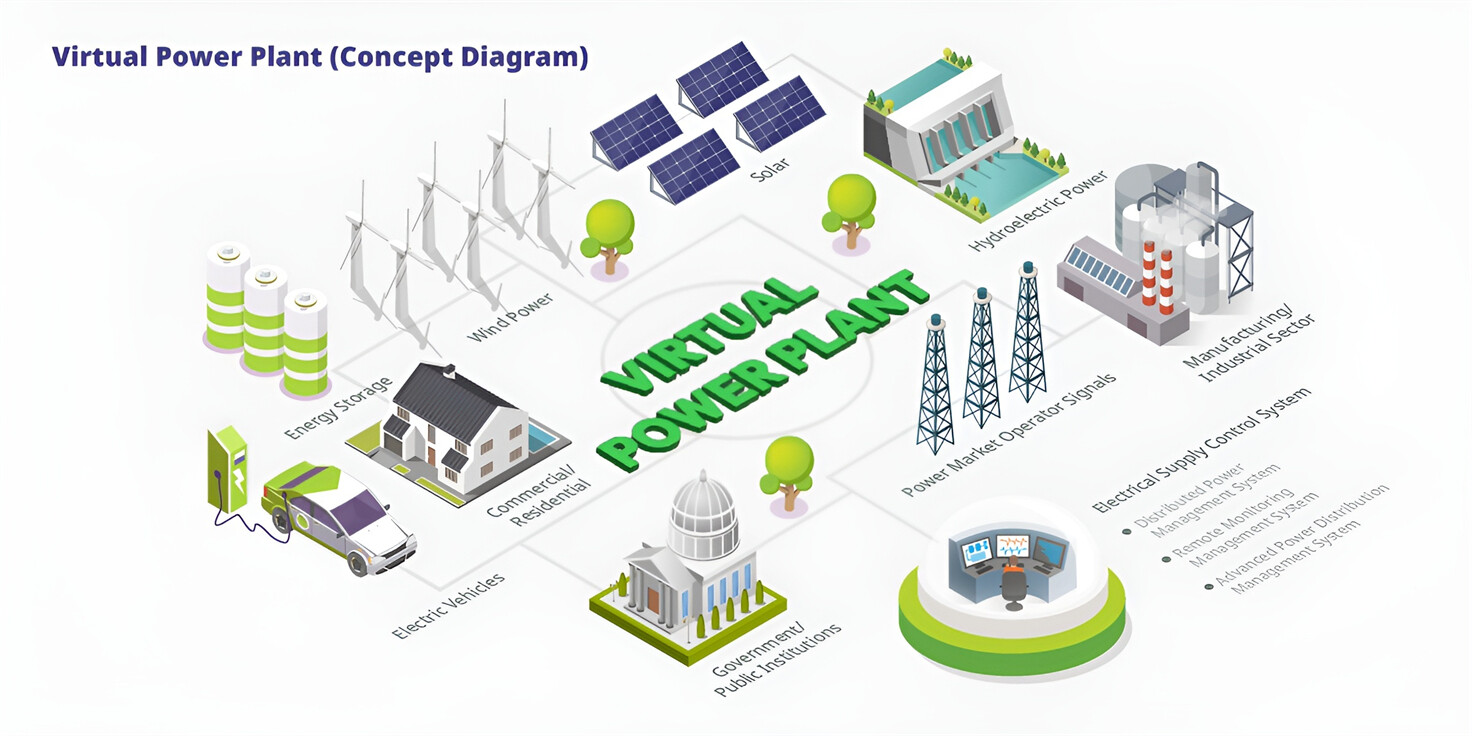
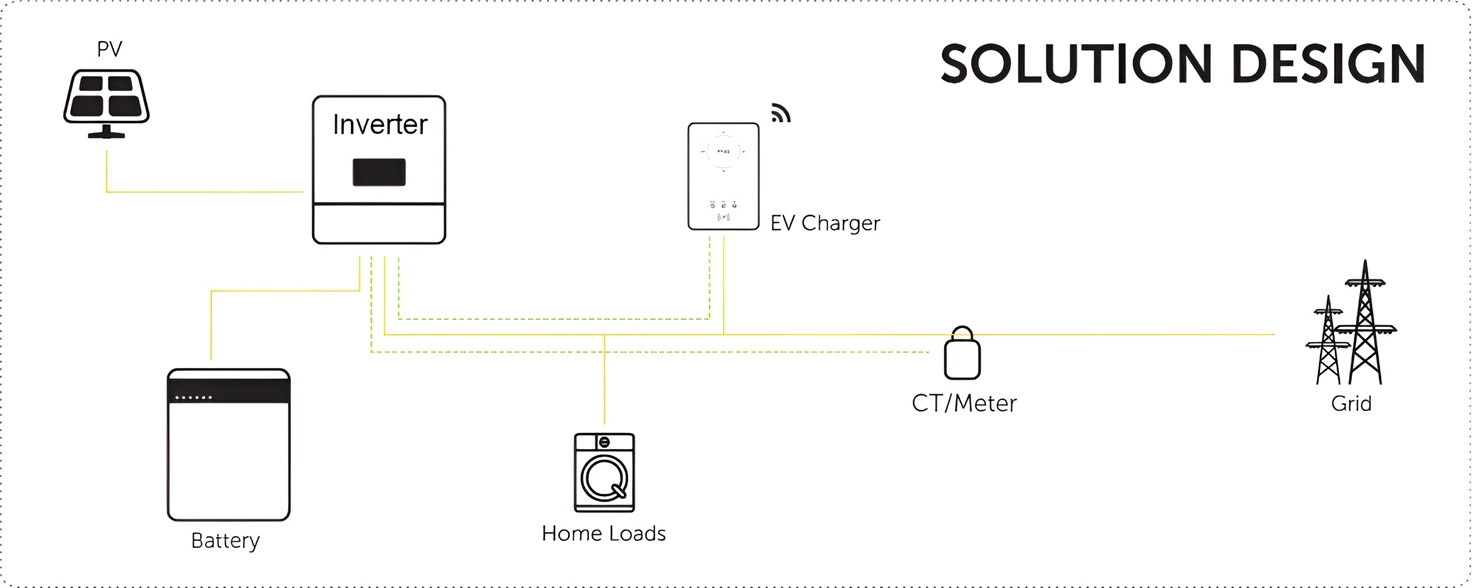
About Our Battery Cells
Our energy storage system products use brand new grade A LiFePO4 cells with a battery lifespan of more than 4,000 charge/discharge cycles.

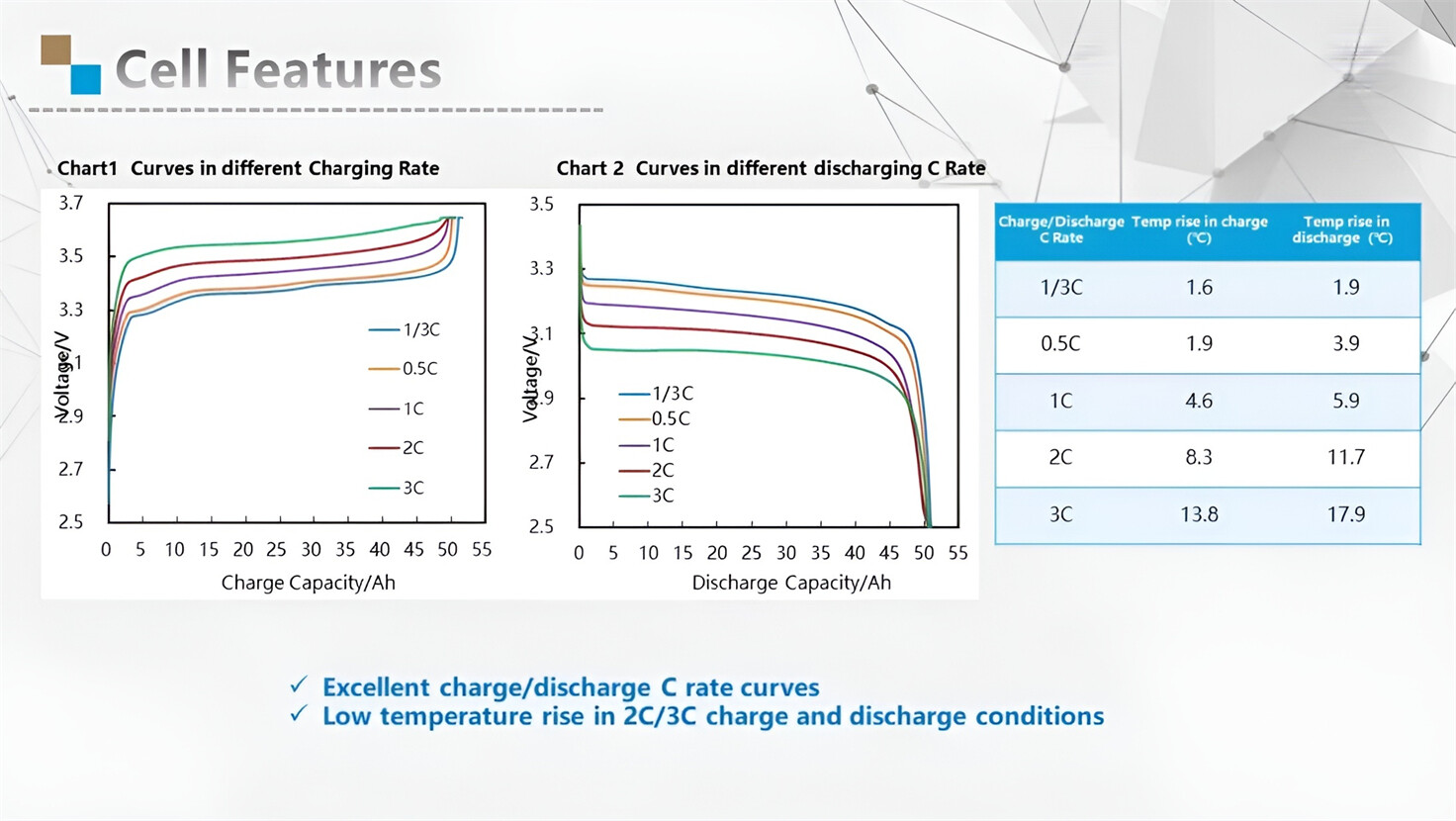
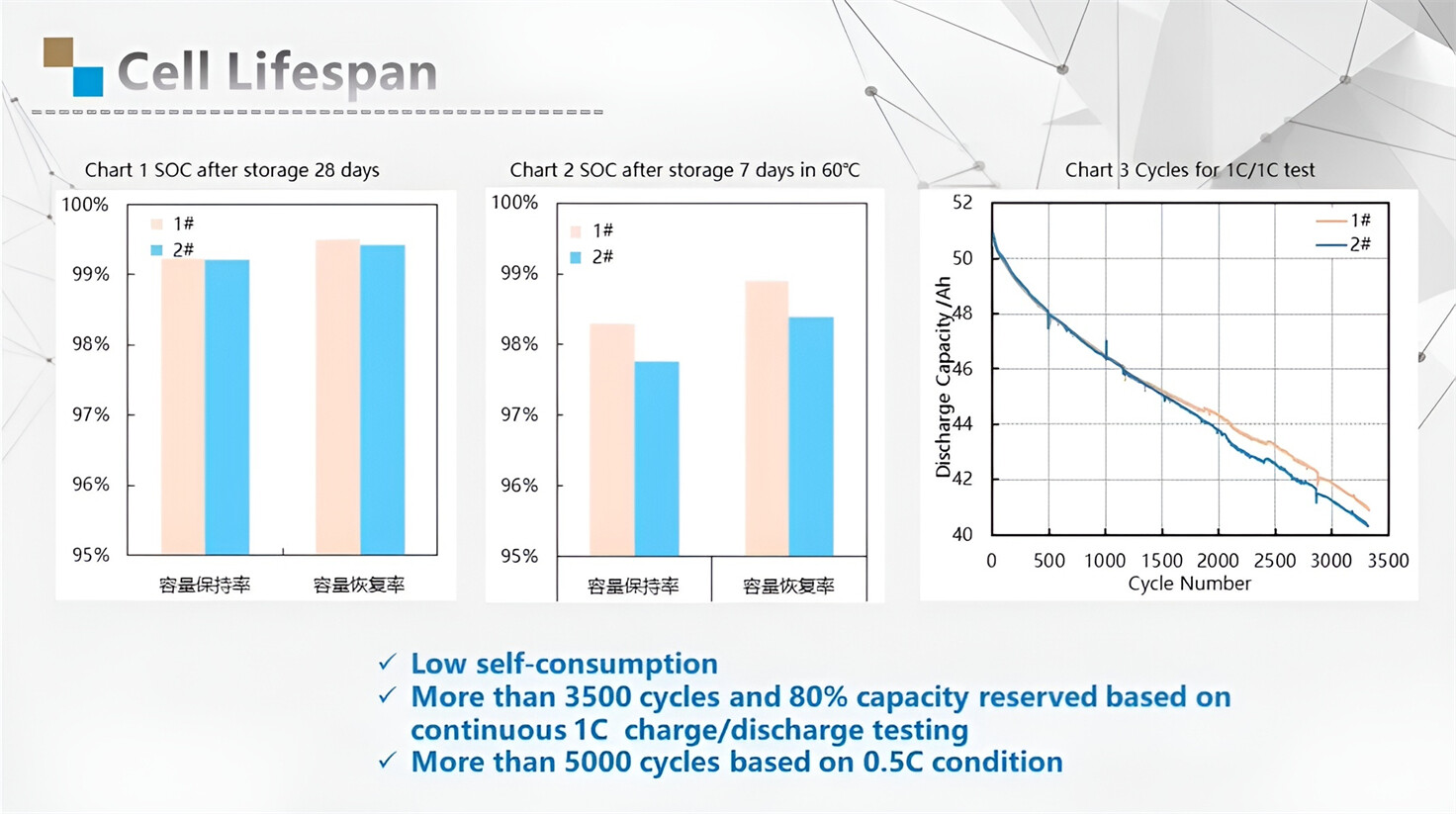
Applications in Different Industries
We supply customized & OEM battery pack, assemble cells with wiring, fuse and plastic cover, all the cell wires connected to PCB plug or built BMS.
Applications: E-bike, Electric Scooter, Golf Carts, RV, Electric Wheelchair, Electric Tools, Robot Cleaner, Robot Sweeper, Solar Energy Storage System, Emergency Light, Solar Power Light, Medical Equipment, UPS Backup Power Supply.
We can provide you with customized services. We have the ability to provide a vertical supply chain, from single cells to pack/module and to a complete power solution with BMS, etc.

HomSolar (Shenzhen) Technology Co., Ltd
























